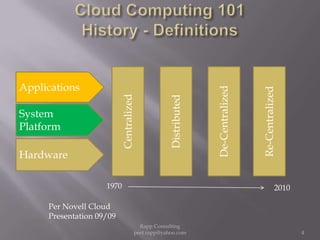
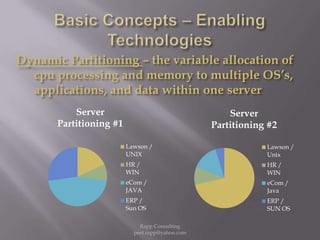
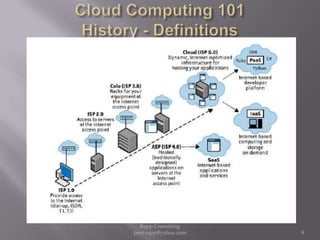
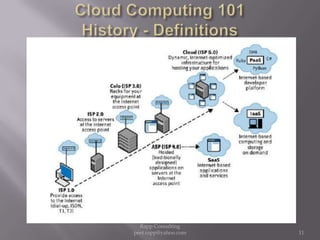
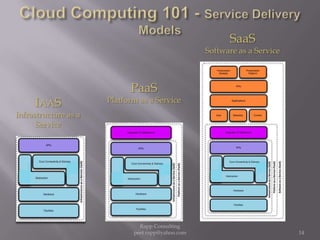
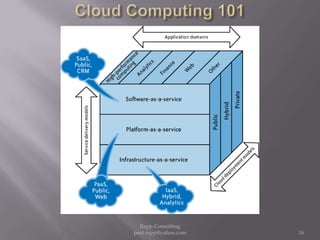
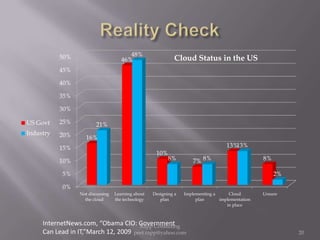
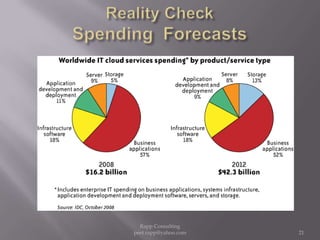
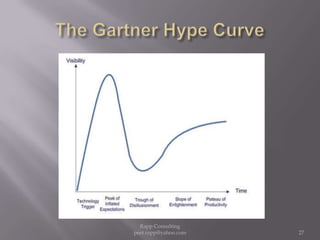
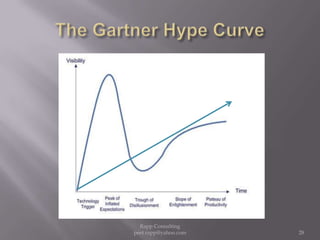
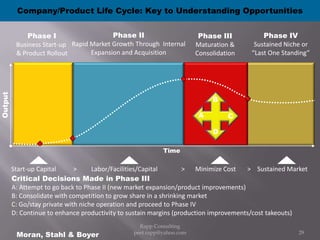
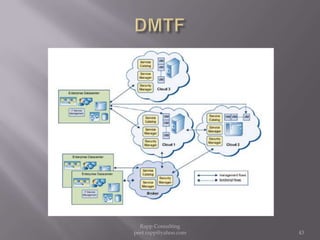
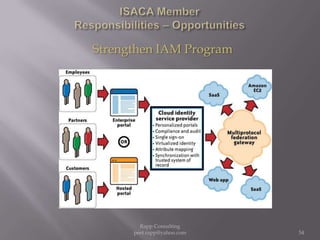
The document provides an overview of cloud computing, outlining its definitions, historical context, and key concepts such as IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS. It highlights significant security concerns surrounding cloud adoption, including data integrity, system integration, and compliance issues, while also calling attention to responsibilities for ISACA members in addressing these challenges. Additionally, it emphasizes the need for robust audit and security practices in cloud services to ensure accountability and transparency.