Embed presentation
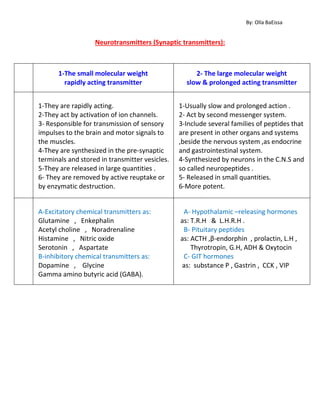

Neurotransmitters can be categorized as either small molecular weight transmitters that act rapidly through ion channels or large molecular weight neuropeptides that act more slowly through second messenger systems. Small molecular transmitters are synthesized in presynaptic terminals, stored in vesicles, released in large quantities upon stimulation, and removed by reuptake or enzymatic degradation. In contrast, neuropeptides are synthesized by neurons in the central nervous system, released in smaller quantities, and more potent. Examples of excitatory and inhibitory chemical transmitters are provided. Hormones produced by the hypothalamus, pituitary, and gastrointestinal tract are also listed.
