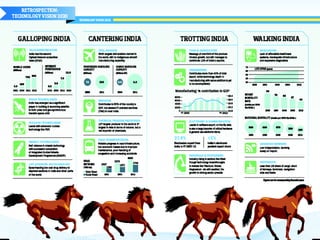
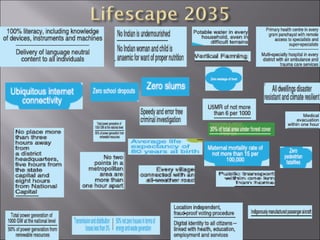
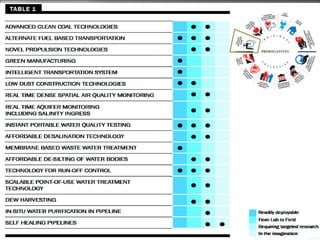
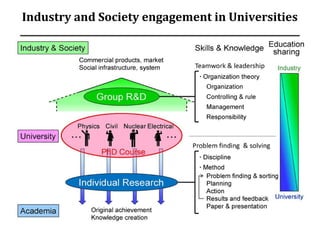
The document discusses the importance of technology in empowering citizens and nations, and ensuring strategic autonomy and security. It argues that India needs robust technological solutions that address disparities and ensure food, energy, and material security through accessible education, resilient infrastructure, and demand-driven research. It outlines key areas for technological development, including education, healthcare, agriculture, water, energy, transportation and more. The document proposes various initiatives to make India's R&D more productive and industry-engaged, such as science centers, industry internships, research parks, and smoothing barriers for industry-academia partnerships.