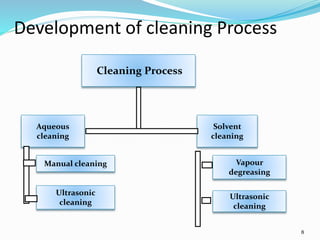
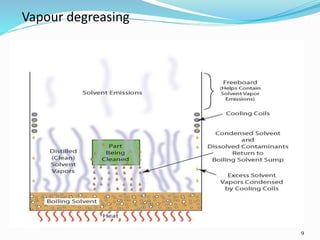
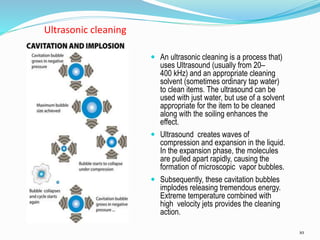
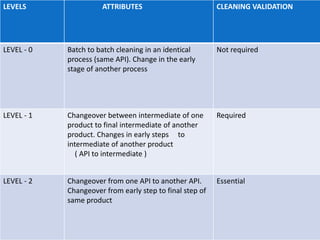
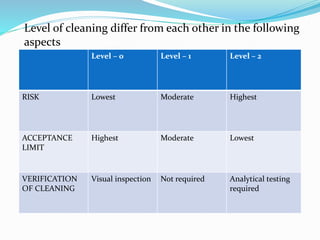
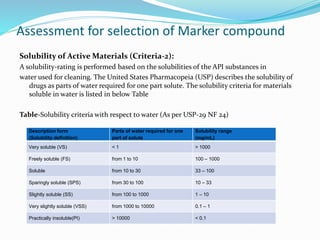
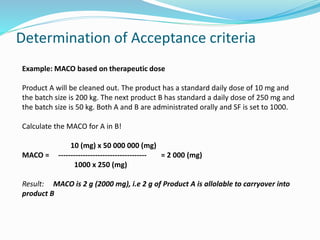
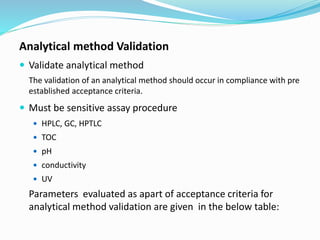
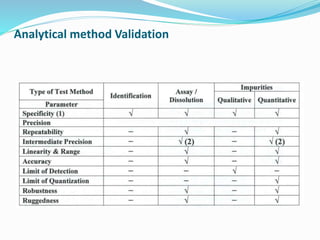
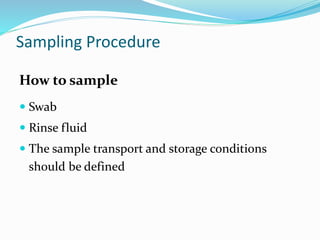
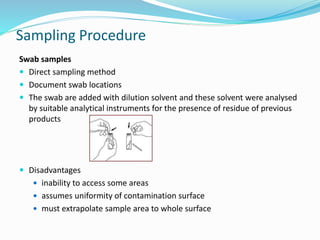
The document outlines the cleaning validation strategy and regulatory requirements in the pharmaceutical industry. It emphasizes the importance of cleaning validation to ensure the safety and purity of products and details the processes for developing cleaning strategies, determining acceptance criteria, and selecting marker compounds. Compliance with good manufacturing practices and specific regulatory agency guidelines is critical in maintaining the quality of active pharmaceutical ingredients and formulations.