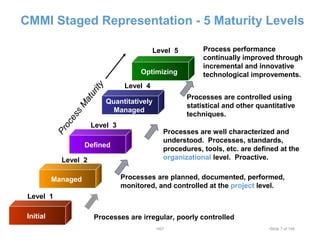
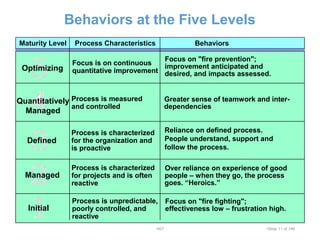
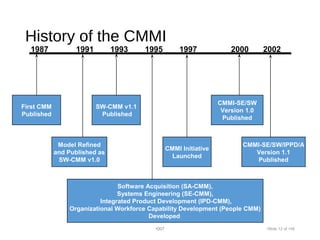
This document provides an overview of the Capability Maturity Model Integration (CMMI) framework. It discusses that CMMI was developed by the US Department of Defense and Carnegie Mellon University to improve product quality and development efficiency. CMMI uses five maturity levels to describe an organization's process improvement, from initial/ad hoc processes to optimized, continuously improving processes. The document outlines the behaviors and characteristics associated with each of the five maturity levels.