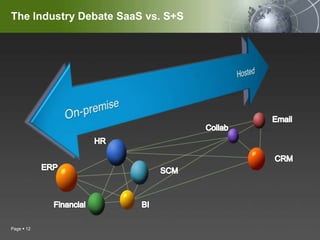
The document discusses Software as a Service (SaaS), defining it as software provided over the internet on a subscription basis. It outlines opportunities of SaaS like lower costs, flexibility, and focus on core business. Considerations include integration with existing systems, customization needs, and data security risks from storing information remotely. SaaS adoption is growing, with over 10 million companies expected to use it in the next 5-10 years and more than half of Fortune 500 companies already using it. Major software companies are heavily investing in SaaS.