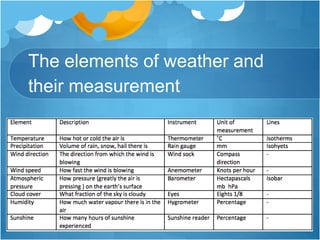
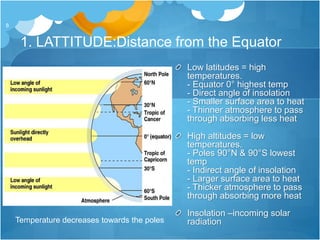
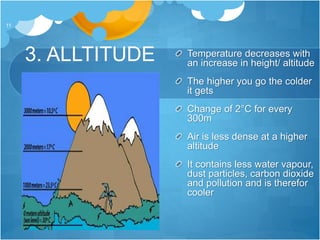
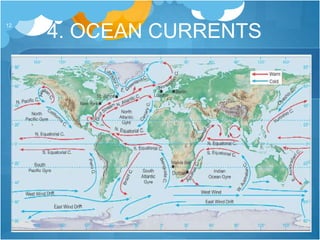
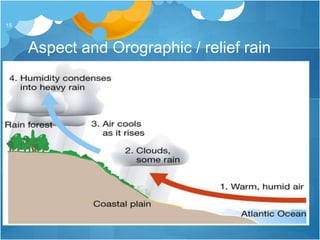
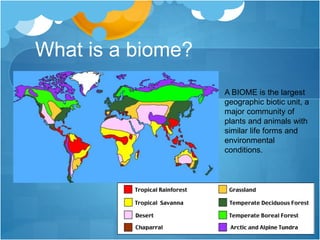
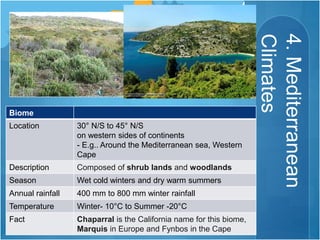
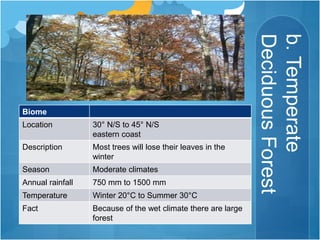
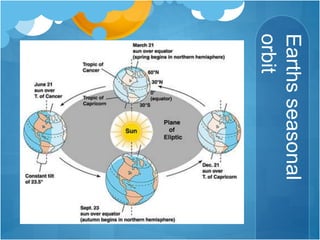
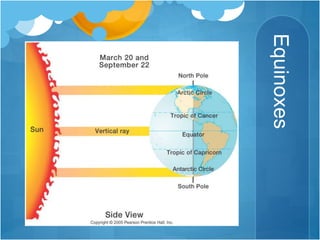
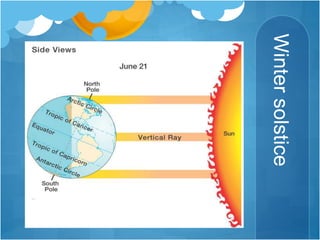
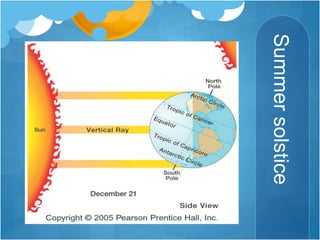
The document discusses different climates and biomes around the world. It begins by explaining the difference between climate, which is average weather over 20+ years, and weather, which is conditions over a shorter time period like days or weeks. It then discusses six main biomes: equatorial, savanna, desert, Mediterranean, tundra, and monsoon climates. Each biome is characterized by its location, description, seasons, rainfall, temperature, and example regions. Other biomes like grasslands, deciduous forests, and boreal forests are also briefly outlined. Factors influencing climate like latitude, distance from oceans, altitude, and ocean currents are explained.