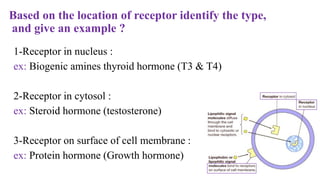
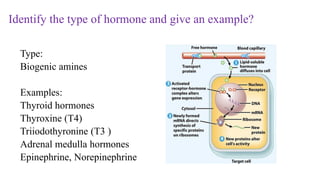
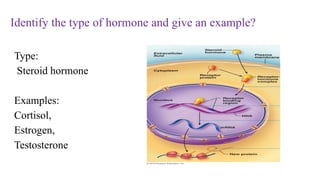
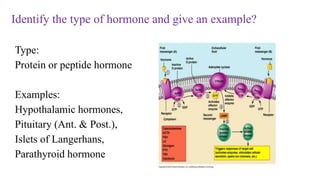
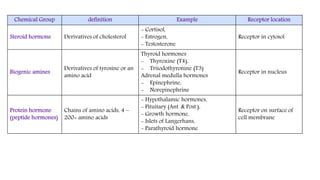
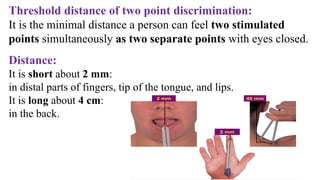
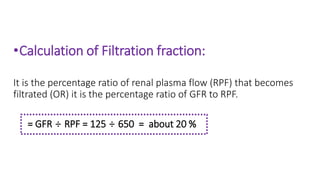
The document outlines various clinical diseases and disorders related to hormonal imbalances, including dwarfism, gigantism, acromegaly, and conditions affecting thyroid function such as goiter, Graves' disease, myxedema, and cretinism. It discusses the impact of adrenal disorders like Cushing's syndrome and Addison's disease, as well as diabetes mellitus, providing details on their causes, affected glands, and characteristic features. Additionally, it explores renal functions including urine formation processes, filtration pressure calculations, and assessment of glomerular filtration rate.