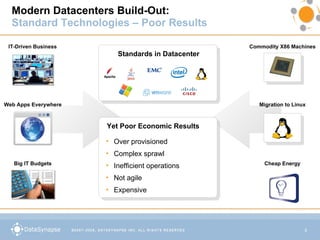
The document discusses moving corporate computing to the cloud to reduce costs and inefficiencies. While security and integration concerns prevent fully moving to public clouds, companies can learn from cloud providers like Amazon and Google. The document proposes a solution using a cloud of commodity infrastructure to automatically provision and optimize applications on demand according to performance, costs and changing requirements. It argues this could reduce costs, improve utilization and agility compared to traditional datacenter models.