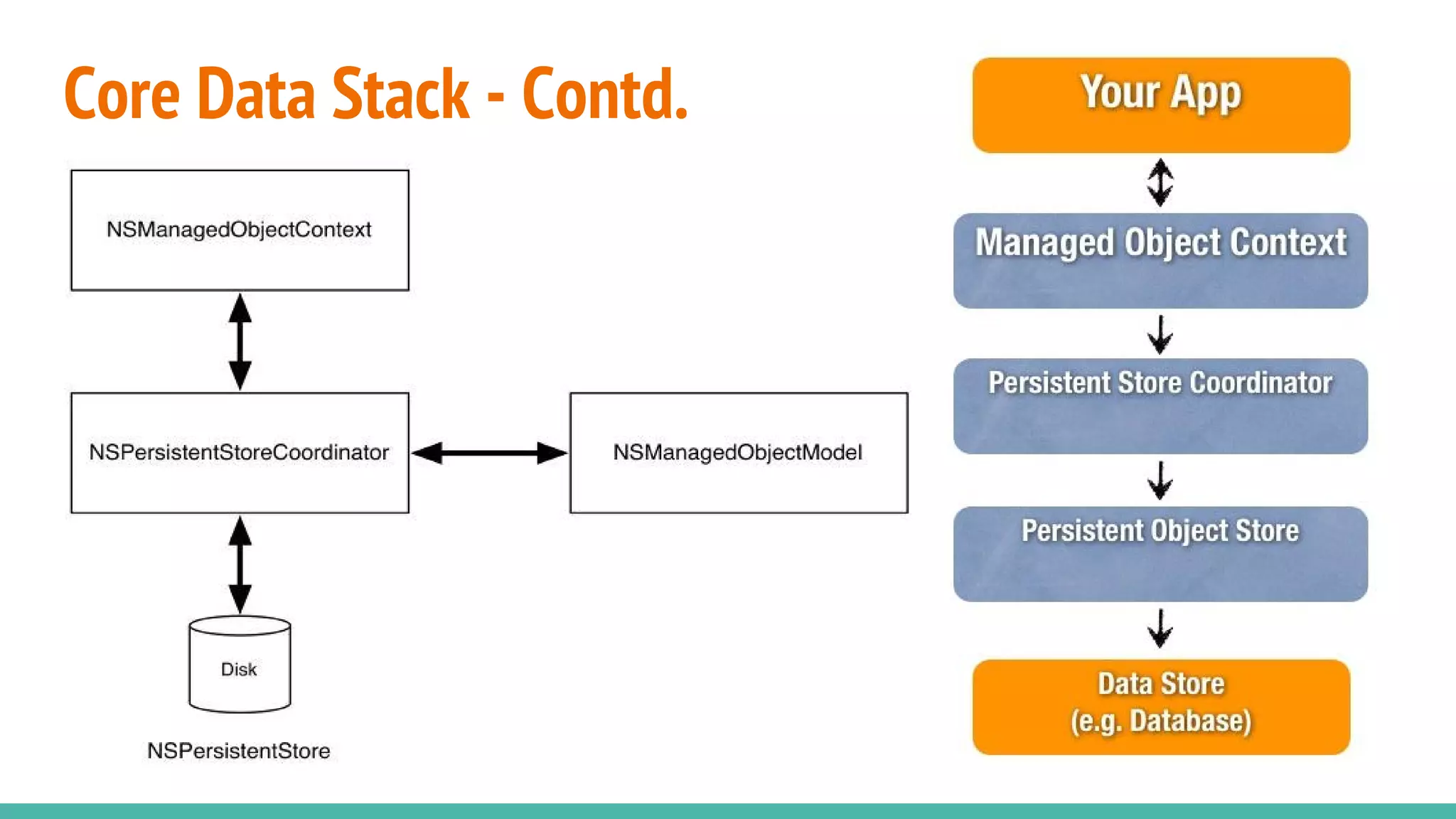
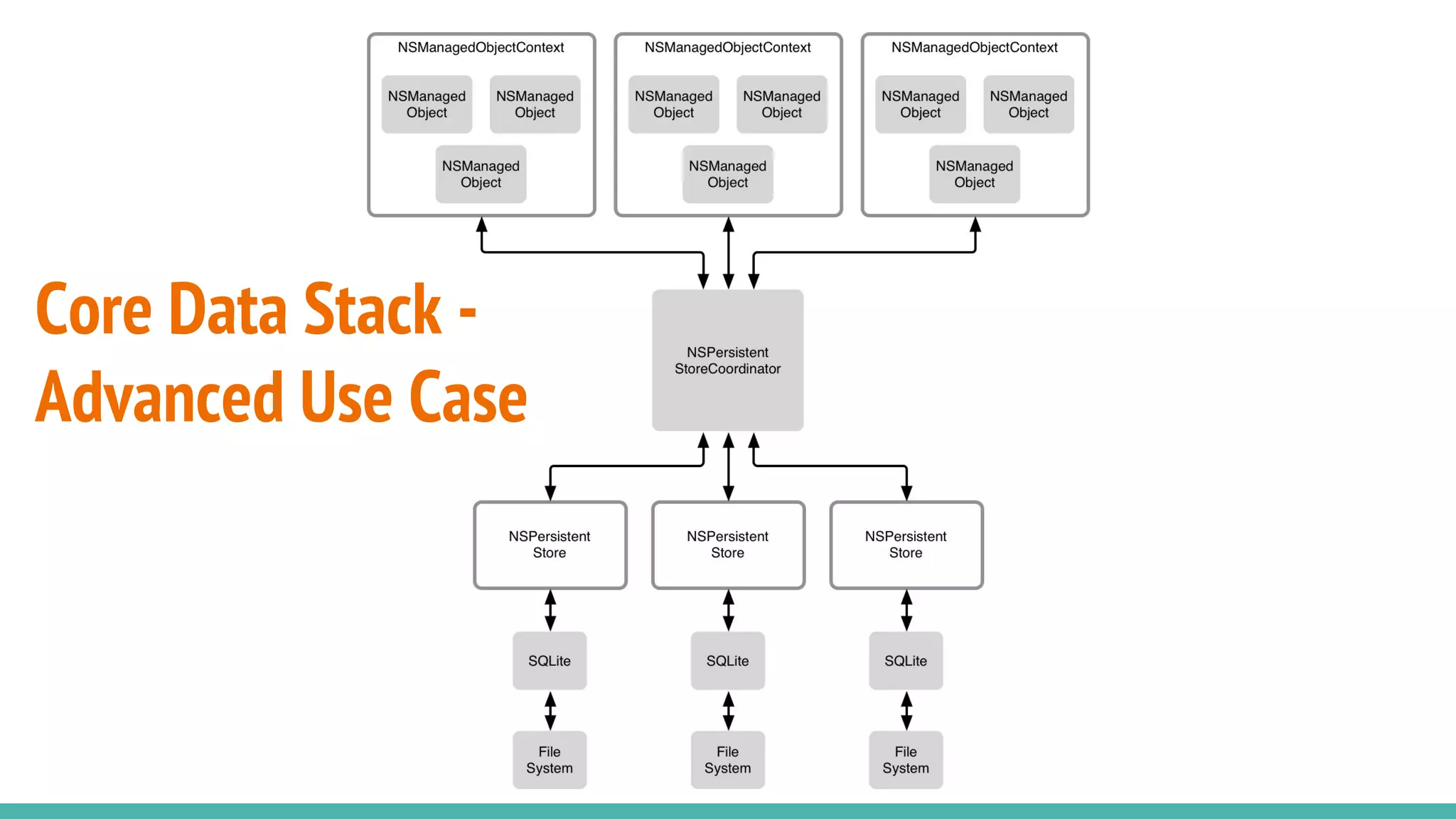
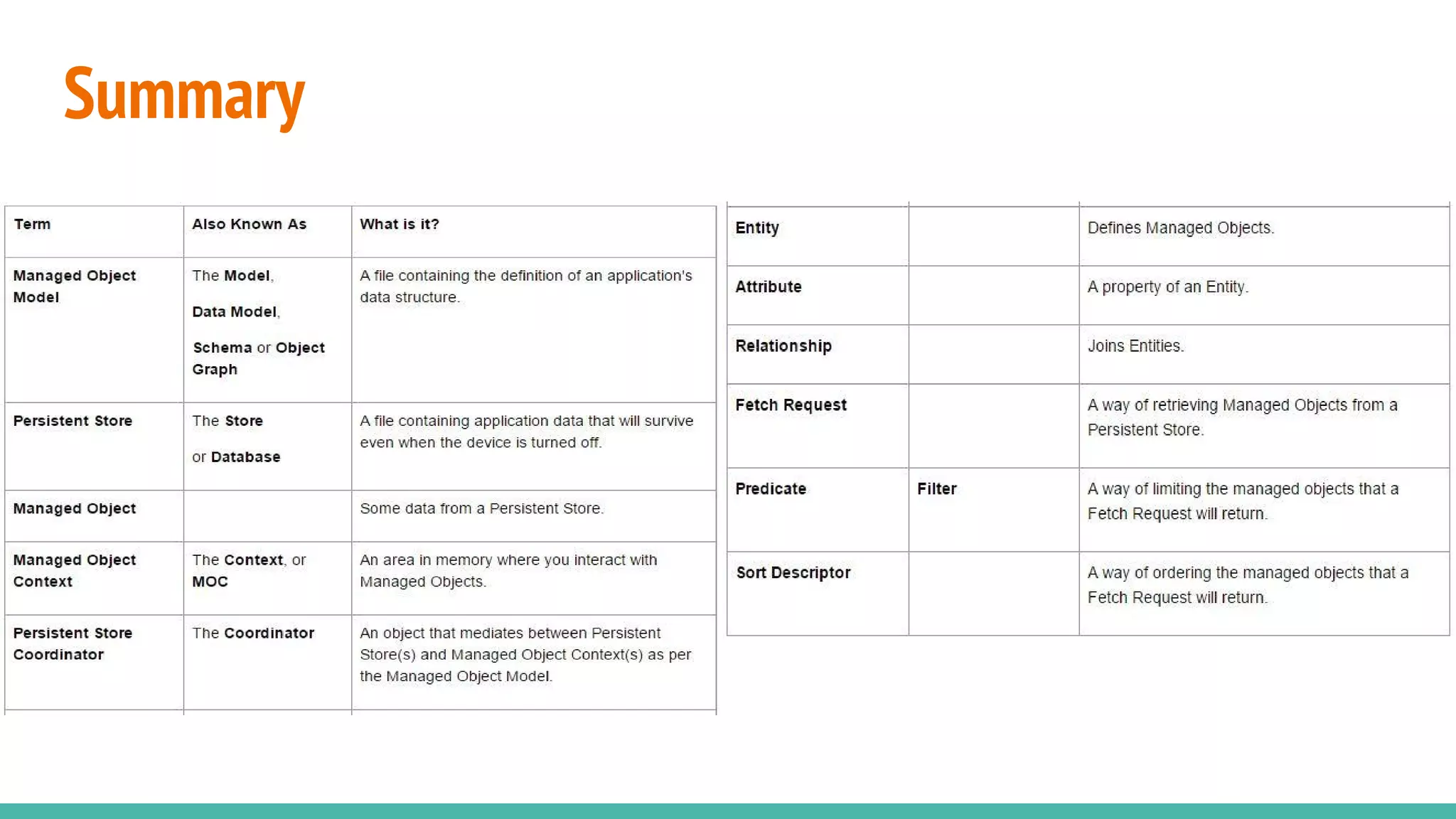
The document introduces core data as a framework for iOS development, outlining its role as an object-relational mapping (ORM) tool that bridges SQLite and Objective-C. It discusses core data's functionality, its components such as NSManagedObjectModel, NSPersistentStoreCoordinator, and NSManagedObjectContext, and emphasizes that core data is not a database itself but a technology for data management. Additionally, it highlights various data storage options on iOS, including UserDefaults, file storage, and remote storage solutions.