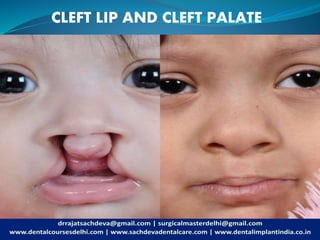
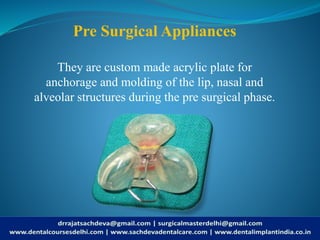
Cleft lip and cleft palate are among the most common birth defects, particularly affecting Asians, with a range of causes including genetic factors and maternal health during pregnancy. These conditions can lead to significant feeding, speech, and social challenges, necessitating a multidisciplinary approach to treatment that includes surgical and non-surgical solutions. Organizations like Smile Train and Operation Smile provide crucial support, emphasizing that effective treatment can transform the lives of affected individuals.