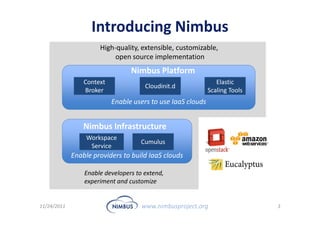
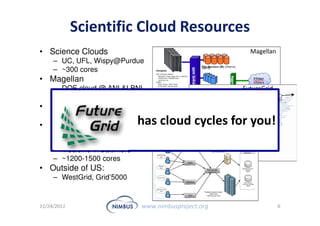
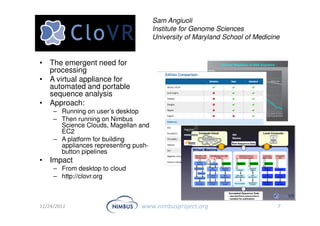
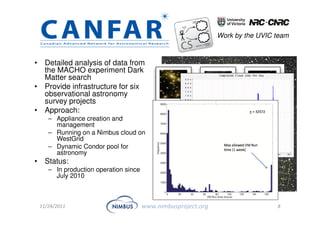
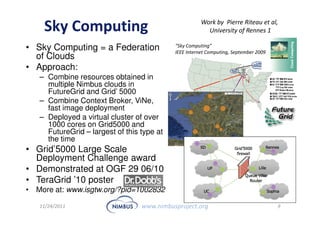
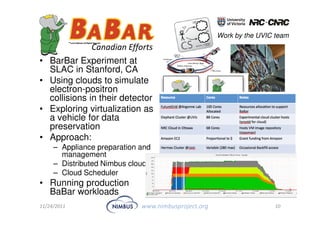
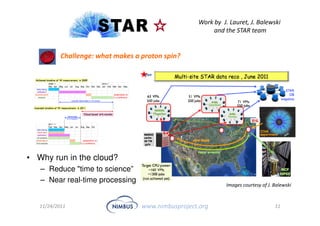
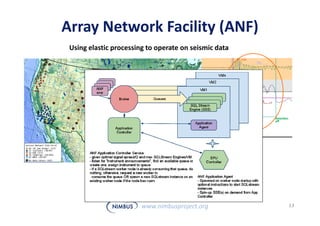
This document discusses building an outsourcing ecosystem for science using the Nimbus platform. Nimbus provides tools that enable users to access infrastructure-as-a-service clouds, providers to build IaaS clouds, and developers to extend cloud capabilities. The platform is being used for various scientific applications including genome sequencing, astronomy surveys, particle physics experiments, and seismic data processing. These applications demonstrate trends toward on-demand, elastic processing across multiple cloud providers to scale from desktops to large-scale, production runs.