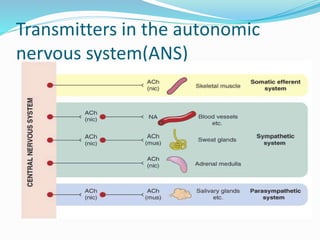
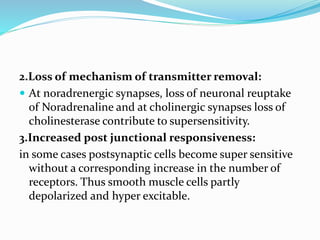
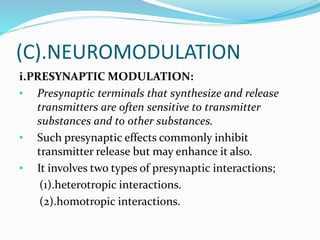
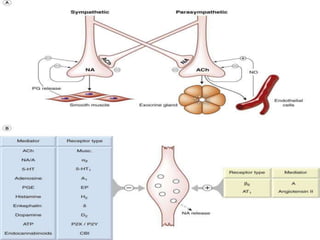
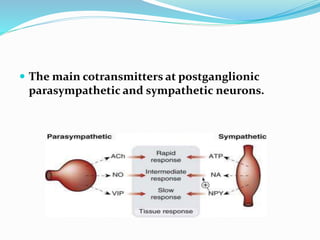
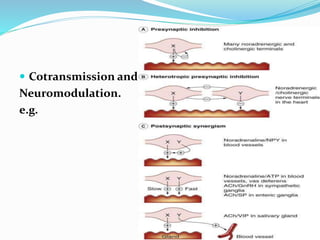
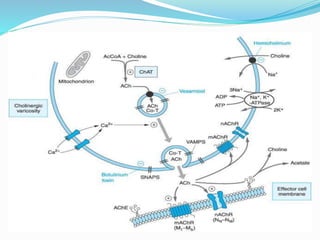
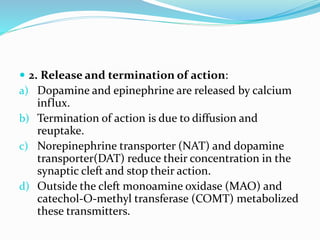
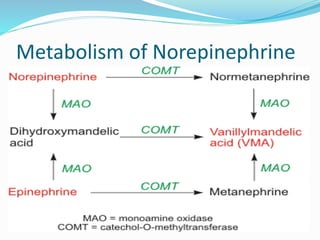
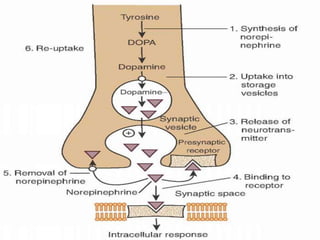
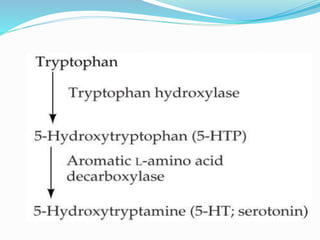
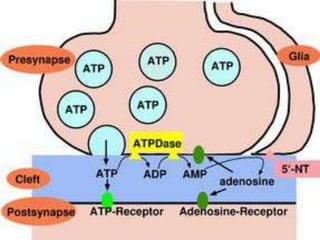
This document discusses neurohumoral transmission and the criteria for identifying neurotransmitters. It describes several major neurotransmitters like acetylcholine, adrenaline, norepinephrine, dopamine, serotonin, and others. It explains the principles of chemical transmission including Dale's principle and denervation supersensitivity. The document provides details about the synthesis, storage, release and termination of various neurotransmitters including acetylcholine, adrenaline, serotonin, ATP and others. It also discusses cotransmission and neuromodulation in neurotransmission.