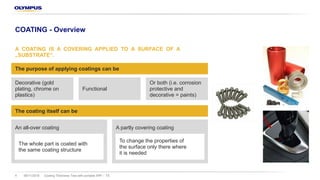
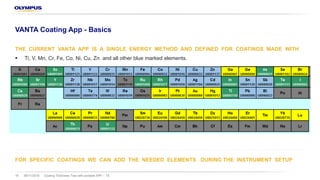
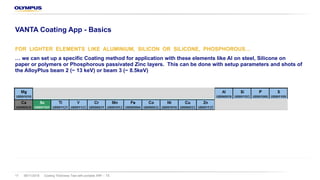
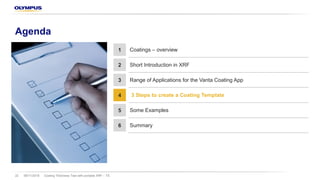
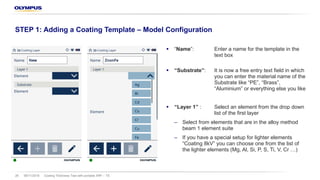
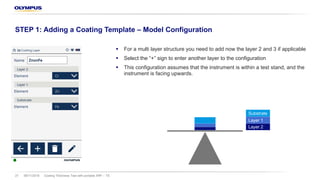
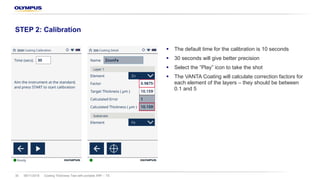
The document discusses the Vanta portable X-ray fluorescence (XRF) technology for coating thickness testing across various industries, emphasizing its non-destructive testing capabilities. It outlines the process of creating coating templates and calibrations, detailing the types of coatings, their functions, and the importance of layer thickness. The summary highlights that multiple layer coating systems can be assessed quickly with minimal calibration effort.




![08/11/2018 Coating Thickness Test with portable XRF – TS10
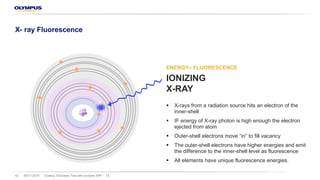
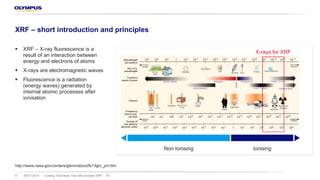
XRF – short introduction and principles
§ Every element has a unique and known X-ray
fluorescence
§ The detector and the AXON electronics can acquire
radiation from up to 40 elements from Mg to Pu,
simultaneously
Ni
Fe
Cr
Mo
Energy [keV]
Counts[cps]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/coatingthicknesstestwithportablexrf-181108142405/85/Coating-Thickness-Test-with-Portable-XRF-10-320.jpg)
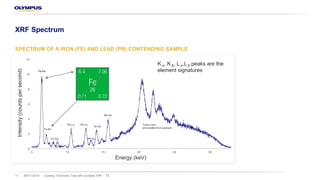


![08/11/2018 Coating Thickness Test with portable XRF – TS19
XRF for Coating Thickness Testing - Basics
§ As heavier the elements used in the coating layers are as lower the penetration depth and with that the range of
measurable thicknesses are
§ The mass attenuation factor of each elemental layer has an strong impact of the detectable thickness for the layers
closer to the substrate
MASS ATTENUATION COEFFICIENT OF DIFFERENT ELEMENTS
0.1
1
10
100
1000
10000
100000
0 10 20 30 40 50 60
µMassattenuation
Energy [keV]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/coatingthicknesstestwithportablexrf-181108142405/85/Coating-Thickness-Test-with-Portable-XRF-19-320.jpg)

![08/11/2018 Coating Thickness Test with portable XRF – TS21
XRF for Coating Thickness Testing – Detection range
The measurable thickness range with XRF starts at ~ 5 nm and ends at ~ 20 – 45 µm depending on the elements
used in the coating and their XRF emission energies
Element Energy-line Max. Thickness [µm] Element Energy-line Max. Thickness [µm]
Titanium (Ti) Ka 20 Copper (Cu) Ka 30
Vanadium (V) Ka 20 Zinc (Zn) Ka 30
Chrome (Cr) Ka 25 Tantalum (Ta) Lß 30
Mangnese (Mn) Ka 25 Tungsten (W) Lß 30
Iron (Fe) Ka 25 Lead (Pb) Lß 35
Cobalt (Co) Ka 30 Bismuth (Bi) Lß 35
Nickel (Ni) Ka 30 Molybdenum (Mo) Ka 40](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/coatingthicknesstestwithportablexrf-181108142405/85/Coating-Thickness-Test-with-Portable-XRF-21-320.jpg)

![§ Coating method offers a one point calibration
‒ Similar to user factors
‒ Tune calibration to a customer’s sample
§ Coating will display
‒ Thickness [µm, µinch] or Loading [mg/cm², g/m²]
§ Coating will not display
‒ Chemistry
08/11/2018 Coating Thickness Test with portable XRF – TS24
Overview](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/coatingthicknesstestwithportablexrf-181108142405/85/Coating-Thickness-Test-with-Portable-XRF-24-320.jpg)




![§ Example: Cu-Ni coated Cr-steel ring (1 – 1.5µm each)
with differences in the coating layer thickness
§ 16 segments tested (each 10 sec) instead of cutting out
a piece for testing with microscope
11/8/18 Coating Thickness Test with portable XRF – TS33
Non-destructive Coating Thickness Testing saves time
Segment Layer 1 – Cu [µm] Layer 2 – Ni [µm]
1 1,129 1,237
2 1,296 1,283
3 1,25 1,21
4 1,404 1,313
5 1,508 1,404
6 1,523 1,454
7 1,424 1,484
8 1,199 1,458
9 1,028 1,343
10 1,186 1,579
11 0,894 1,384
12 0,888 1,439
13 0,991 1,608
14 0,985 1,559
15 0,920 1,346
16 1,043 1,441](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/coatingthicknesstestwithportablexrf-181108142405/85/Coating-Thickness-Test-with-Portable-XRF-33-320.jpg)