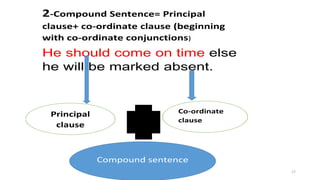
This document introduces clauses and conjunctions. It defines finite and non-finite verbs, and explains that finite verbs agree with subjects and indicate tense while non-finite verbs do not. It also defines simple, compound, and complex sentences. Simple sentences contain one clause and one finite verb. Compound sentences contain two or more principal clauses joined by a coordinating conjunction. Complex sentences contain one principal clause and one or more subordinate clauses joined by a subordinate conjunction. The document provides examples of each sentence type and lists common coordinating and subordinate conjunctions.