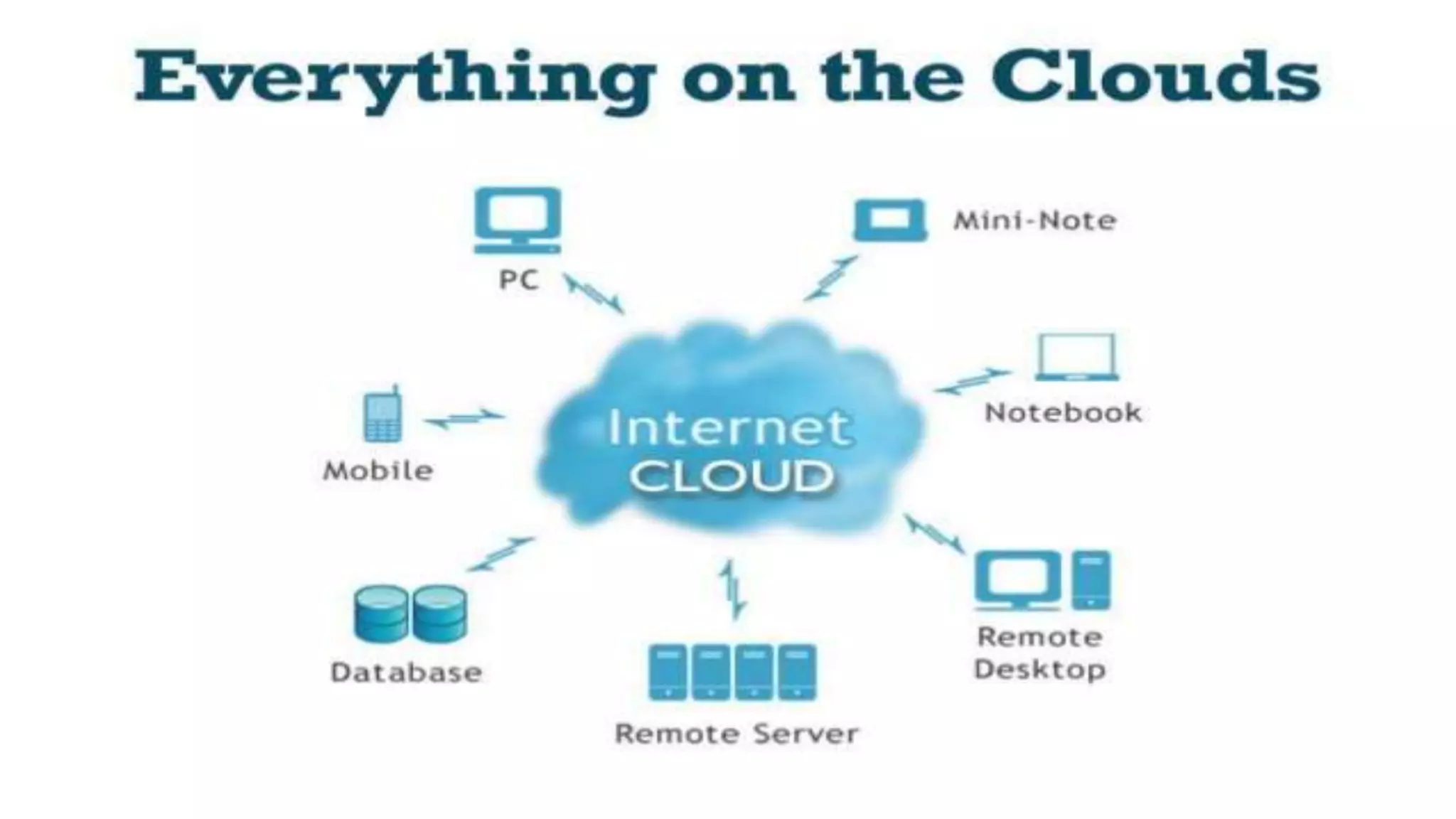
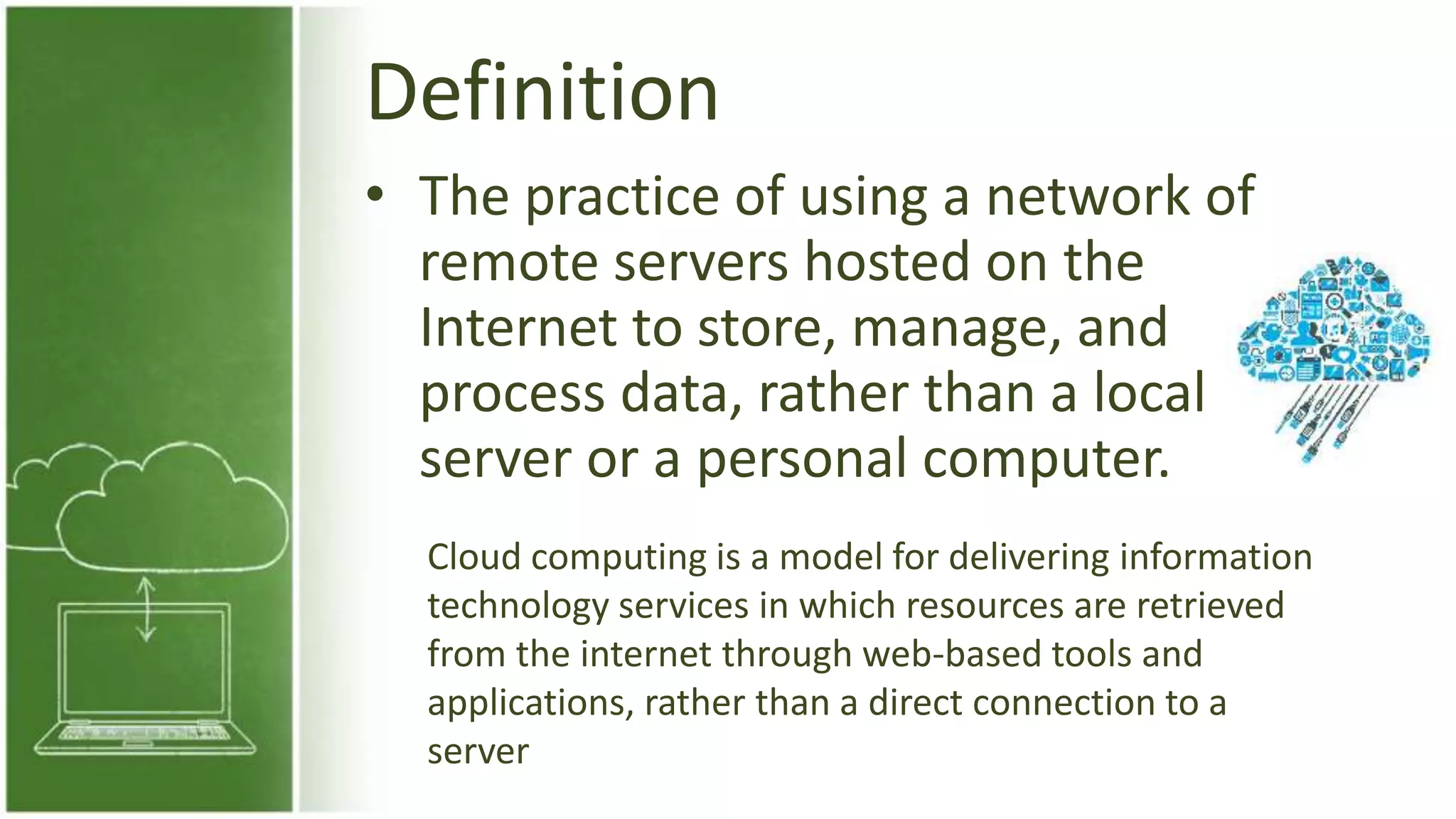
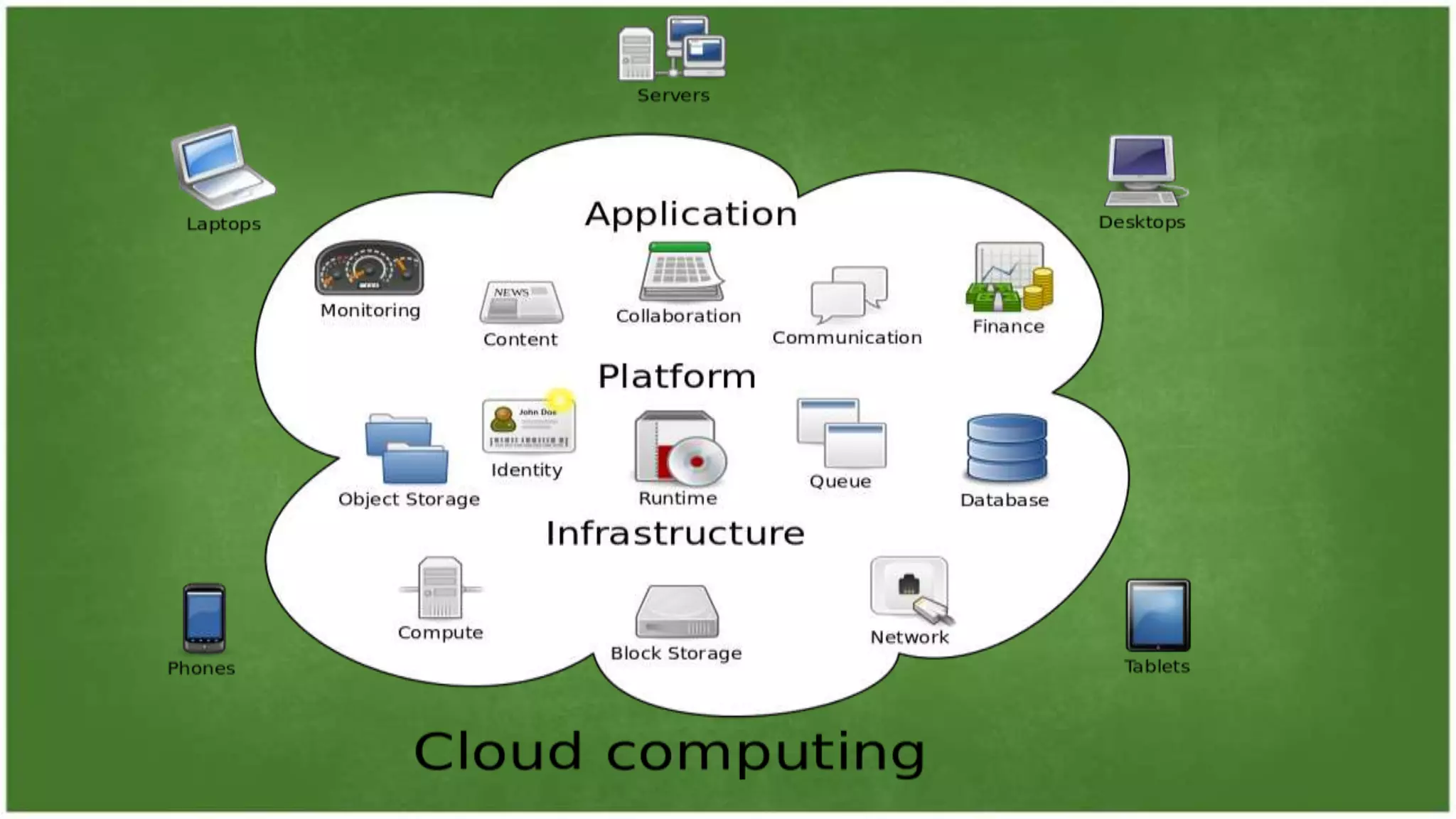
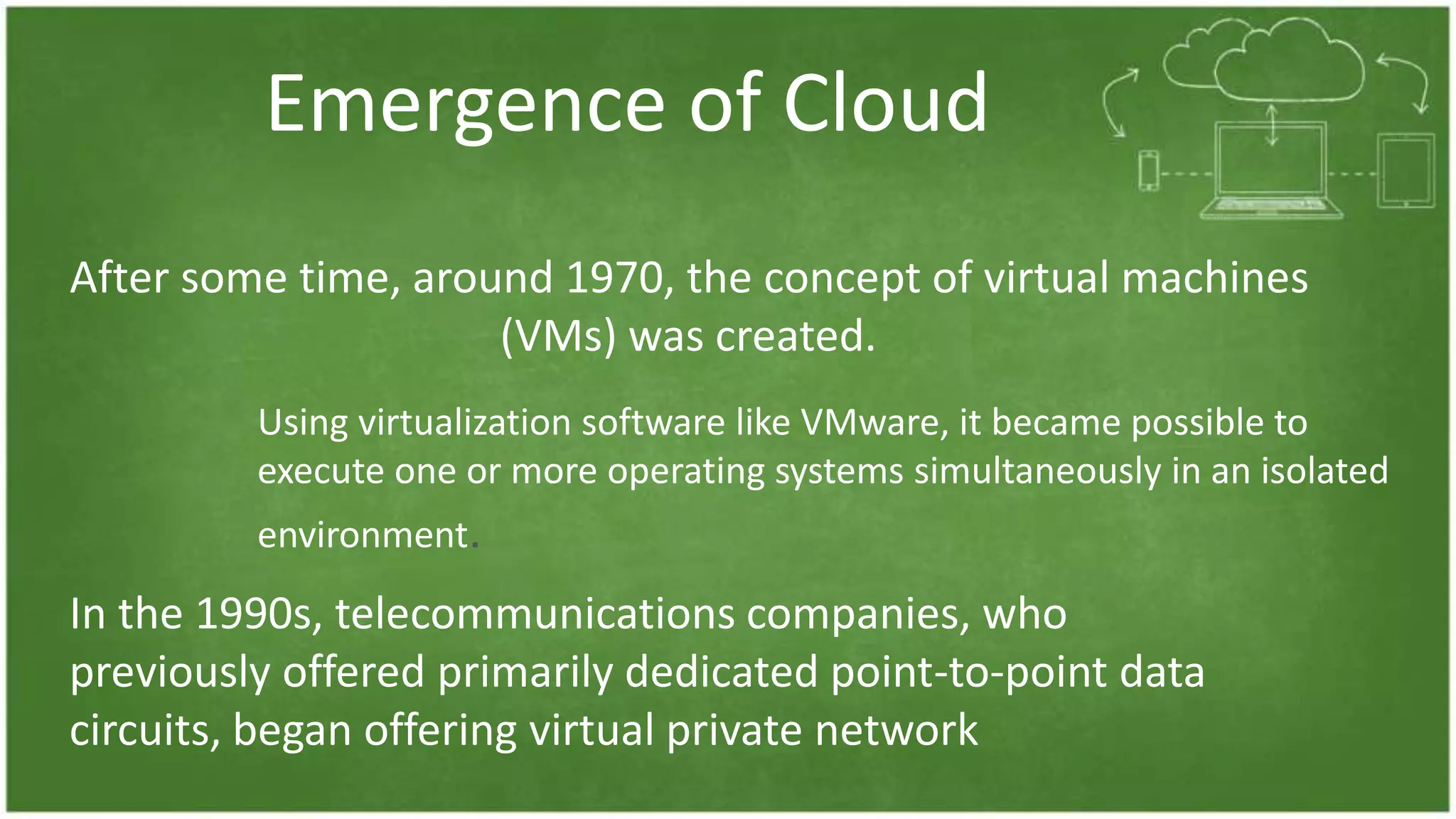
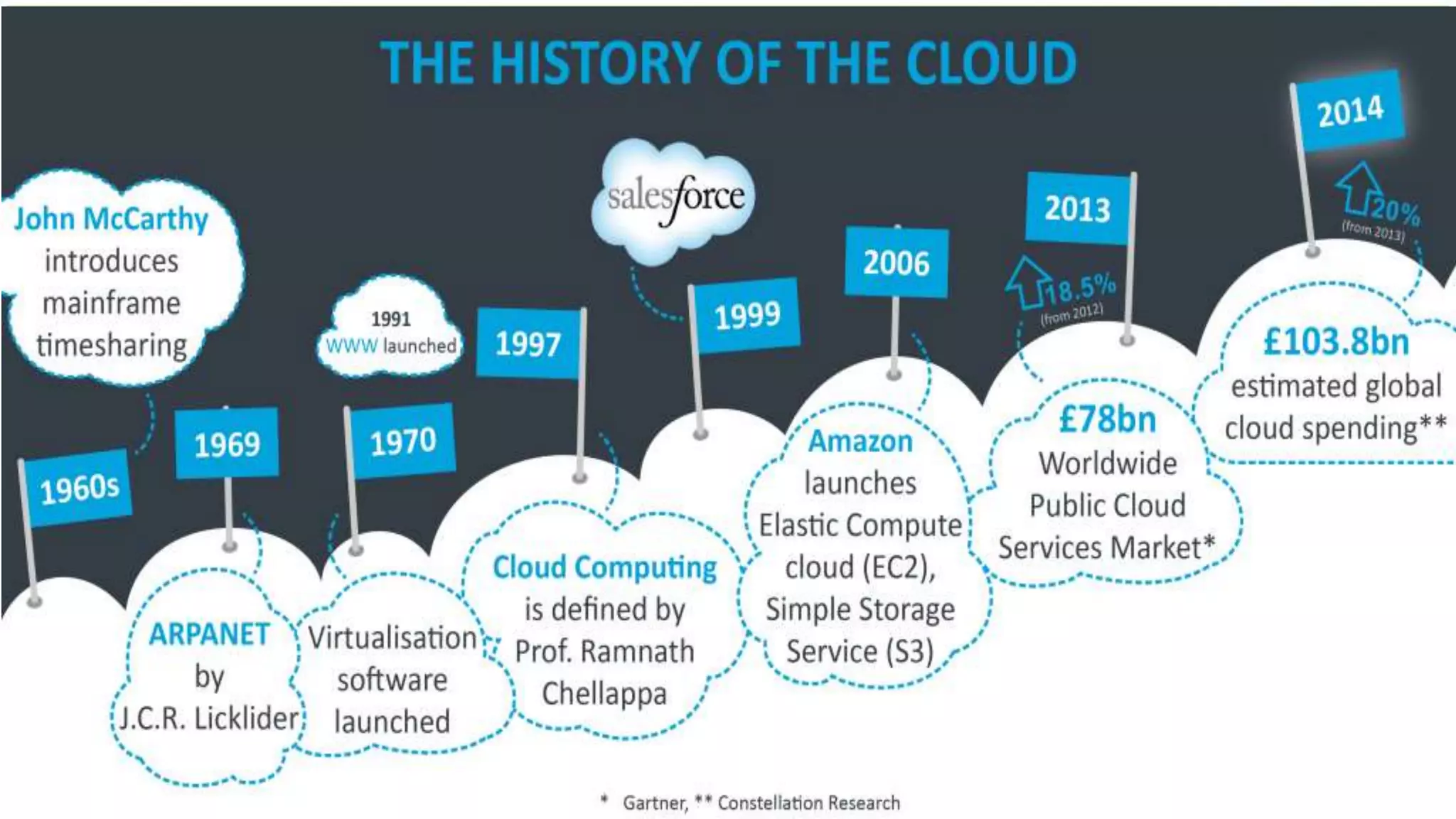
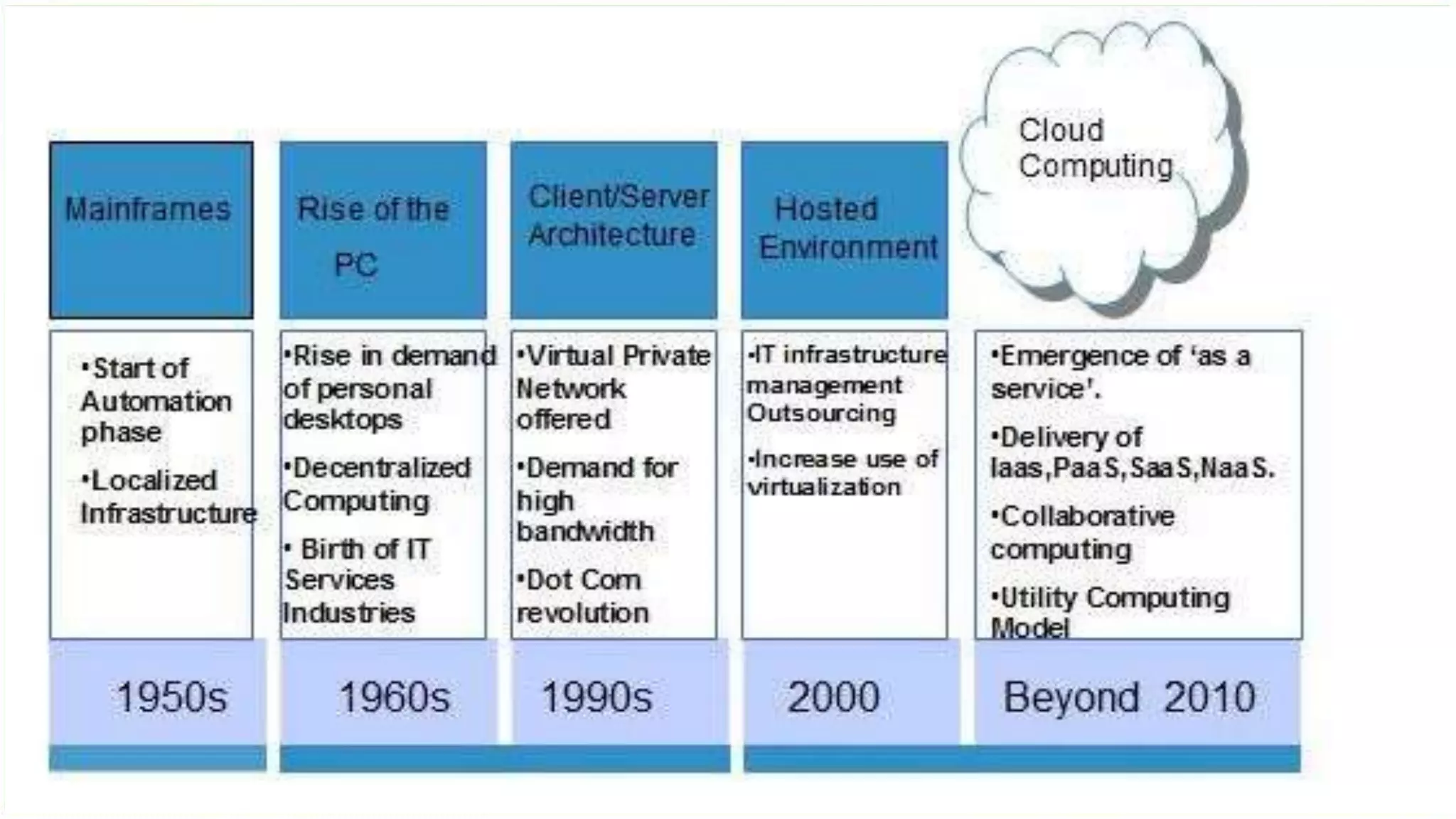
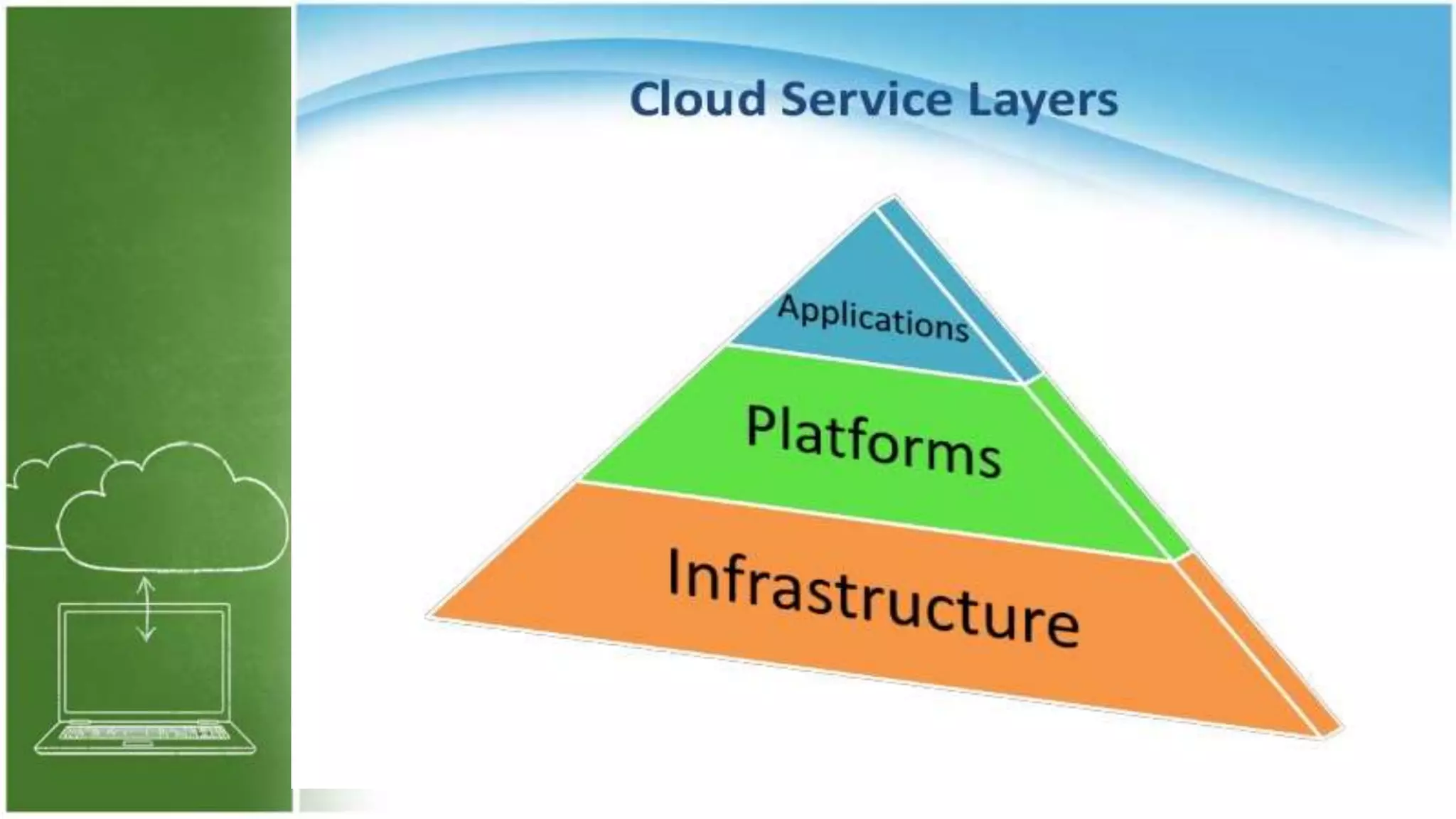
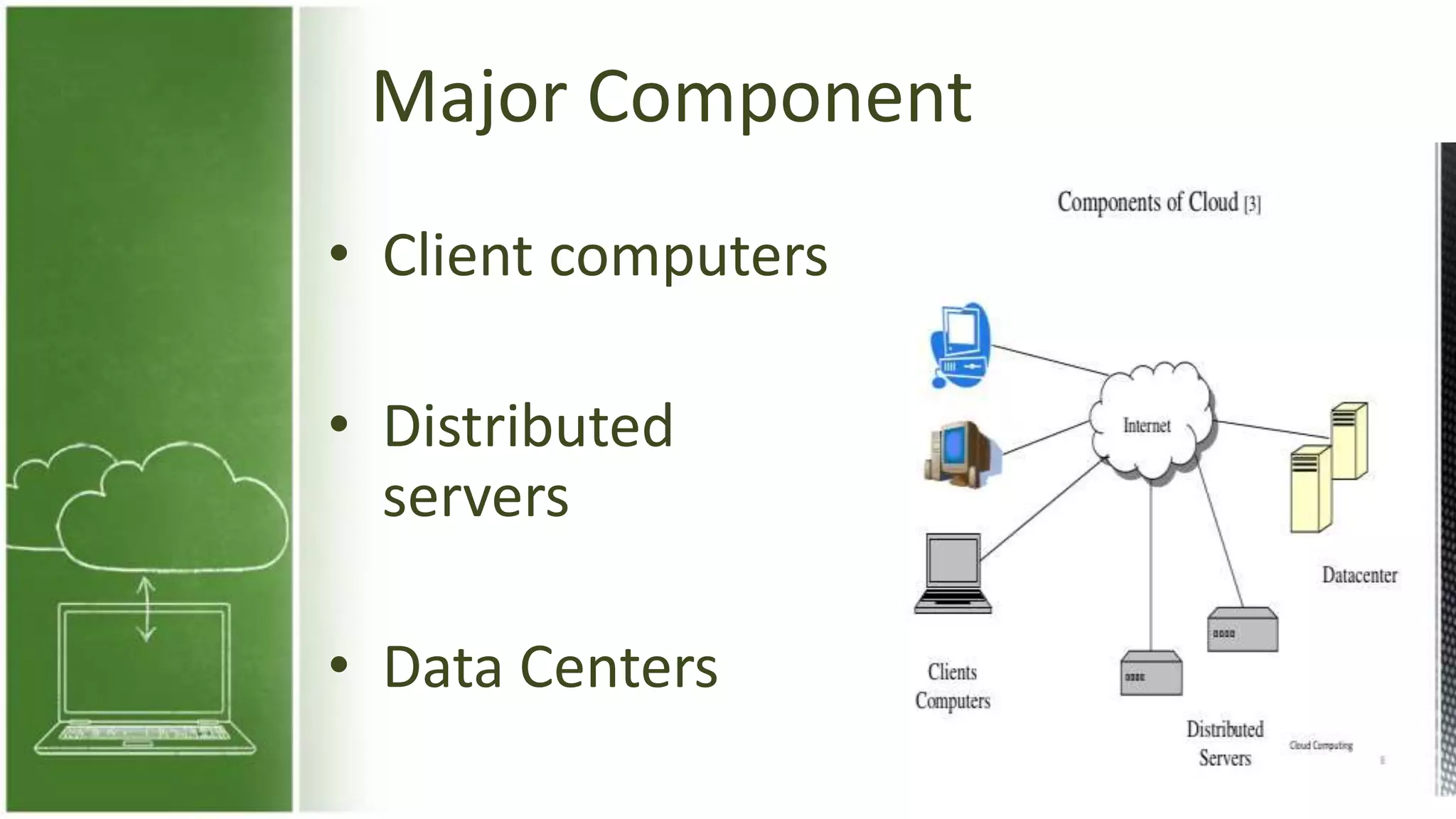
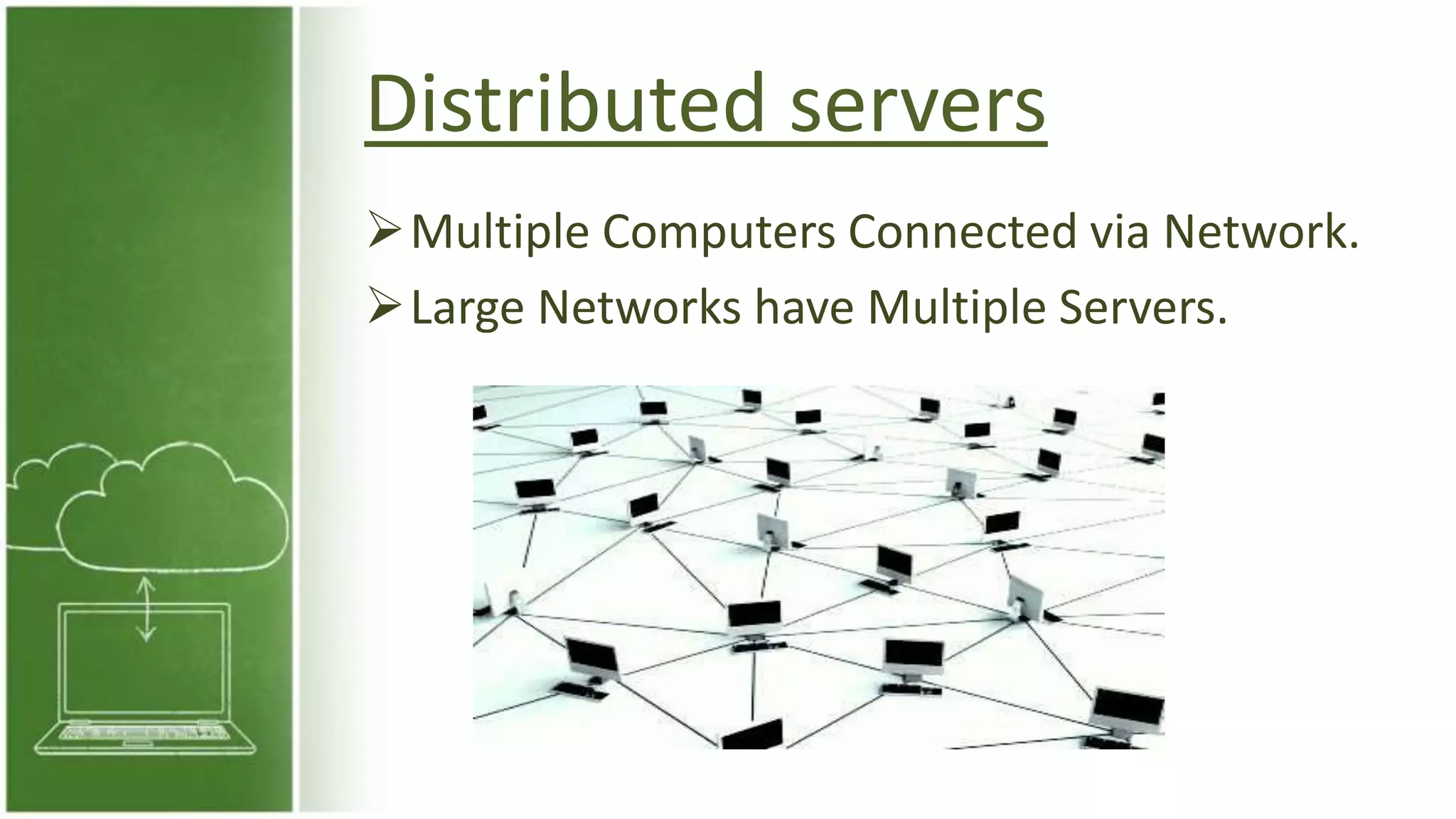
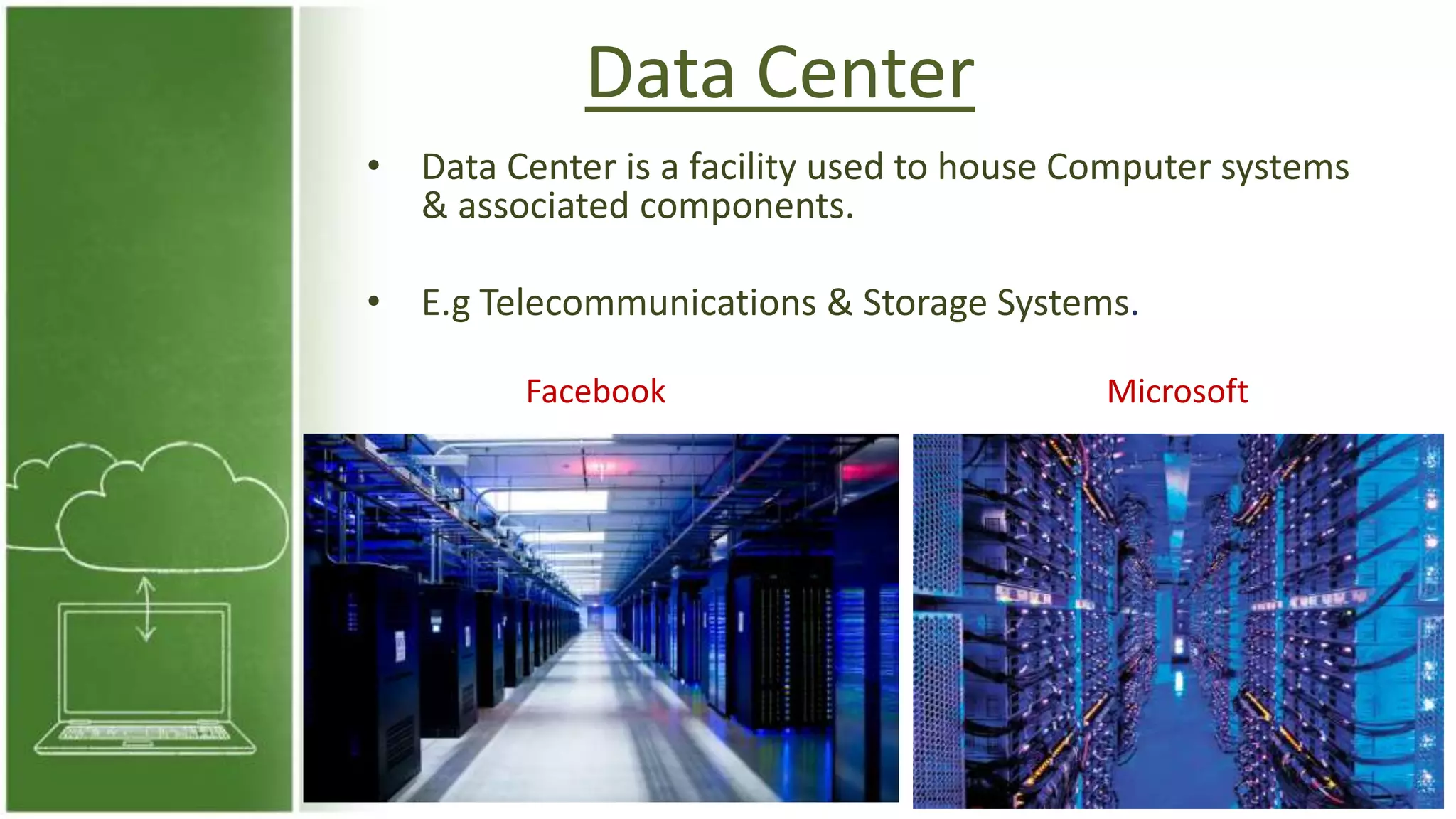
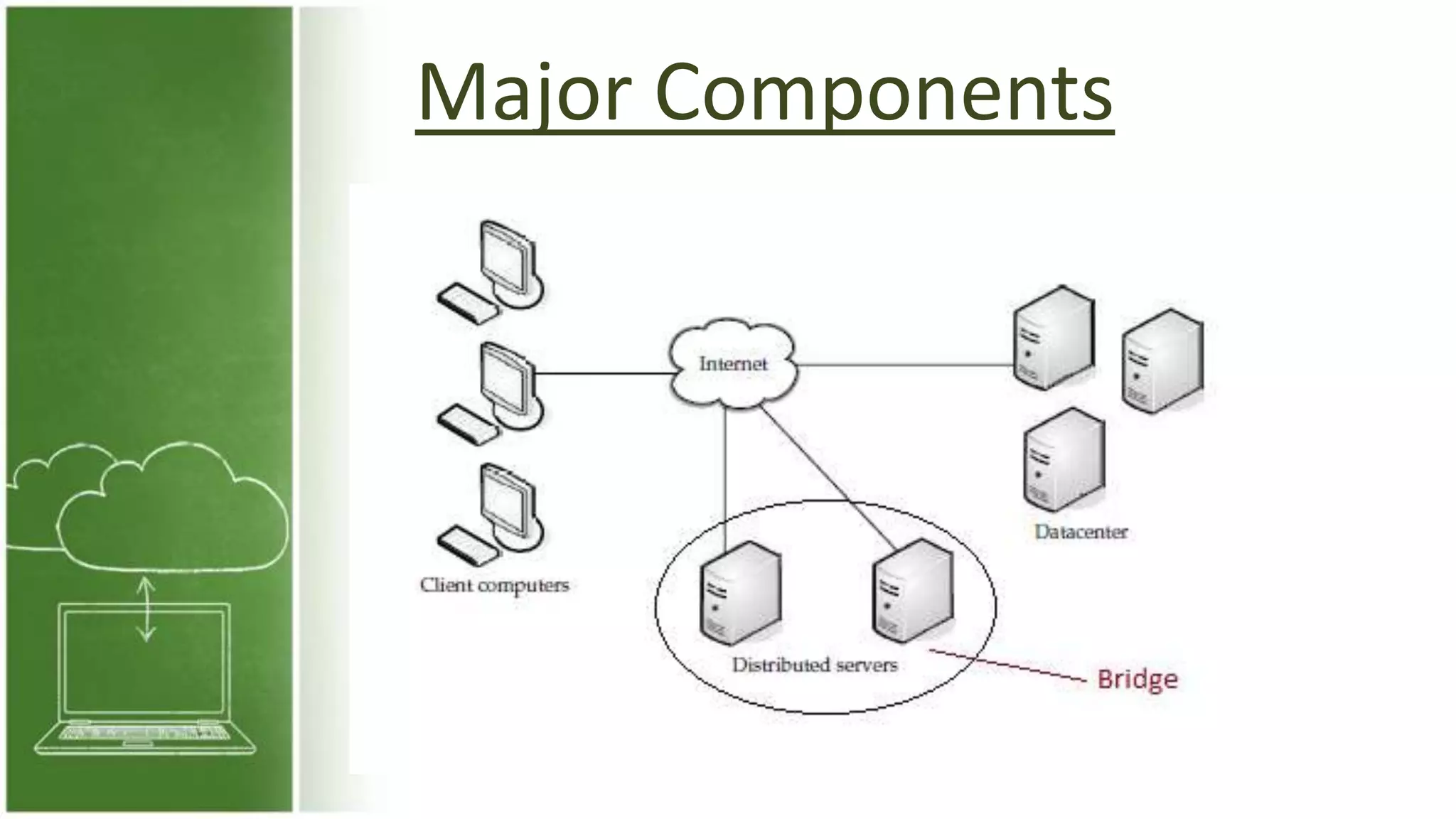
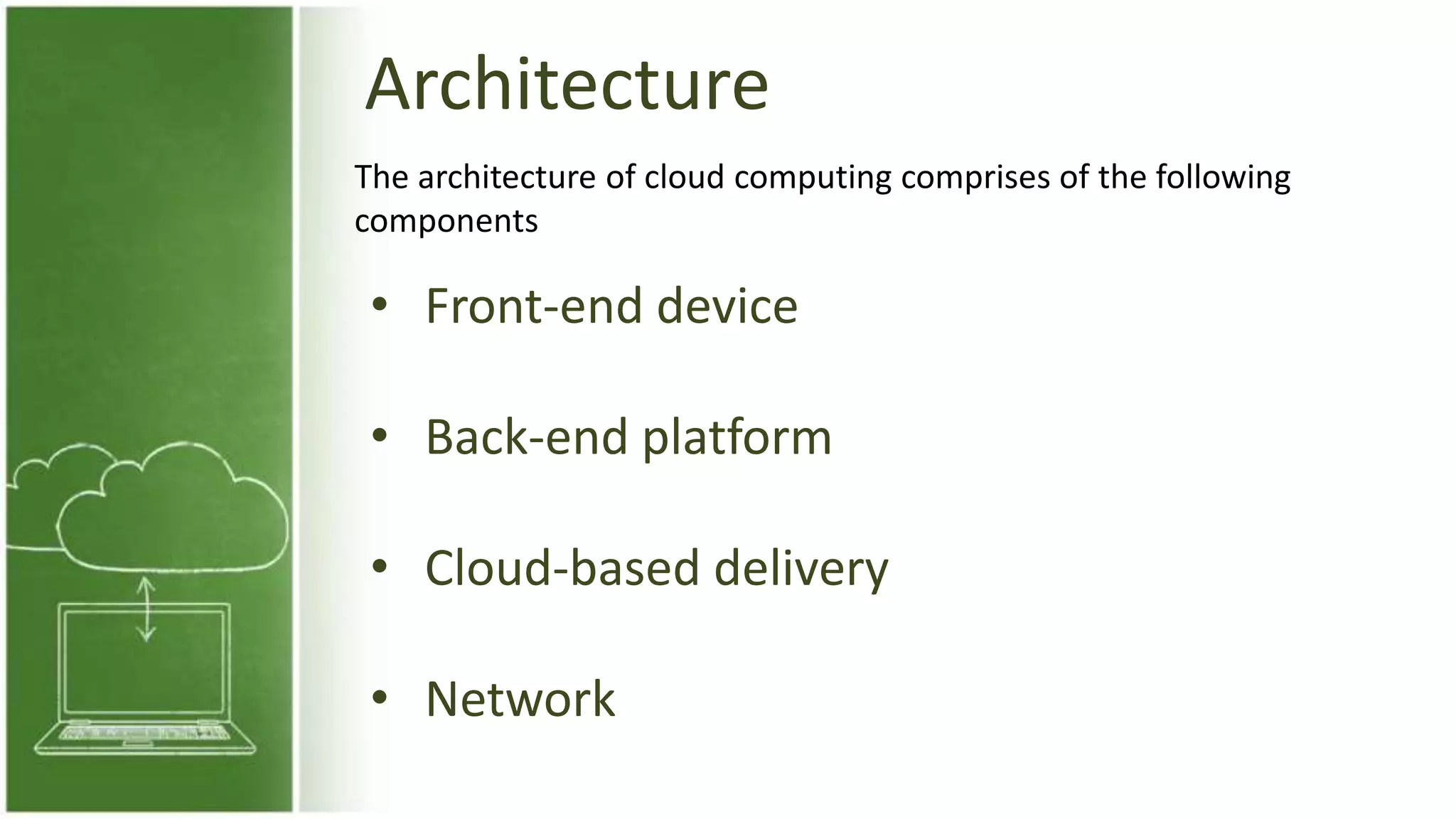
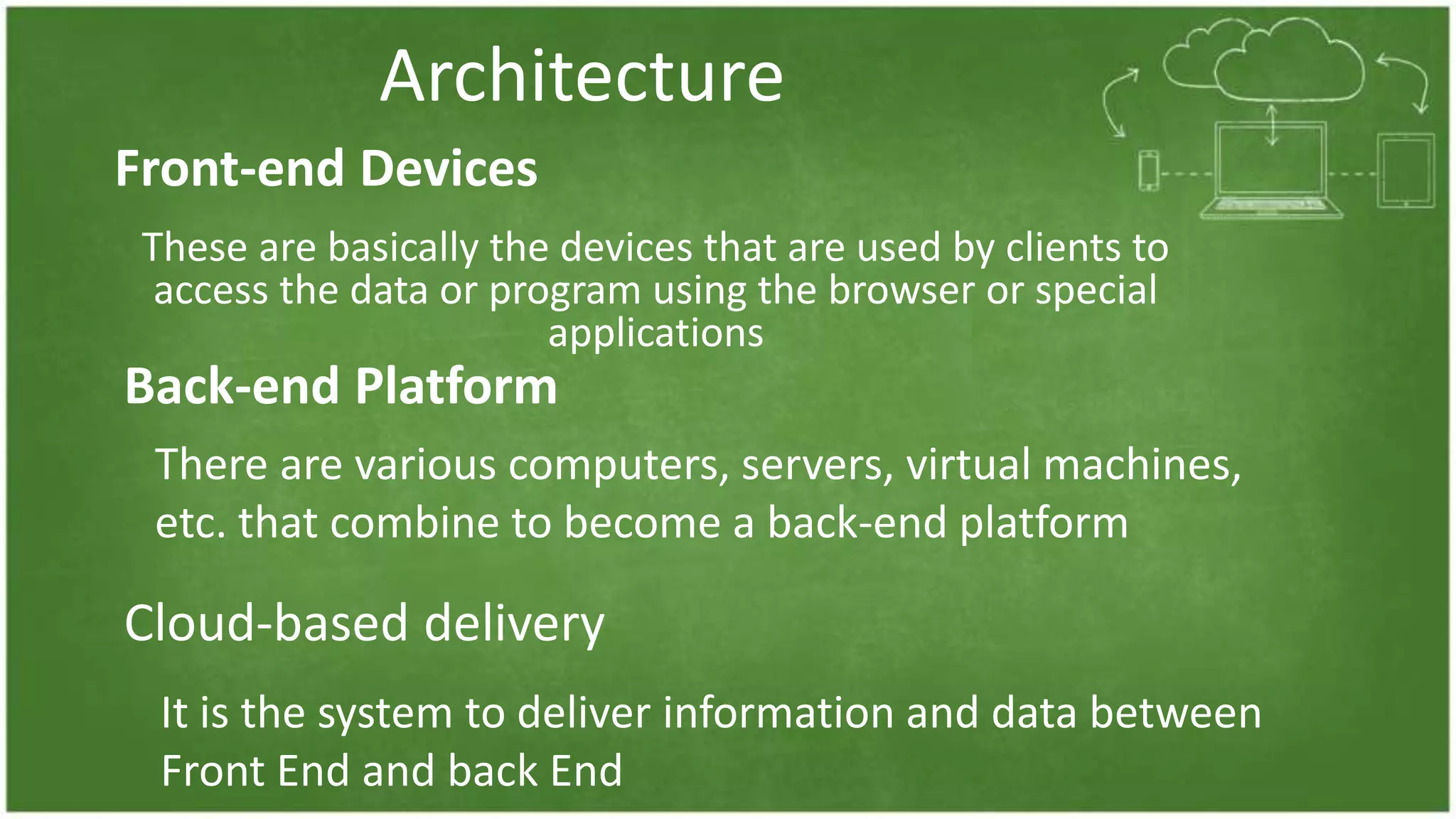
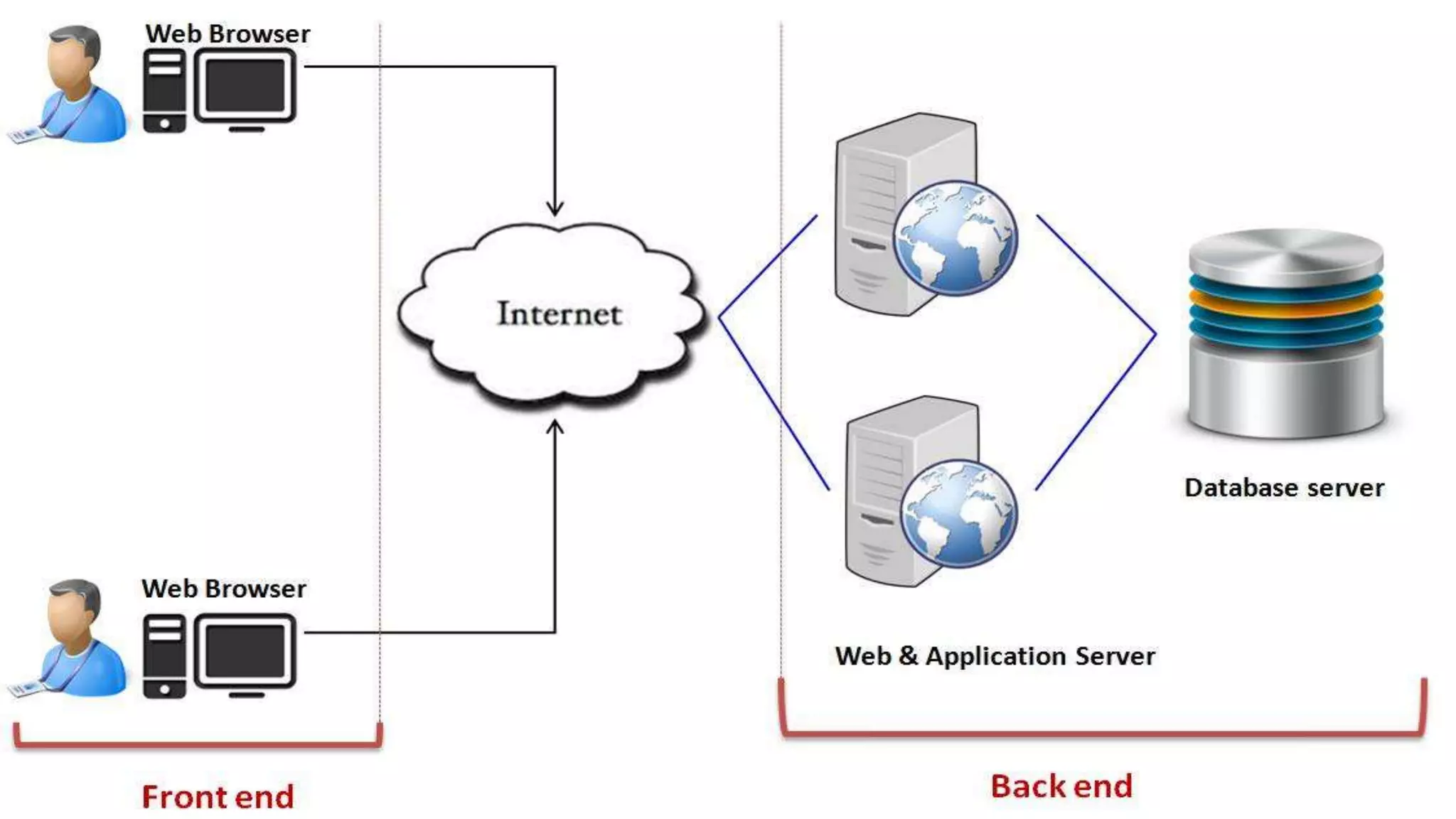
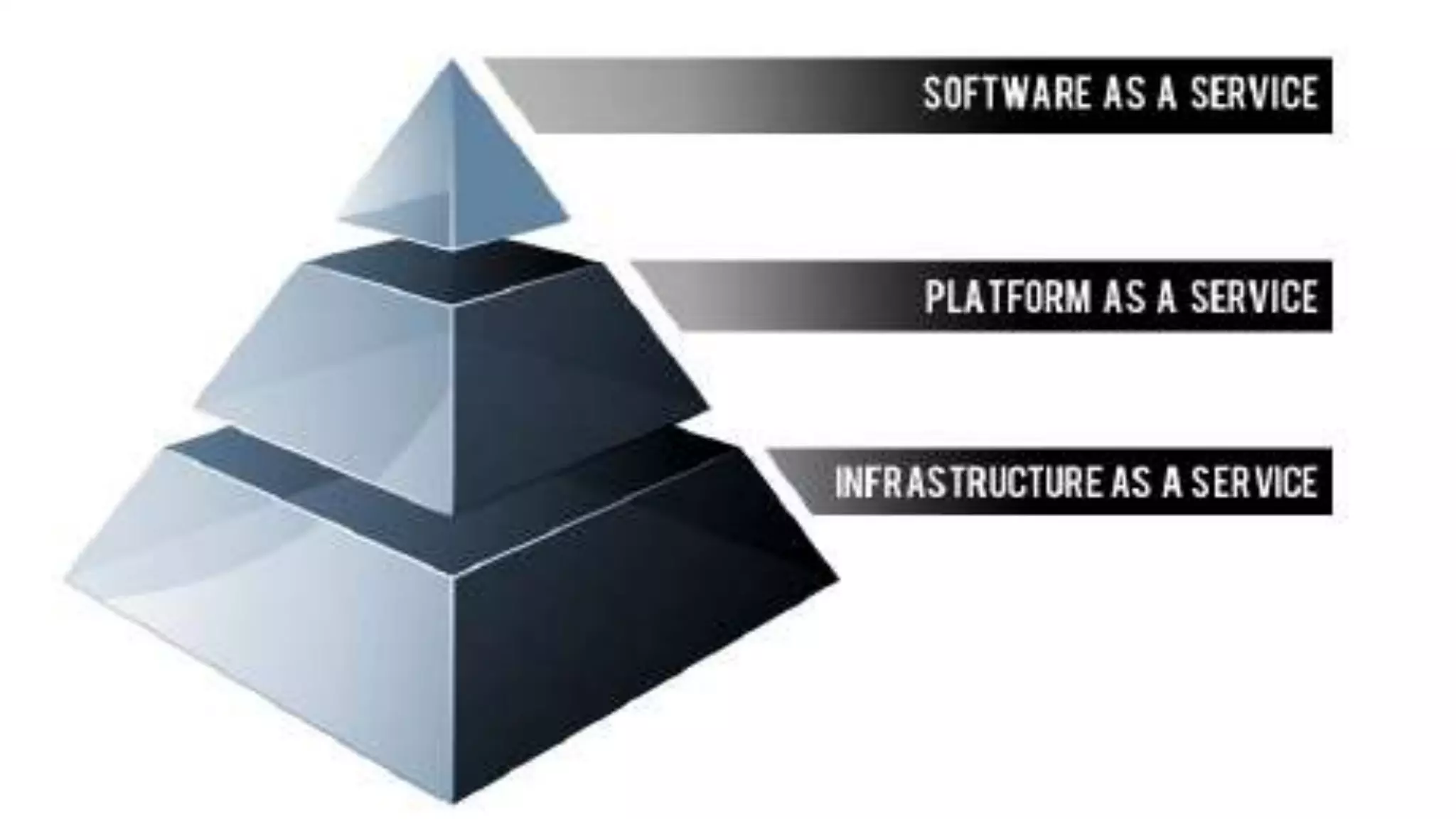
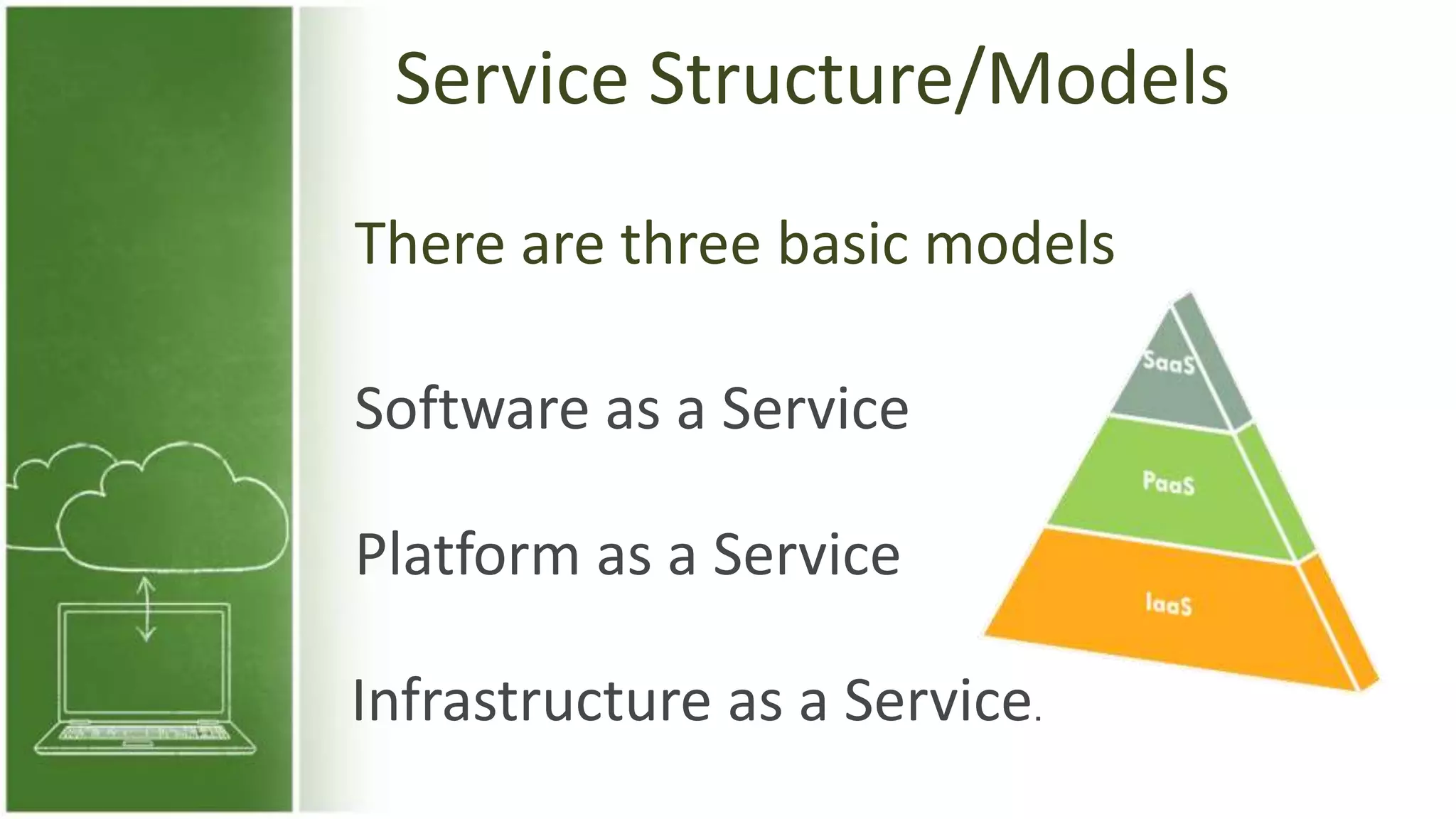
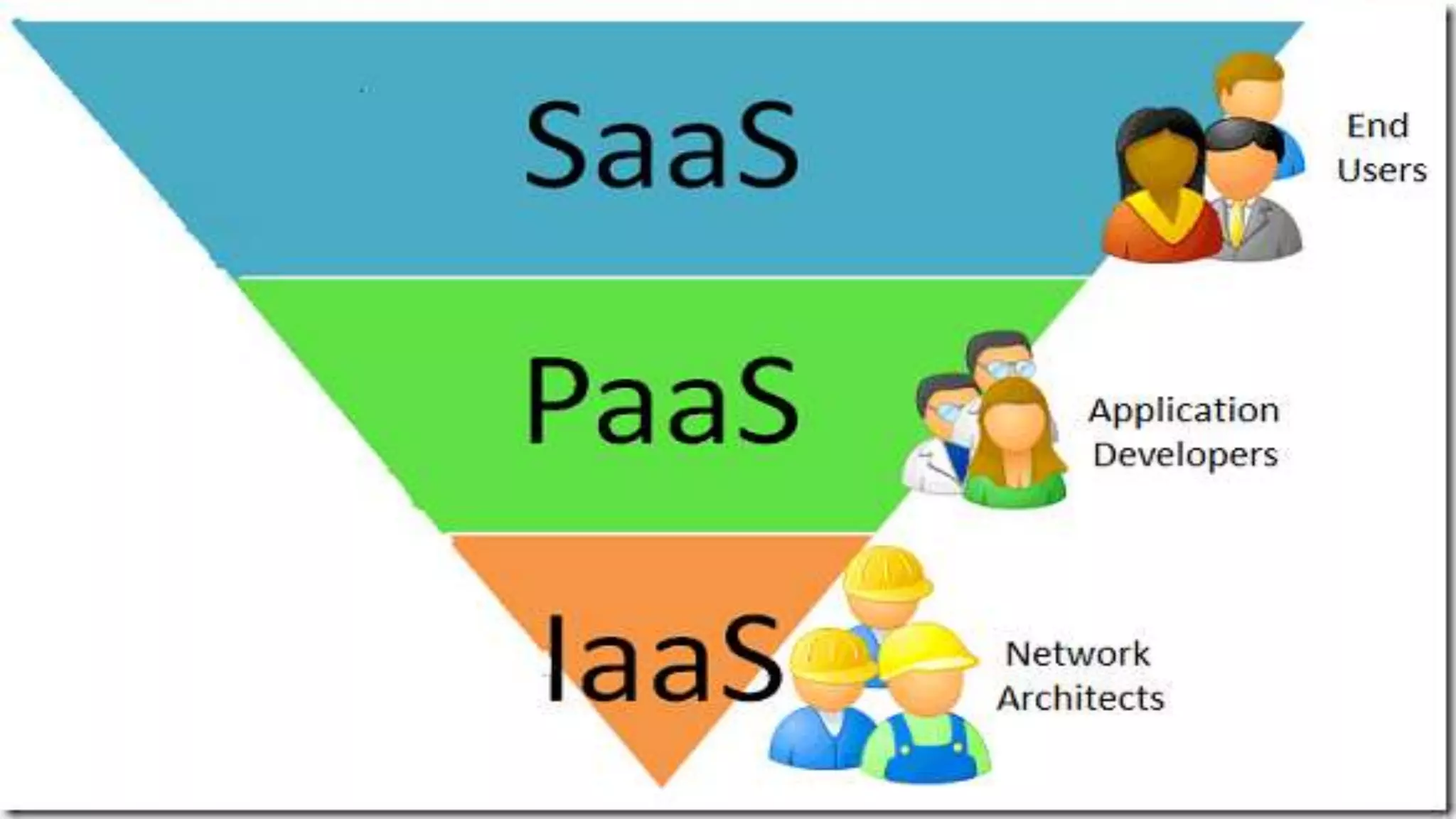
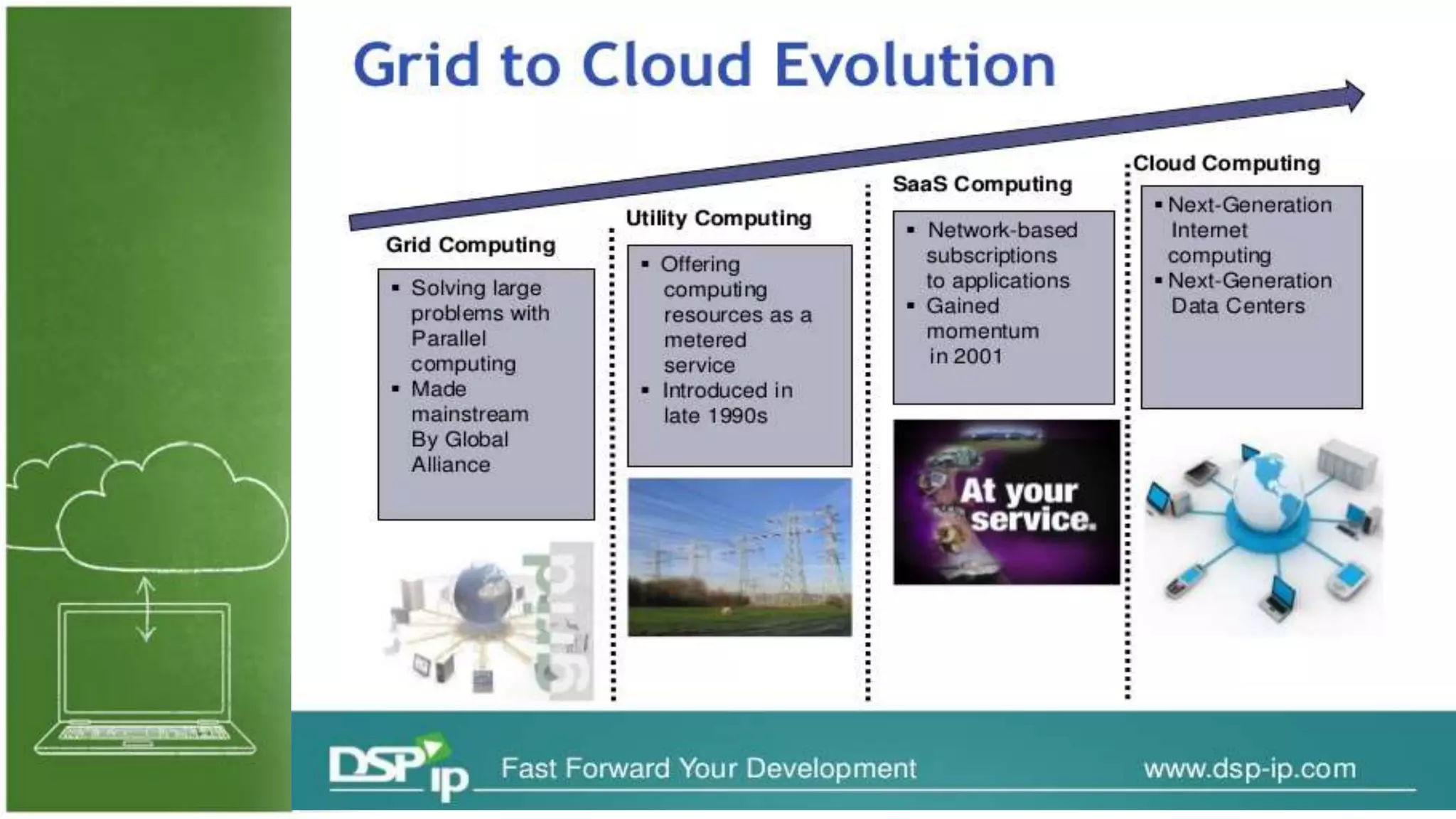
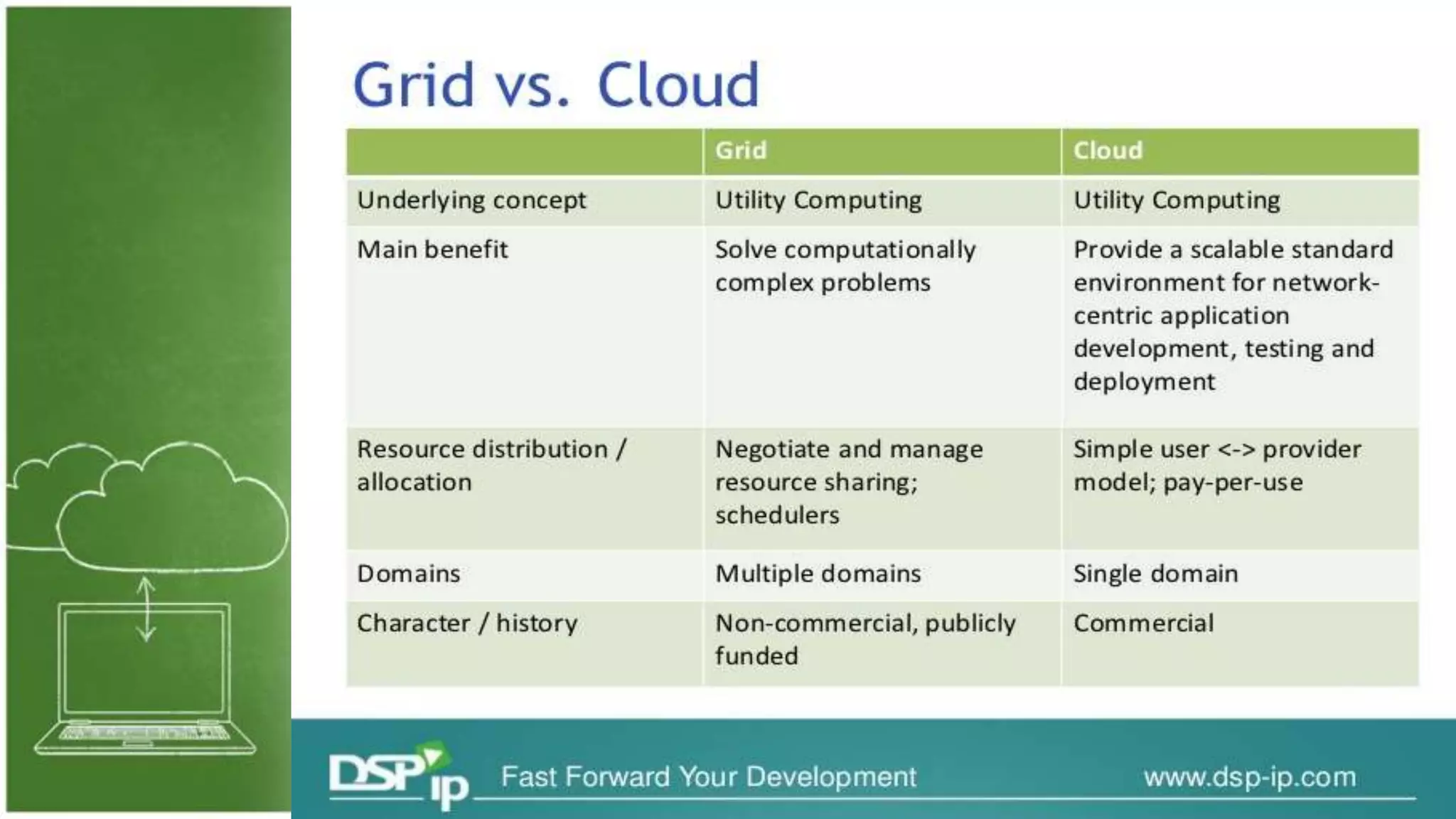
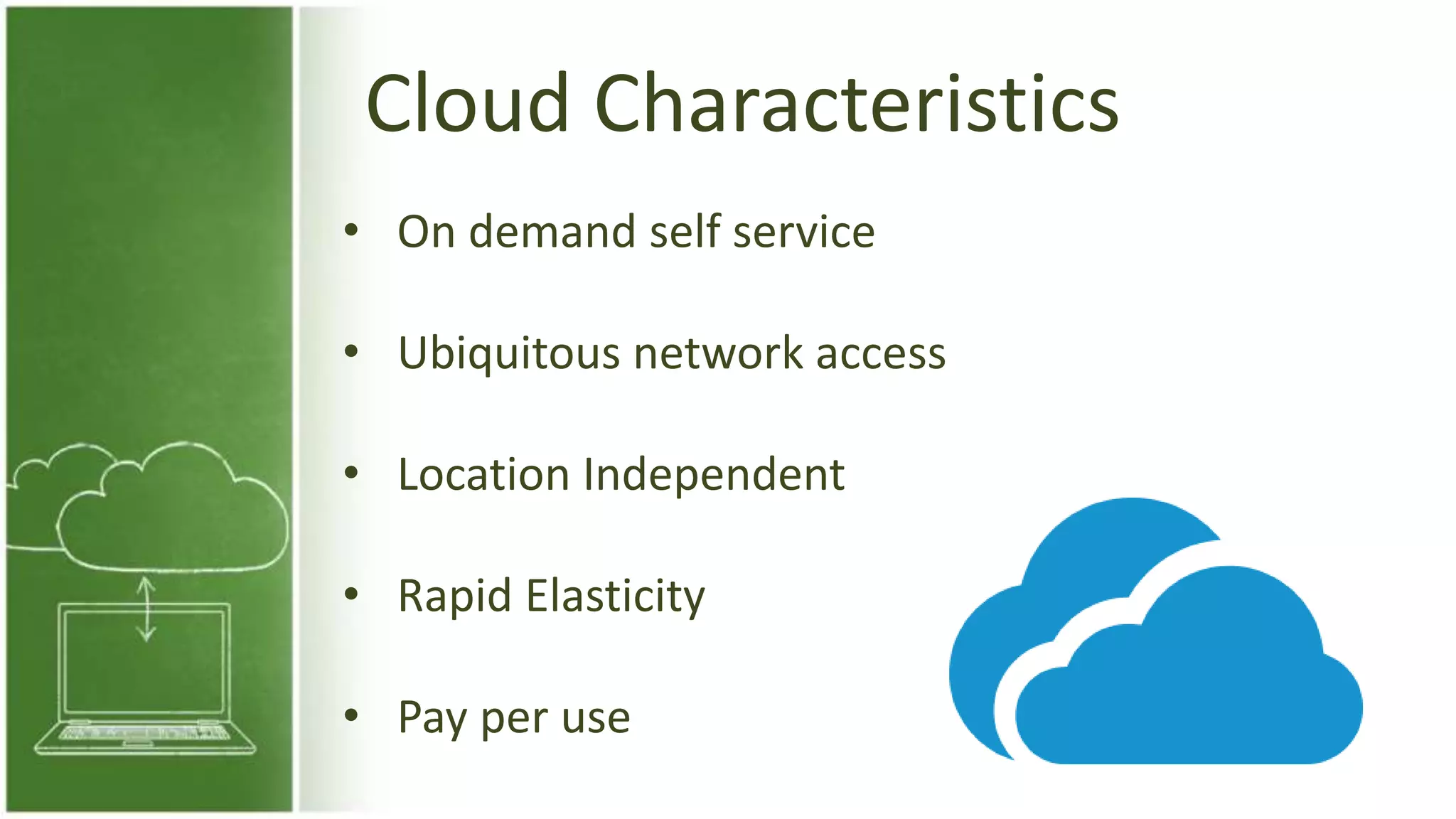
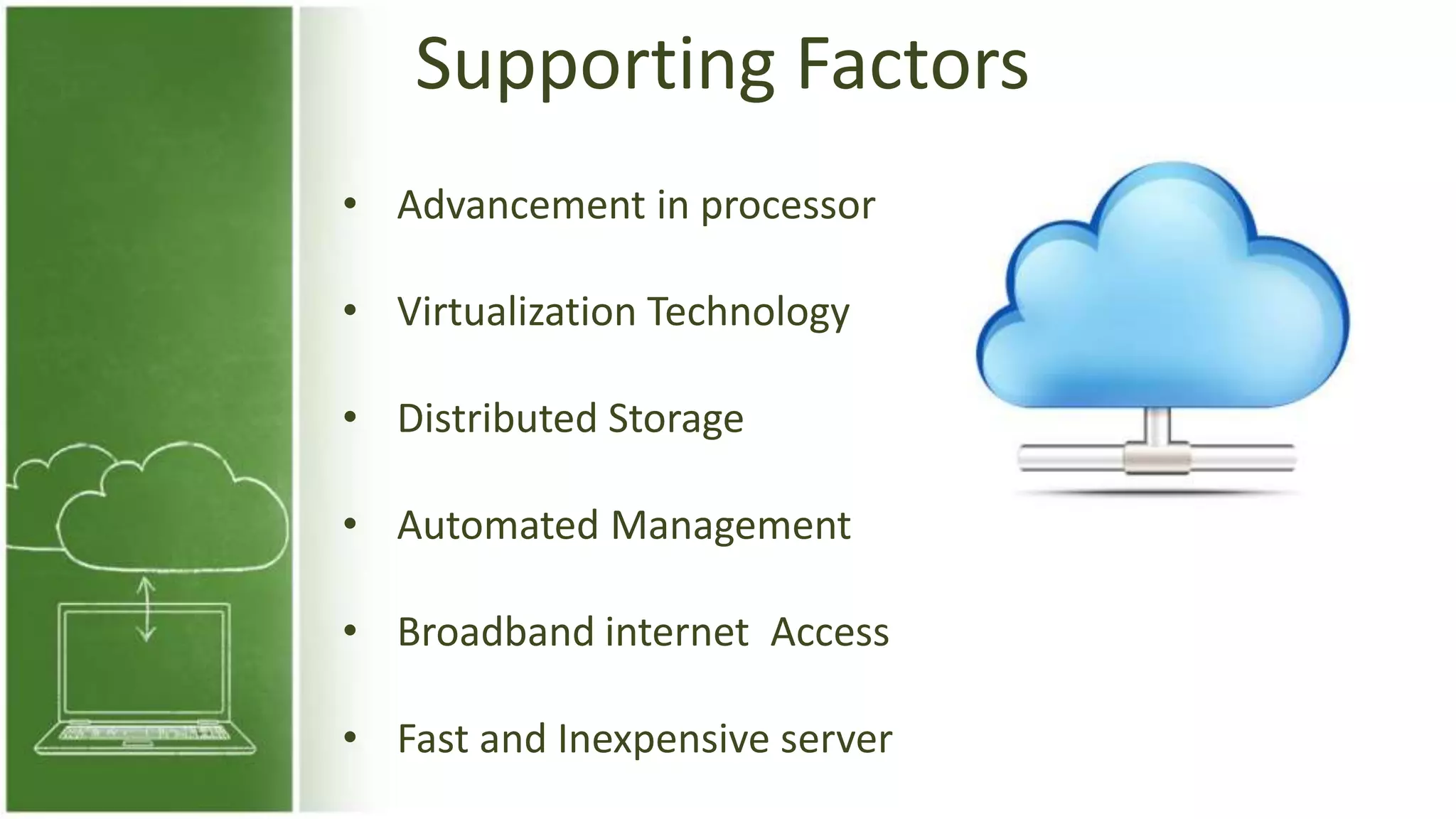
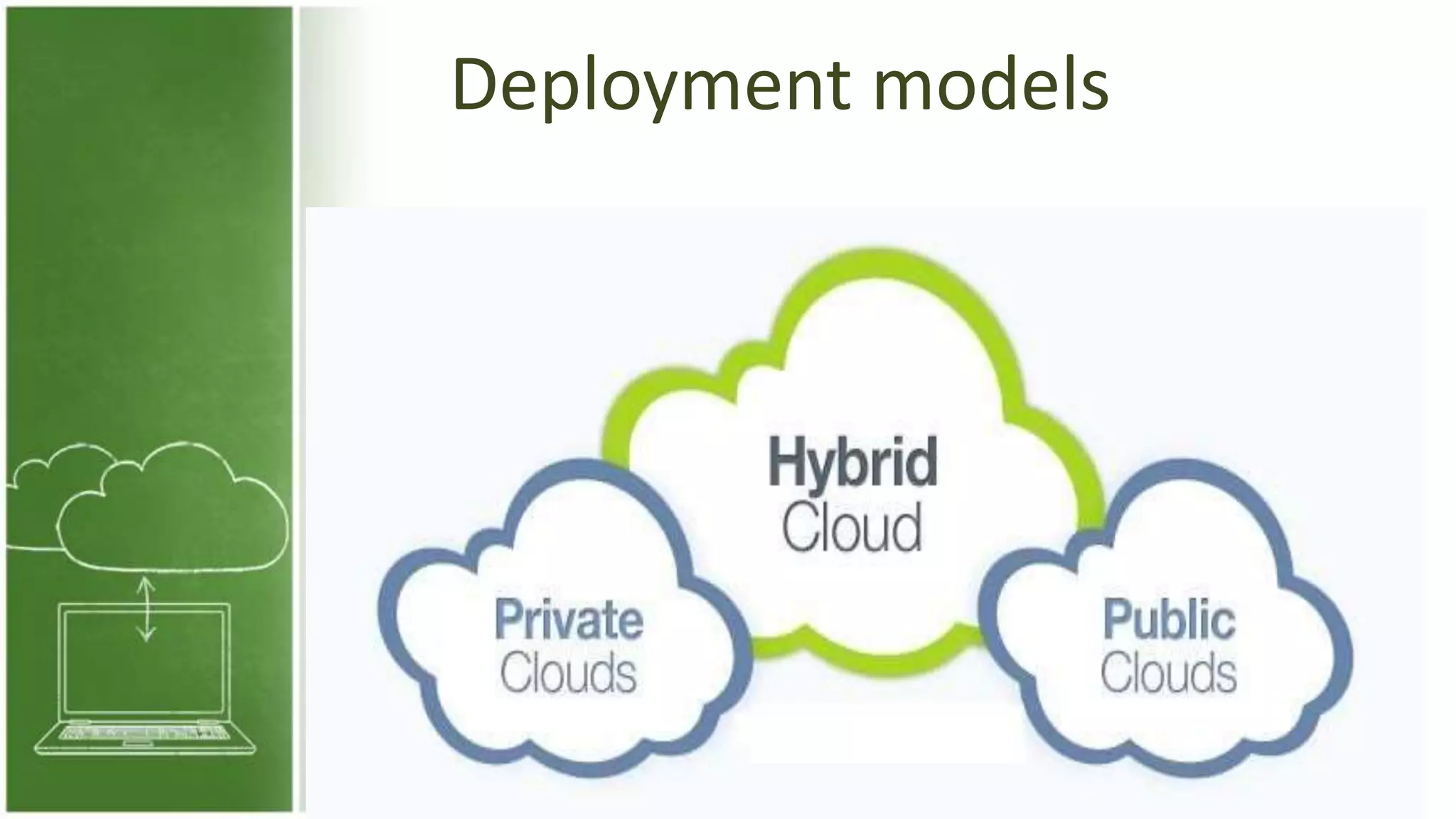
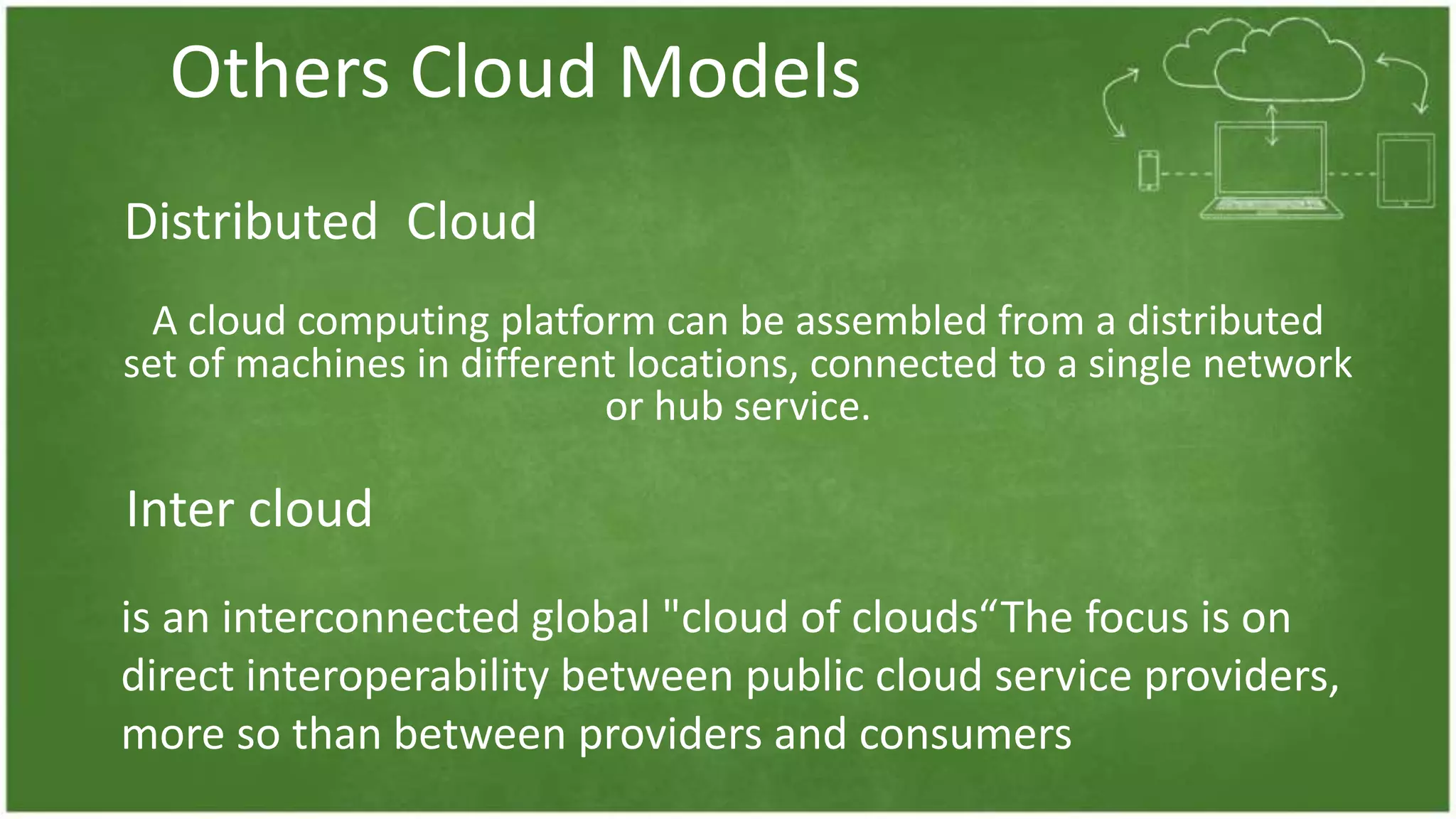
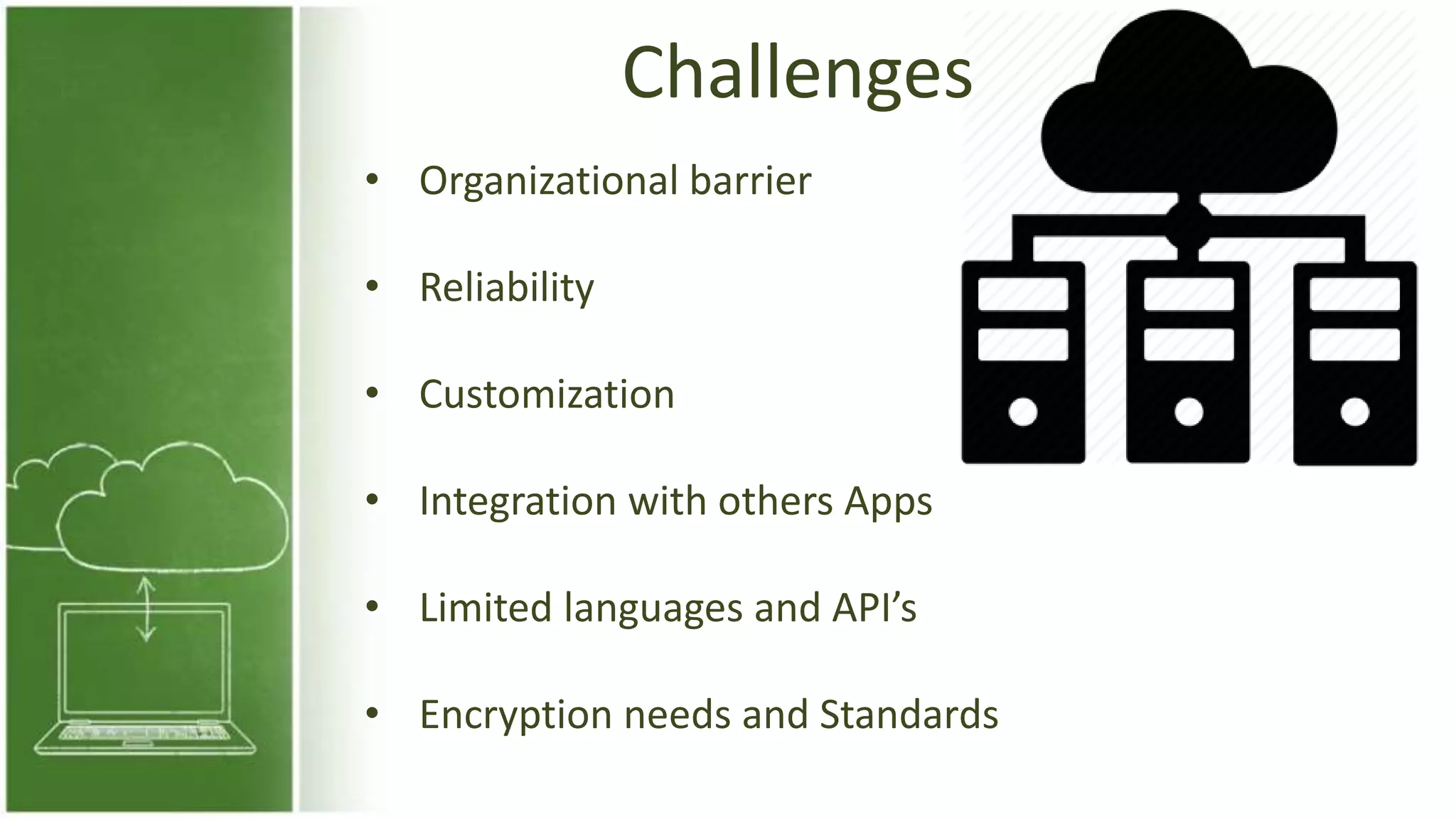
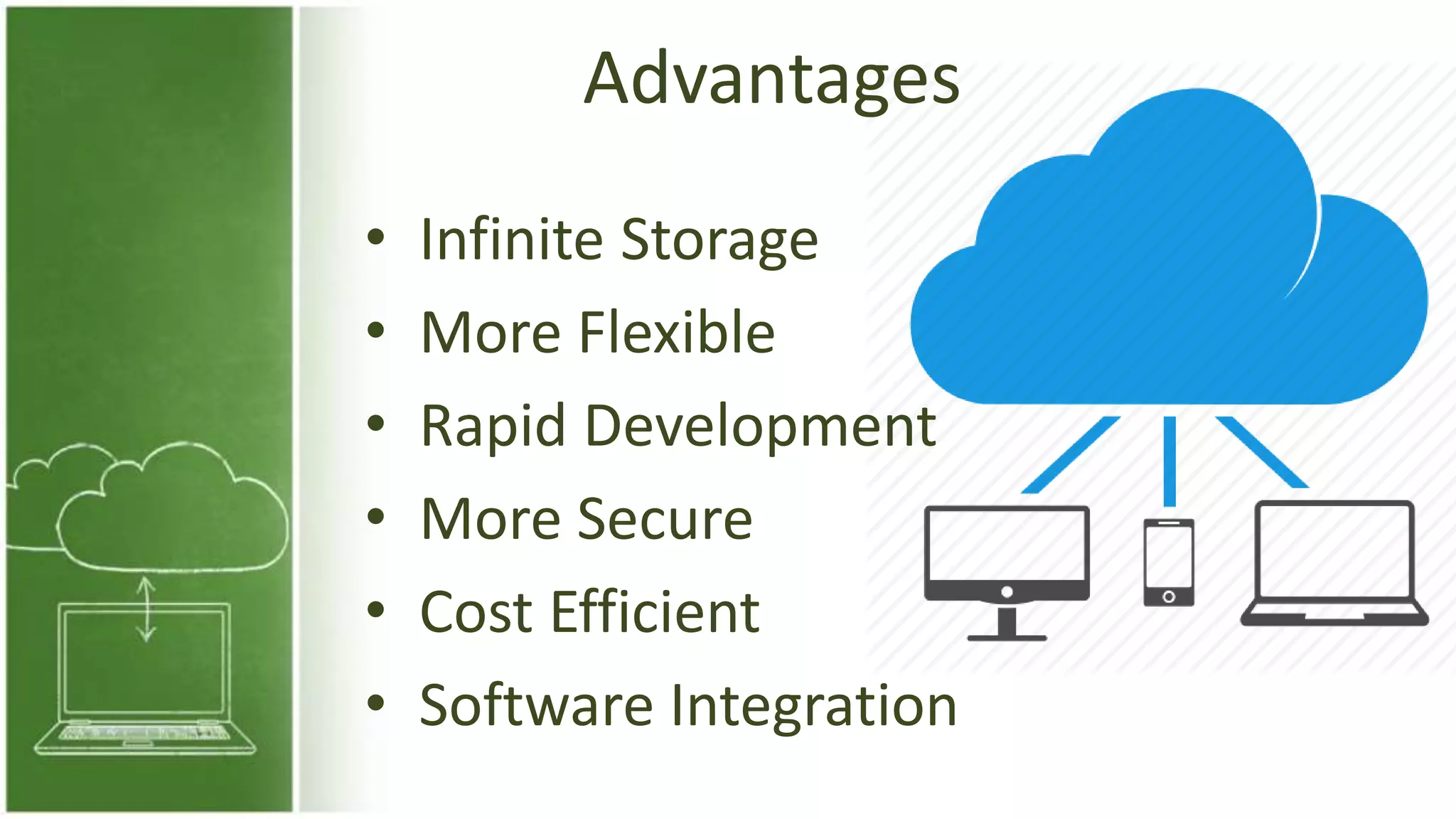
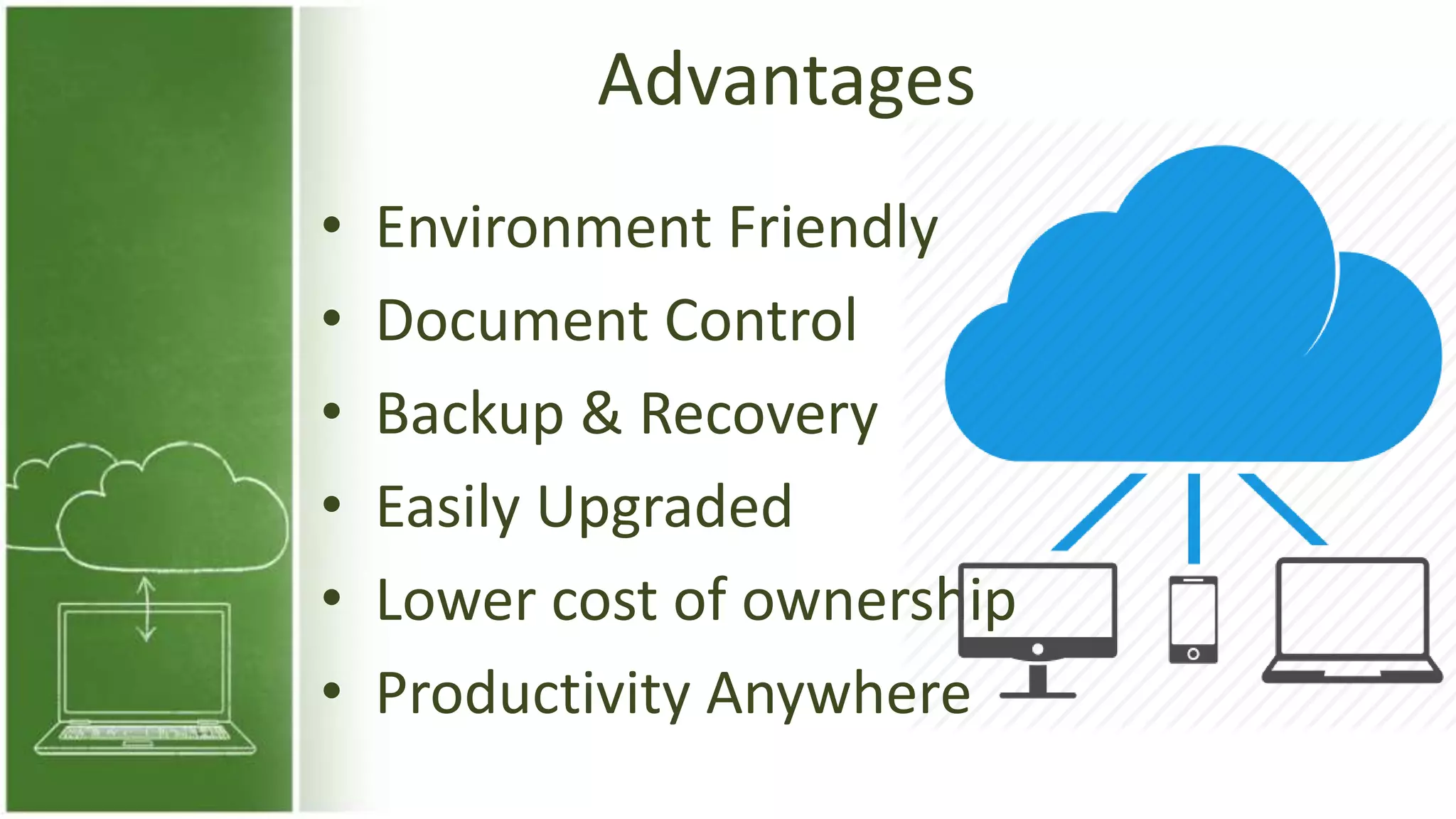
The document discusses cloud computing, defining it as internet-based computing that provides various services through remote servers. It outlines the emergence of cloud computing from the 1960s to present, detailing major components, models like SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS, and deployment strategies such as public, private, and hybrid clouds. Additionally, it highlights the advantages, disadvantages, and security concerns associated with cloud computing, as well as its evolution and future potential.