This seminar presentation provides an overview of cloud computing, including:
- Definitions of cloud computing and motivations for its use such as demand for interactive applications and batch processing.
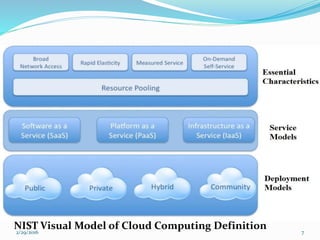
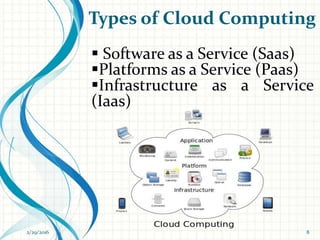
- Descriptions of the main types of cloud computing models: Software as a Service (SaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS).
- Discussions of cloud deployment models like public, private, community, and hybrid clouds.
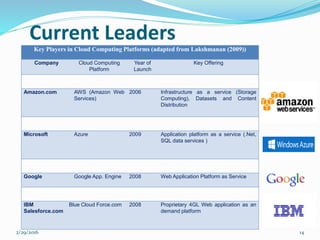
- Examples of current industry leaders in cloud computing platforms like Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure, and Google App Engine.