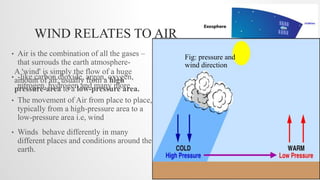
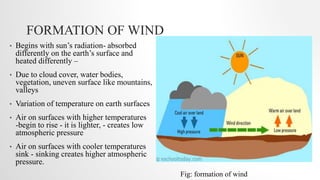
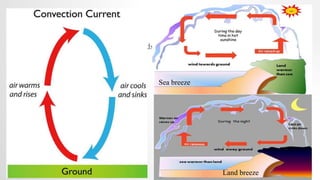
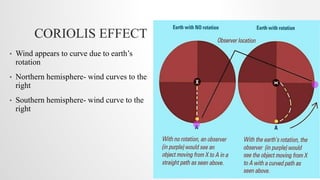
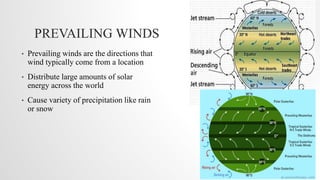
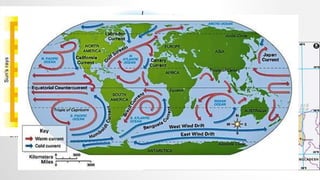
This document discusses global wind patterns. It begins by explaining that wind is the movement of air from high to low pressure areas. It then describes how wind is formed through convection currents caused by uneven heating of the Earth's surface from the sun. The Coriolis effect causes winds to curve due to the Earth's rotation. There are local winds formed by local geographic features and global winds formed by larger air masses. Global wind types include polar easterlies, prevailing westerlies, trade winds, and doldrums. Prevailing winds typically blow from west to east in the mid-latitudes. Nepal experiences a temperate climate due to its location in the Himalayas between the Tropic of Cancer and Arctic