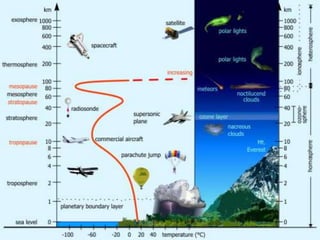
The atmosphere consists of layers that surround the Earth and make life possible. It contains nitrogen, oxygen, argon and carbon dioxide. The layers are the troposphere, where weather occurs; the stratosphere, where the ozone layer absorbs sunlight; the mesosphere, where meteors burn up; the thermosphere, where auroras occur and the space shuttle orbits; and the exosphere, the upper limit of the atmosphere where satellites orbit. Weather describes local short-term atmospheric conditions while climate describes the average weather conditions of a place, including temperature, precipitation, humidity, pressure, wind and other factors influenced by latitude, altitude, land/water distribution, ocean currents and storms.