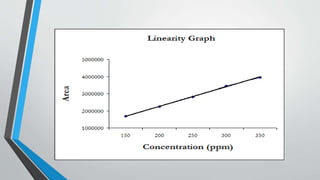
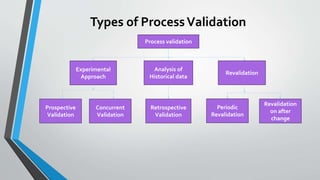
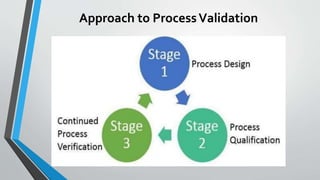
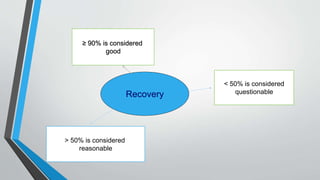
The document provides an overview of validation types in pharmaceutical processes, including analytical method validation, process validation, cleaning validation, and equipment validation. Each type includes detailed definitions, objectives, methodologies, and validation characteristics aimed at ensuring that processes consistently produce products meeting predetermined specifications. Key concepts such as specificity, precision, accuracy, and the significance of validation in quality assurance are emphasized throughout the text.