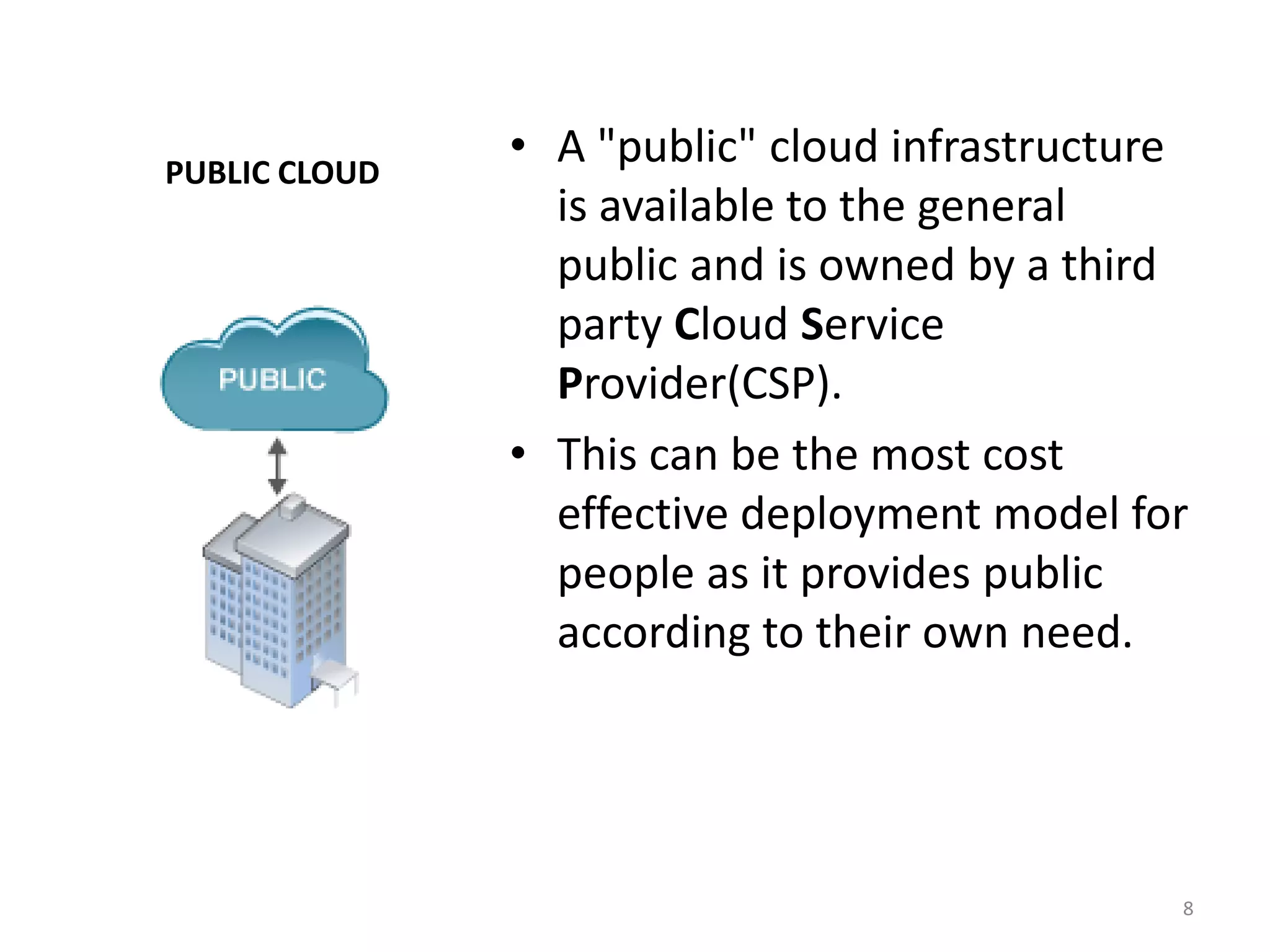
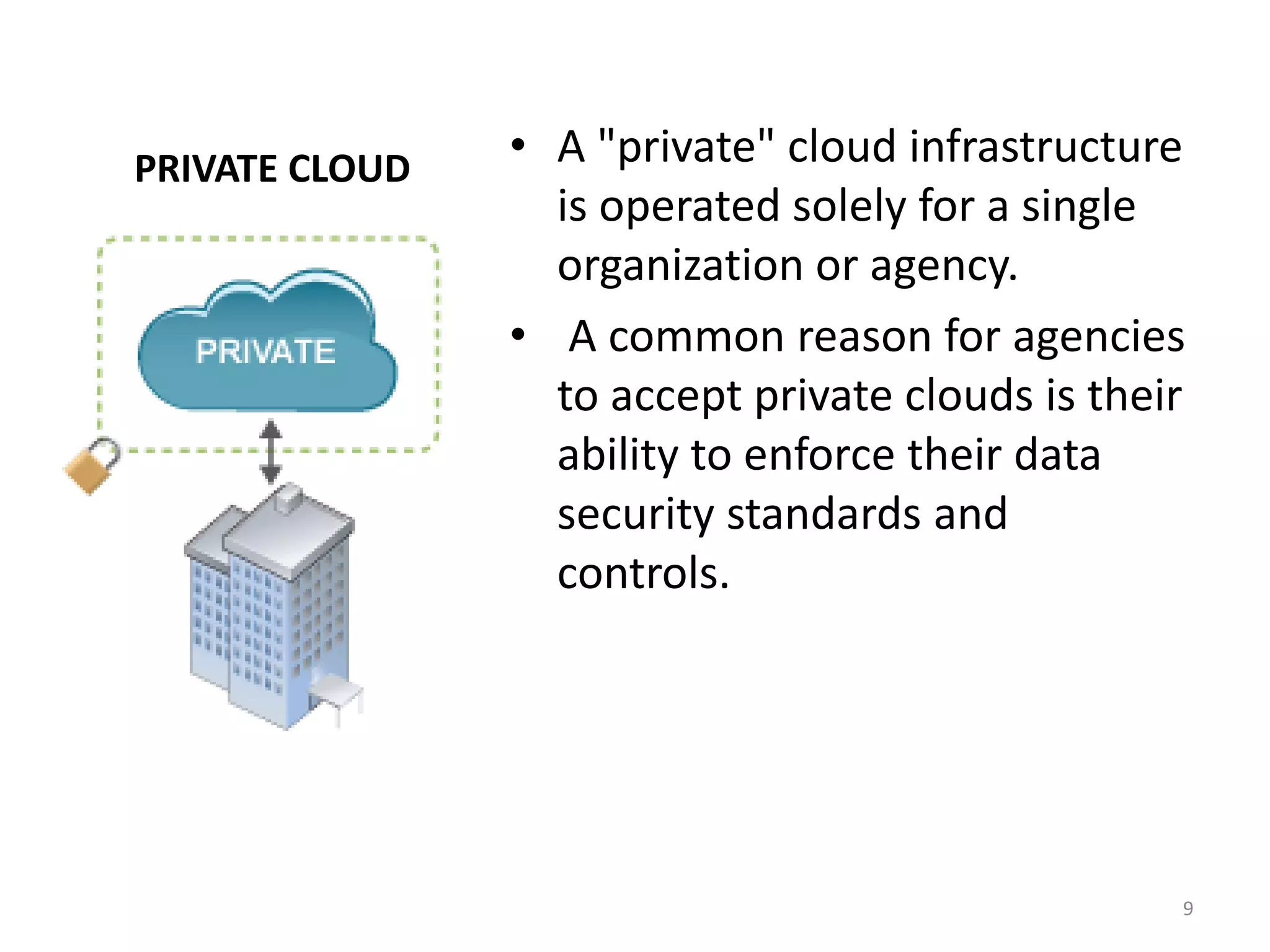
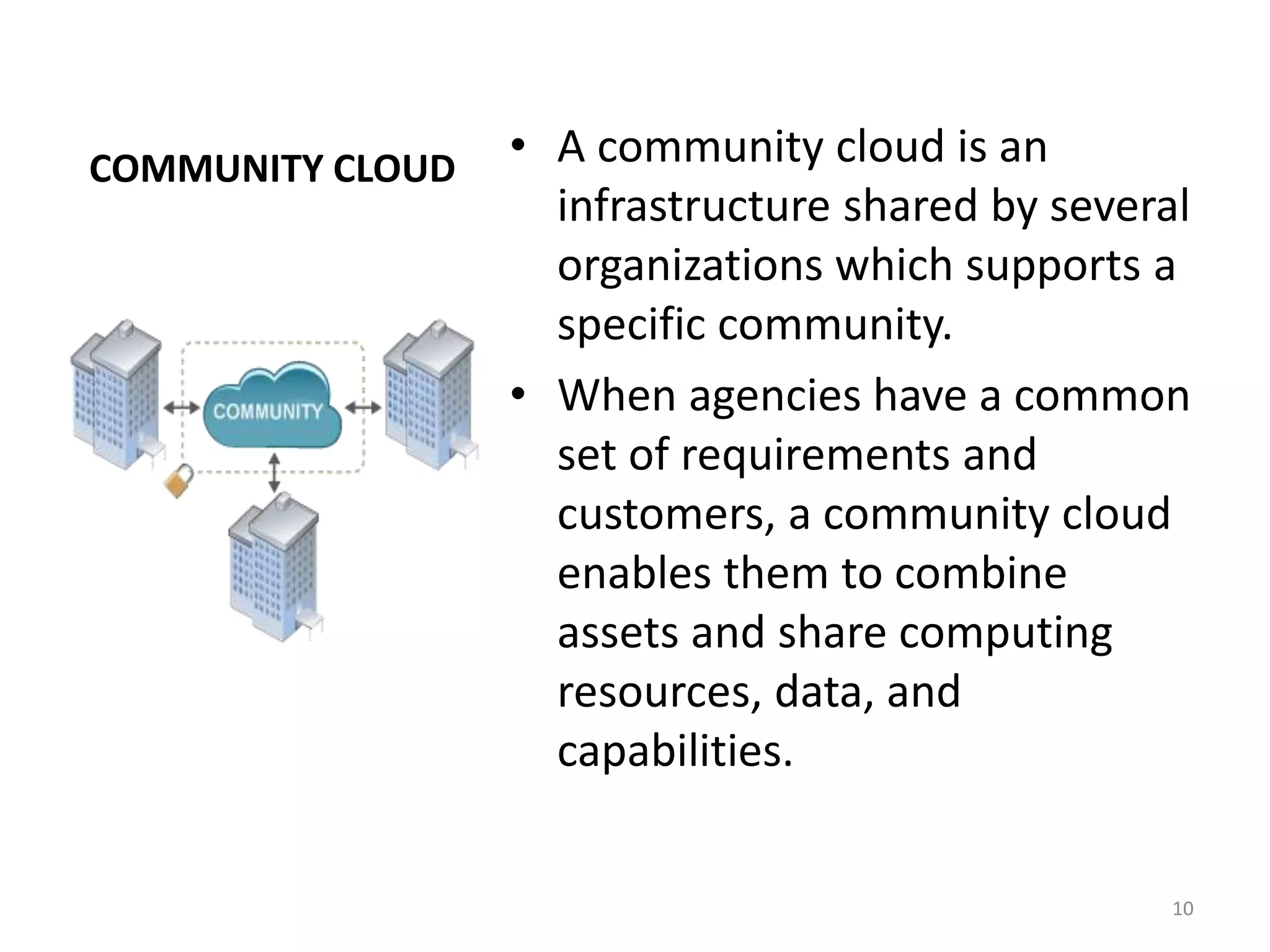
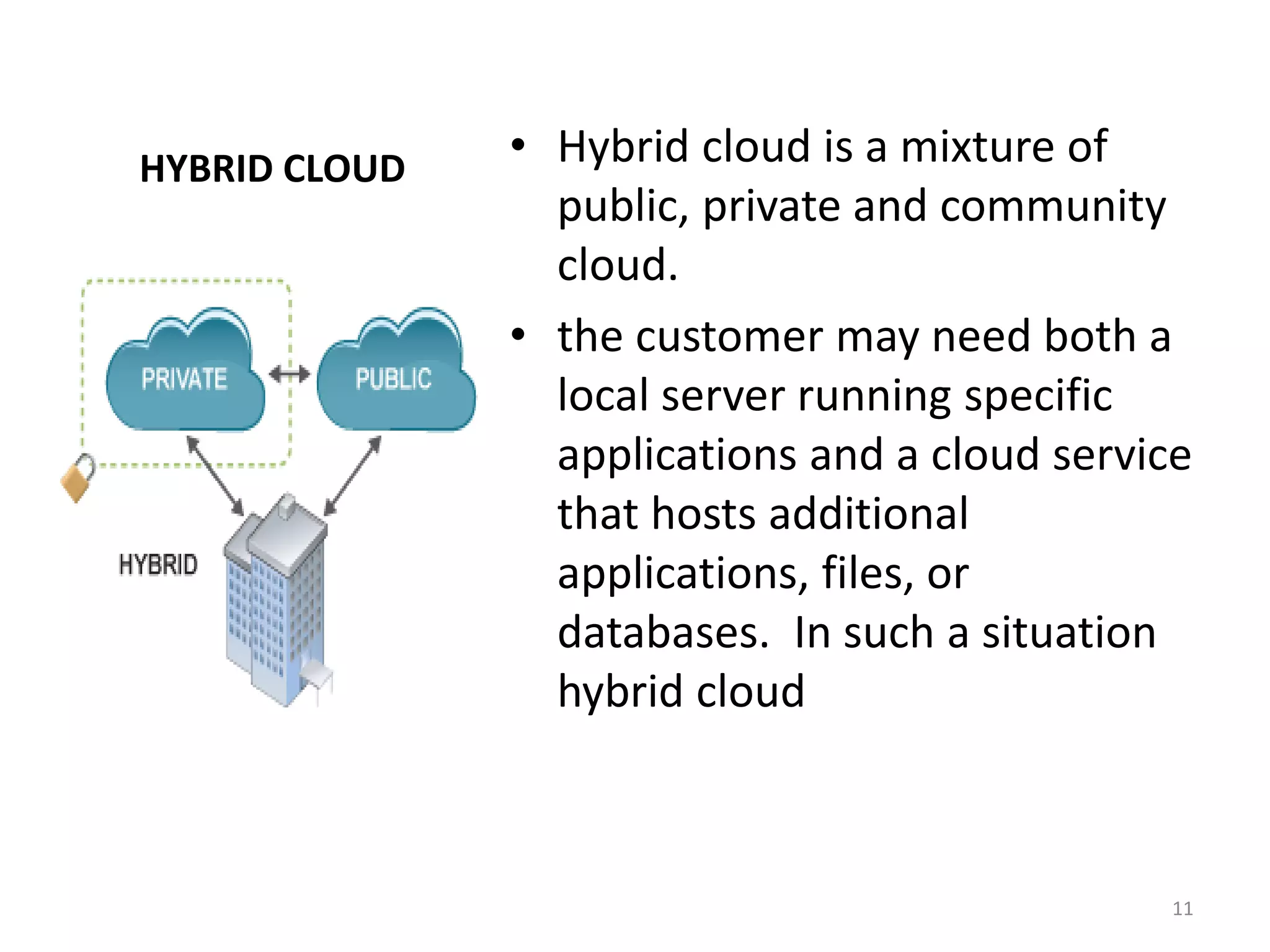
The document discusses the service and deployment models of cloud computing. There are three main service models: Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) which provides basic cloud infrastructure; Platform as a Service (PaaS) which provides developers platforms to build applications; and Software as a Service (SaaS) which provides users access to applications through a web browser. There are four deployment models for cloud services: public cloud which is provided by third-party cloud providers; private cloud which is operated solely for a single organization; community cloud which is shared by specific organizations; and hybrid cloud which uses a combination of public, private and community cloud models.








![References
[1] http://www.cloud-competence-
center.com/understanding/cloud-computing-
deployment-models/
[2] http://www.cloudtweaks.com/2012/07/the-4-
primary-cloud-deployment-models/
[3] http://www.thinkvidya.com/a/cloud-computing-
future-scope
13](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cloudcomputing-150201205459-conversion-gate02/75/Cloud-computing-13-2048.jpg)
