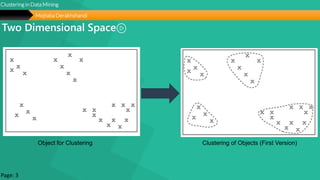
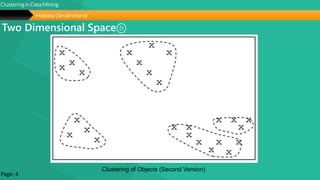
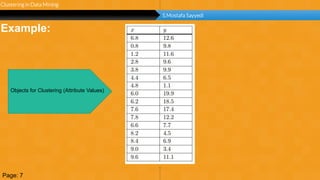
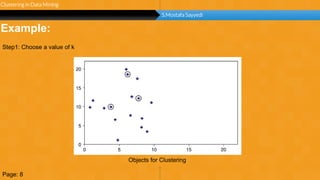
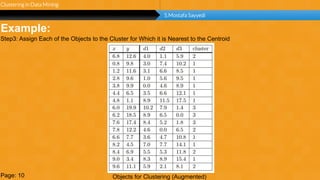
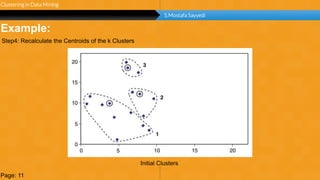
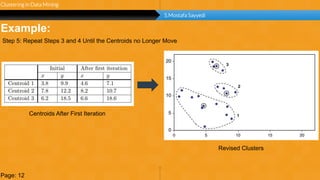
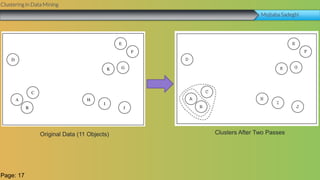
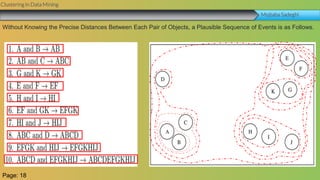
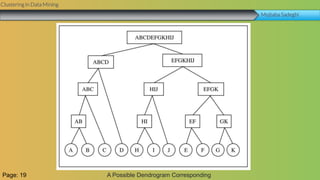
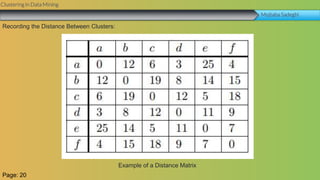
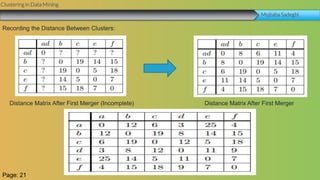
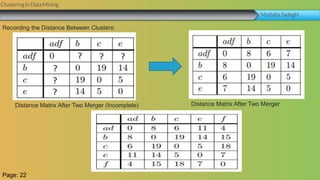
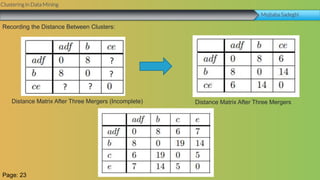
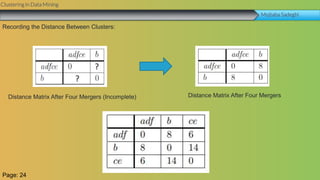
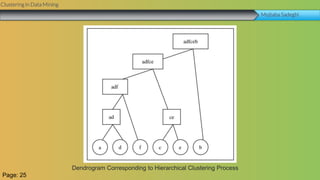
This document summarizes a group project report on clustering in data mining. It discusses different types of clustering algorithms including K-means clustering and agglomerative hierarchical clustering. For K-means clustering, it provides an example showing how clusters are formed by assigning objects to centroids and recalculating centroids over iterations. For hierarchical clustering, it shows how clusters are merged based on distances recorded in a distance matrix and represented through a dendrogram. The document contains examples and diagrams to illustrate key steps and concepts in clustering techniques.