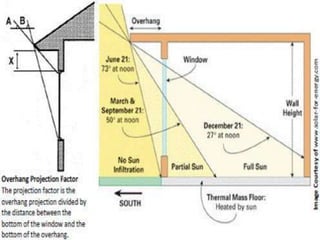
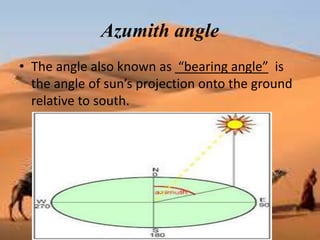
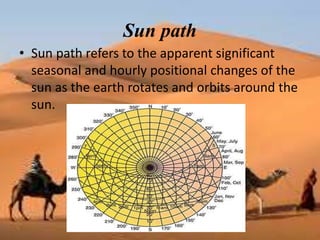
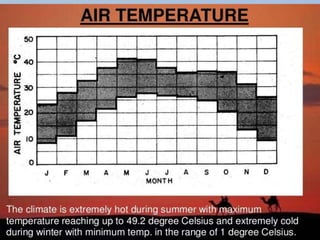
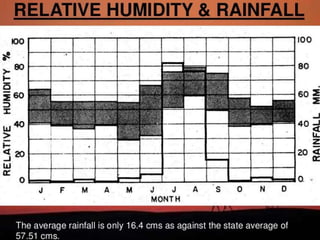
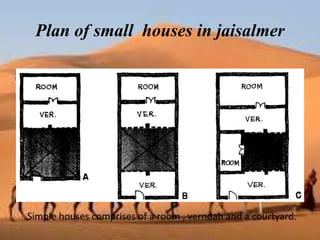
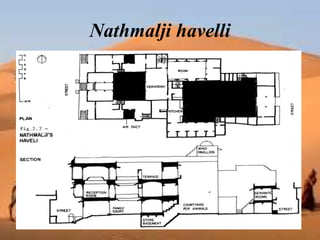
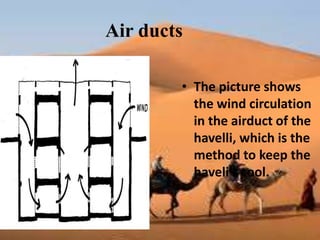
This document discusses shading devices and their use in architecture in Jaisalmer, India. It defines shading devices as purpose-built structures that protect from sunlight and natural light. The document describes different types of shading devices, including vertical, horizontal, and egg-crate devices. It also discusses the climate and location of Jaisalmer and how structures there utilize features like dense clustering, orientation, and courtyards to provide natural cooling without electricity. Specific architectural examples from Jaisalmer like Nathmalji Haveli are also summarized, highlighting shading elements like jharokhas, chatris, and chajjas.