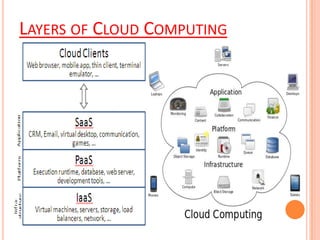
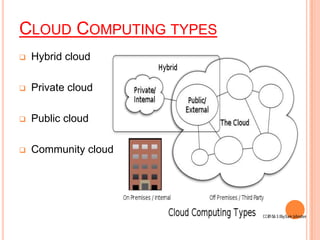
This document provides an overview of cloud computing, outlining its definition, history, layers (including SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS), types (such as private, public, and hybrid clouds), advantages, and disadvantages. It highlights the evolution of cloud computing and its impact on businesses, emphasizing the benefits like lower costs and improved performance, alongside challenges like dependency on internet connectivity. The conclusion suggests that cloud computing is a rapidly growing sector with a mix of opportunities and concerns for its future adoption.