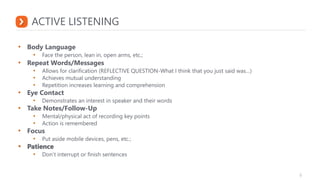
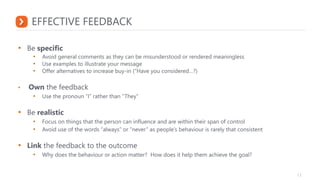
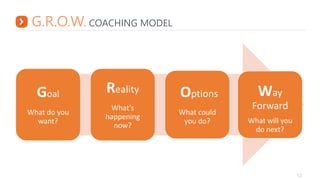
This document outlines critical coaching skills such as establishing trust, asking open-ended questions, listening, giving feedback, and providing guidance. It emphasizes asking open questions to promote different ways of thinking and ensure thoughts are fully developed. Active listening skills are also discussed, such as maintaining eye contact, paraphrasing, and not interrupting. The document provides examples of effective feedback that is specific, balanced, and focused on behavior rather than the person. It concludes with an overview of the G.R.O.W. coaching model to set goals, understand current reality, brainstorm options, and decide on next steps.