Embed presentation
Download to read offline
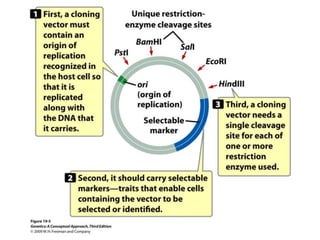
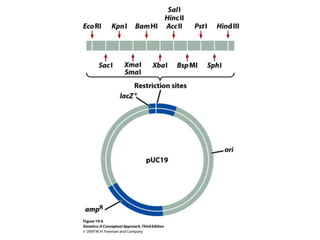
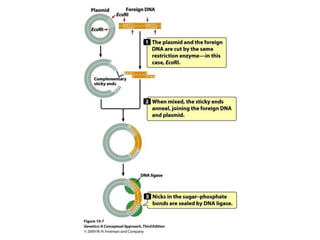
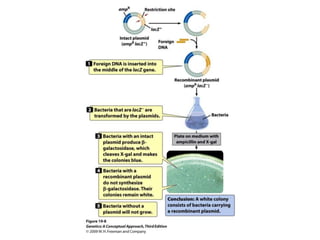
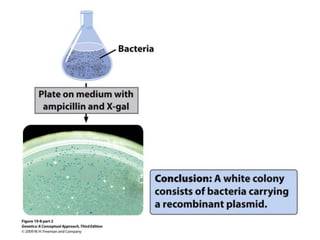
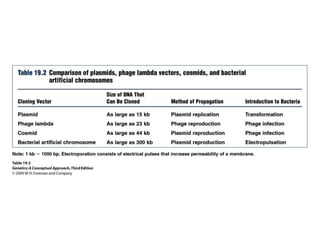
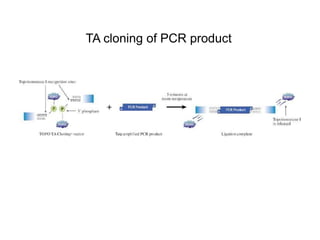

Gene cloning involves amplifying a specific piece of DNA using bacteria and inserting it into a cloning vector, which is a replicating DNA molecule with features like an origin of replication and antibiotic resistance gene that make it easier to insert foreign DNA into a cell. The vector with inserted DNA fragment is then transformed into host bacterial cells, which are treated with calcium chloride and heat shock to take up the DNA, and selectable markers help confirm if the cells were successfully transformed.










