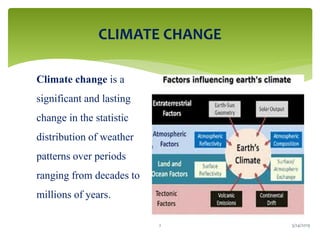
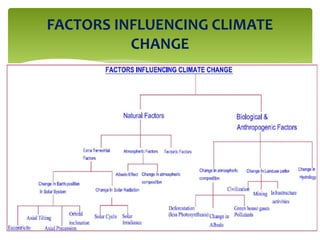
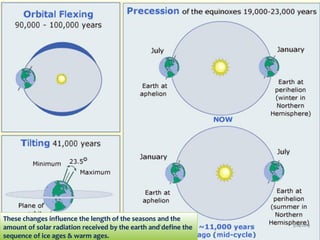
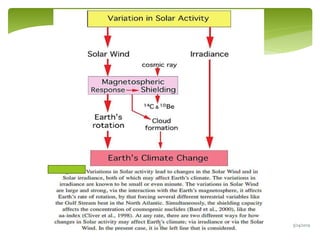
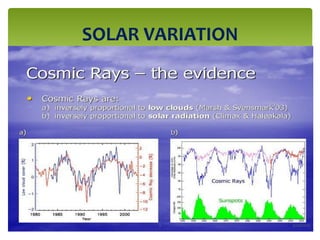
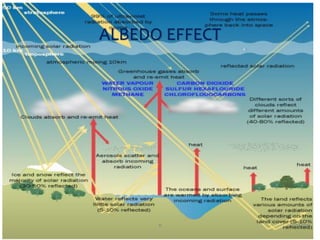
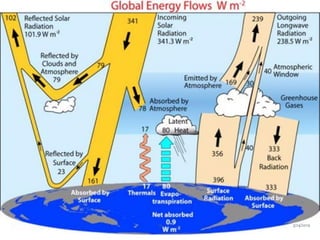
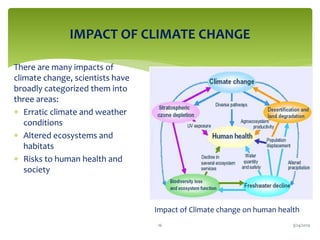
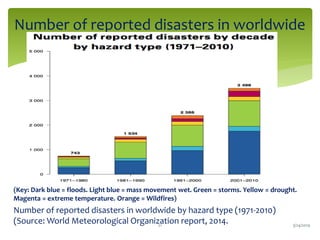
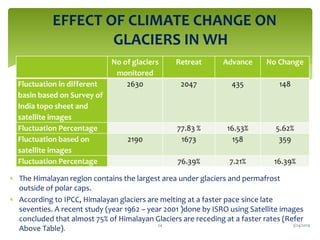
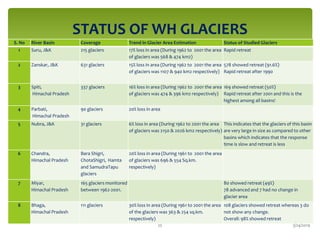
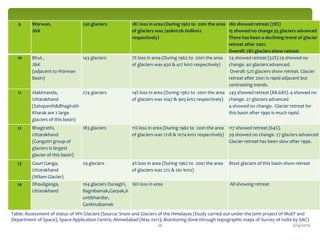
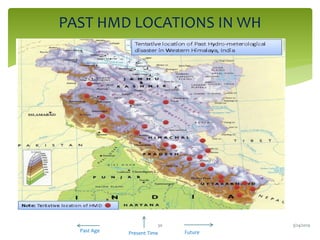
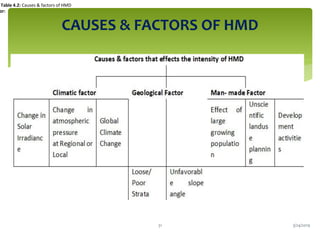
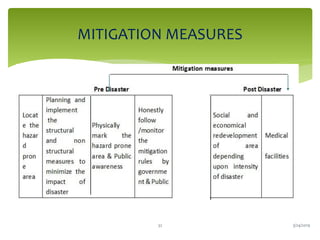
Climate change is causing an increase in hydrometeorological disasters in the Western Himalayas. Glaciers are retreating at accelerated rates due to rising temperatures, which is increasing the likelihood of glacial lake outburst floods and changing rainfall and runoff patterns. Flash floods are the most common type of disaster, often caused by extreme rainfall events. Climate change is also contributing to more erratic weather, like increased monsoon rainfall, strengthening the impacts of disasters on communities in the region. Adaptation measures are needed to build resilience against these climate-linked hydrometeorological risks.