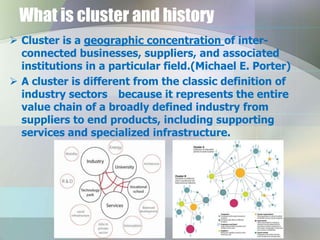
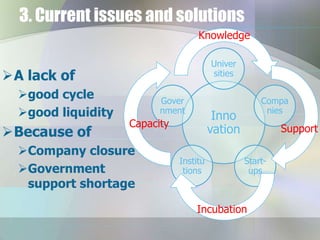
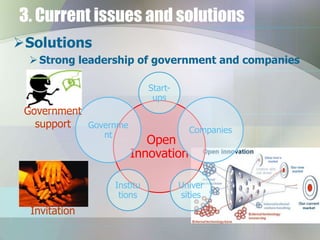
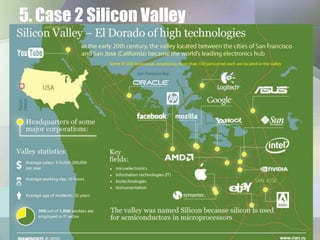
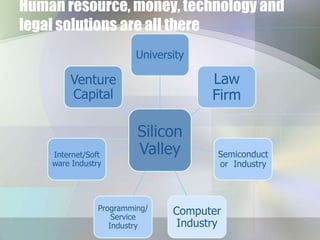
This document discusses industrial clusters through two case studies. It defines a cluster as a geographic concentration of interconnected businesses in a particular field. The semiconductor industry in Silicon Valley and the automobile industry in Detroit are provided as historical examples of successful clusters. Benefits of clusters include access to resources, information, institutions, customer needs and technology. Potential downsides are homogeneousness, monopolization and high business costs. Current issues facing clusters include lack of knowledge sharing, liquidity and government support. Solutions proposed are strong leadership, start-up support, open innovation and collaboration between government, institutions, universities and companies. Case studies of the Tsukuba Science City cluster in Japan and the Silicon Valley cluster in the US are then described.