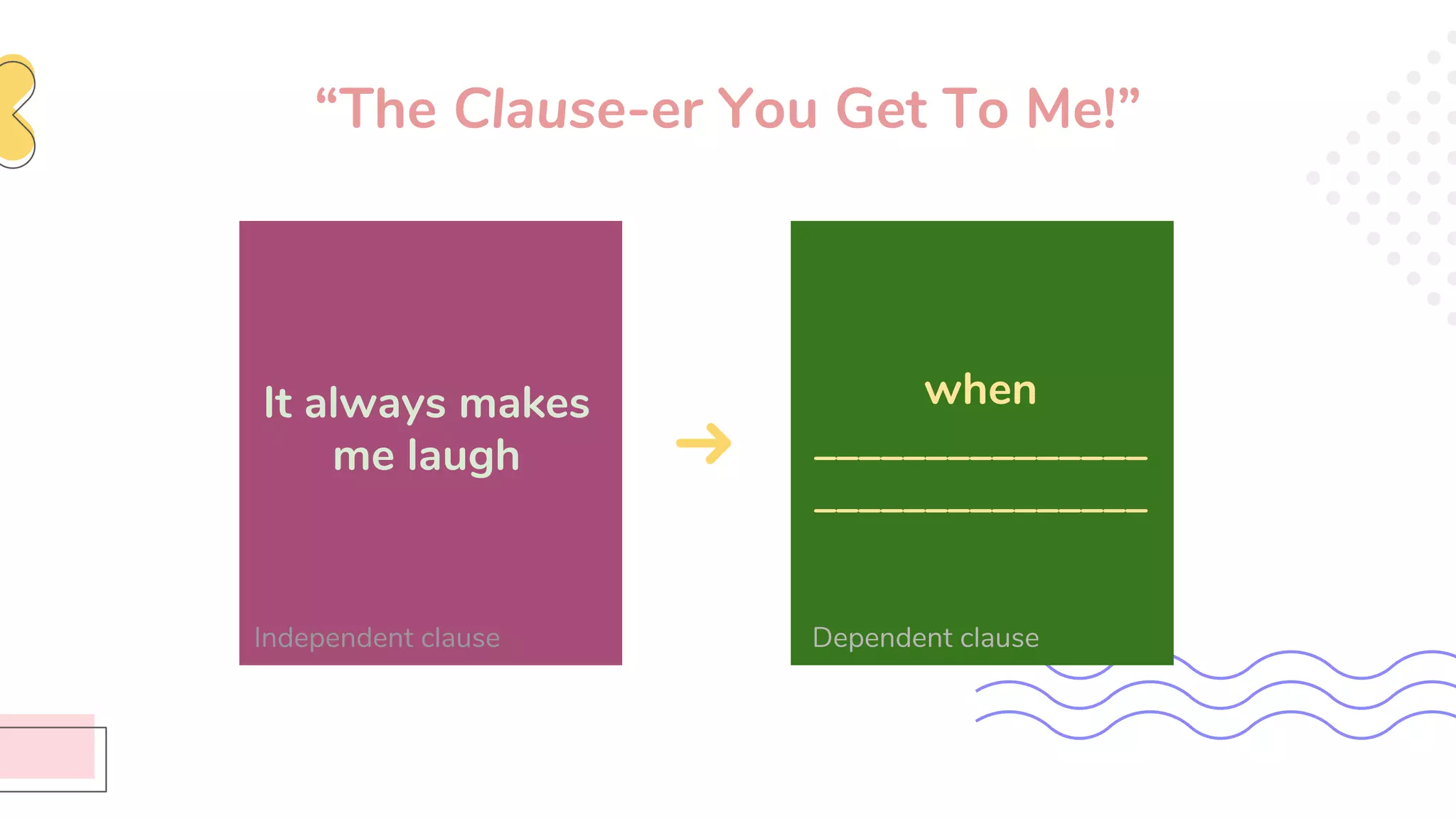
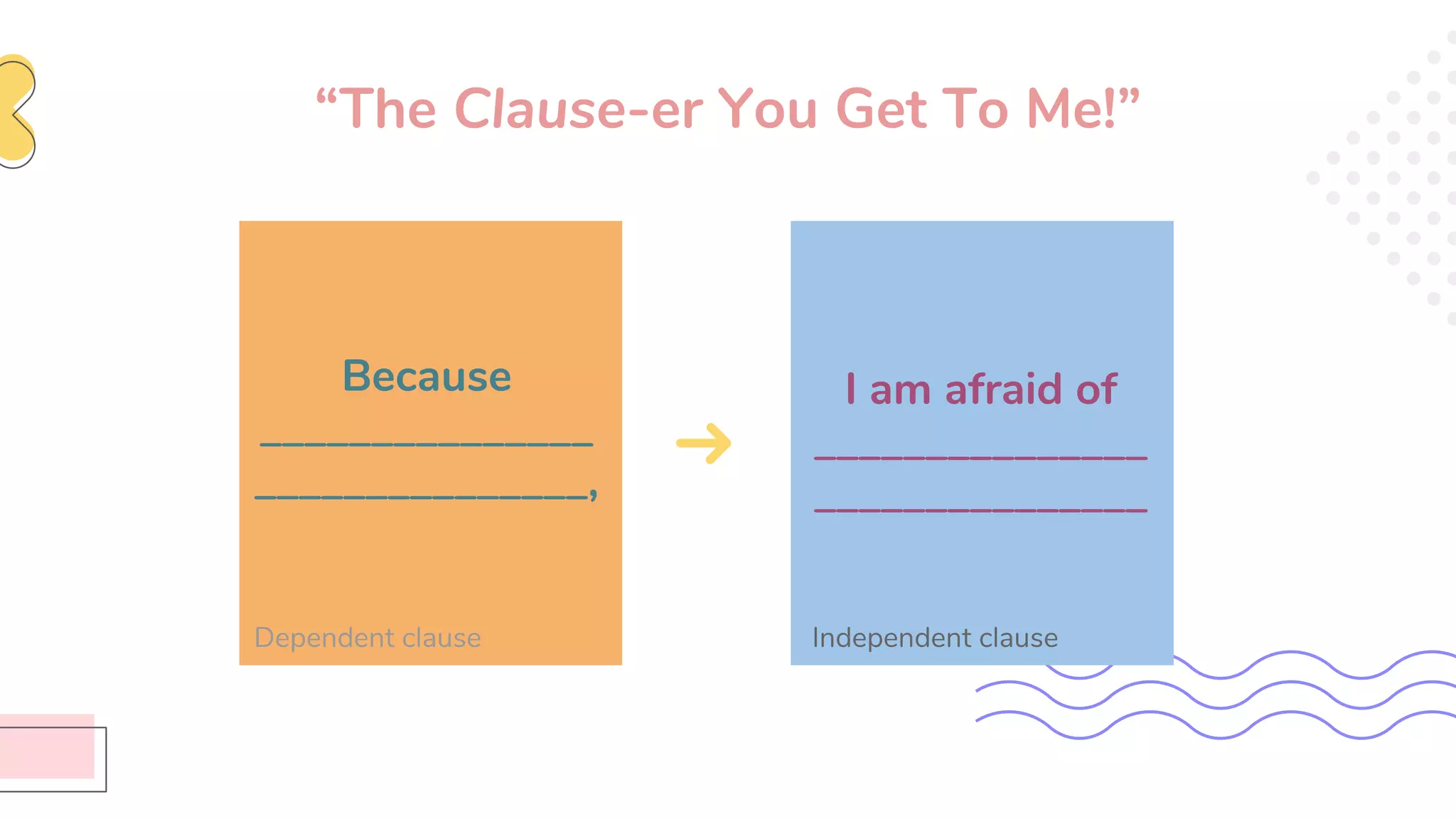
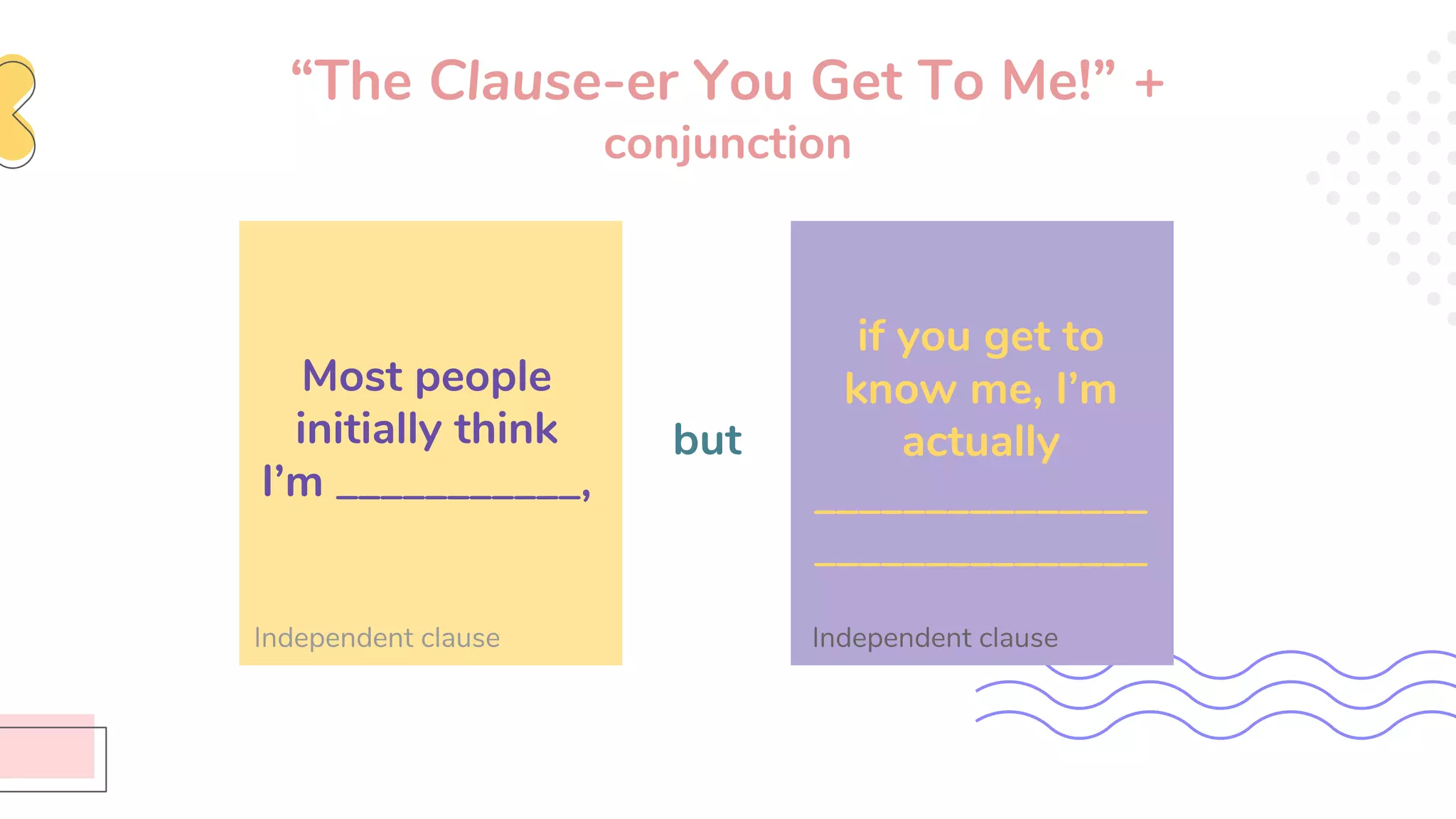
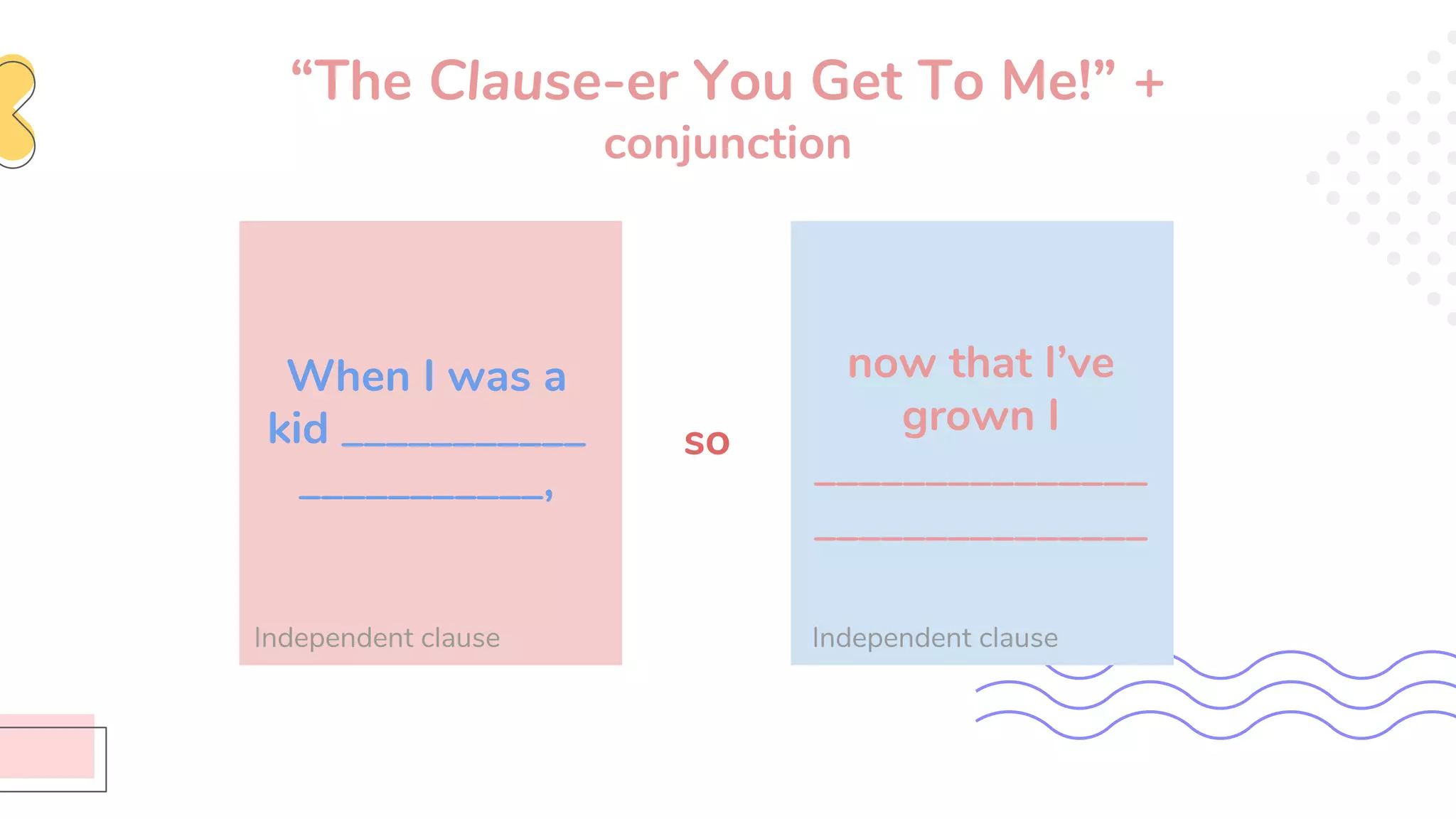
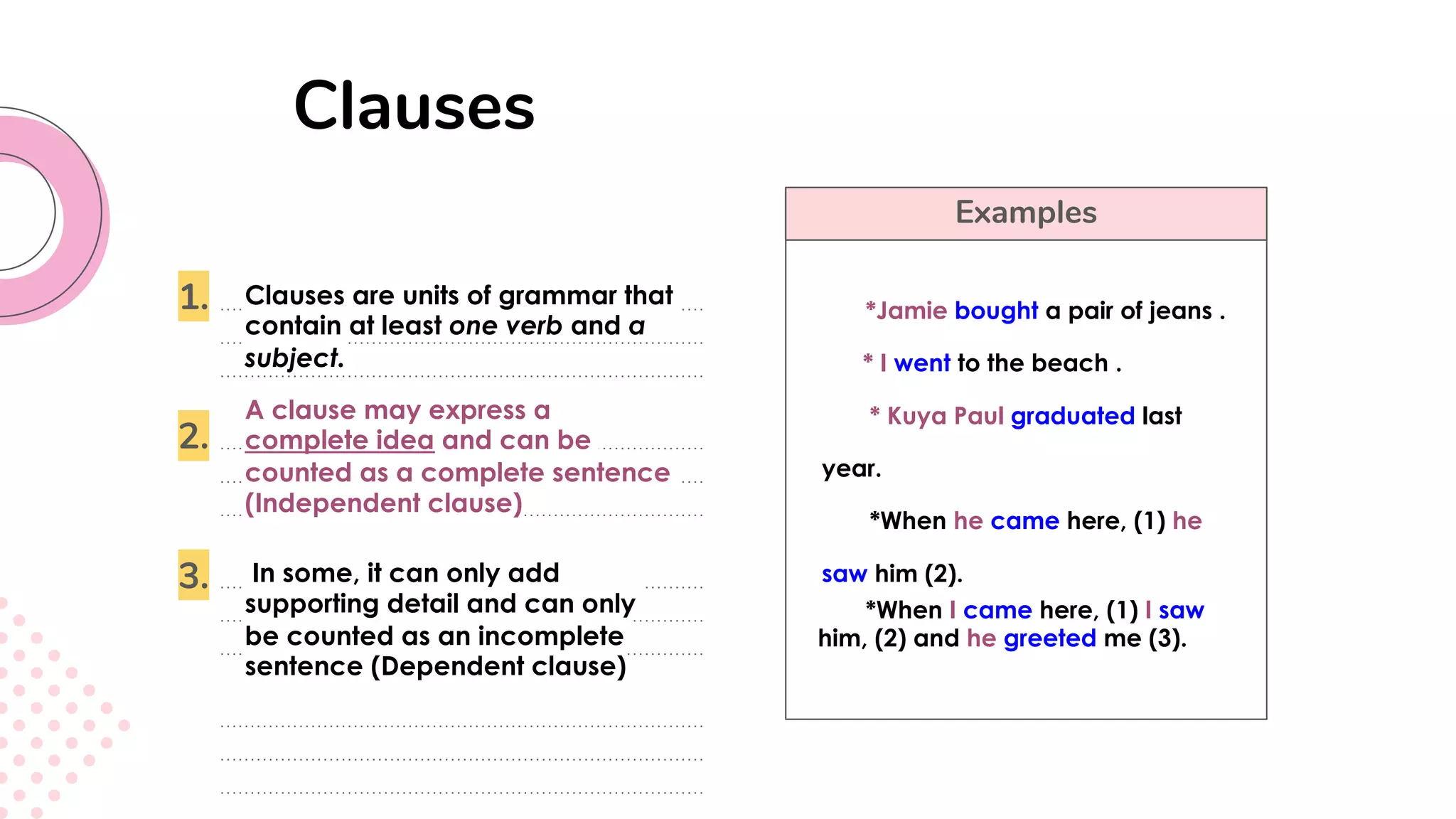
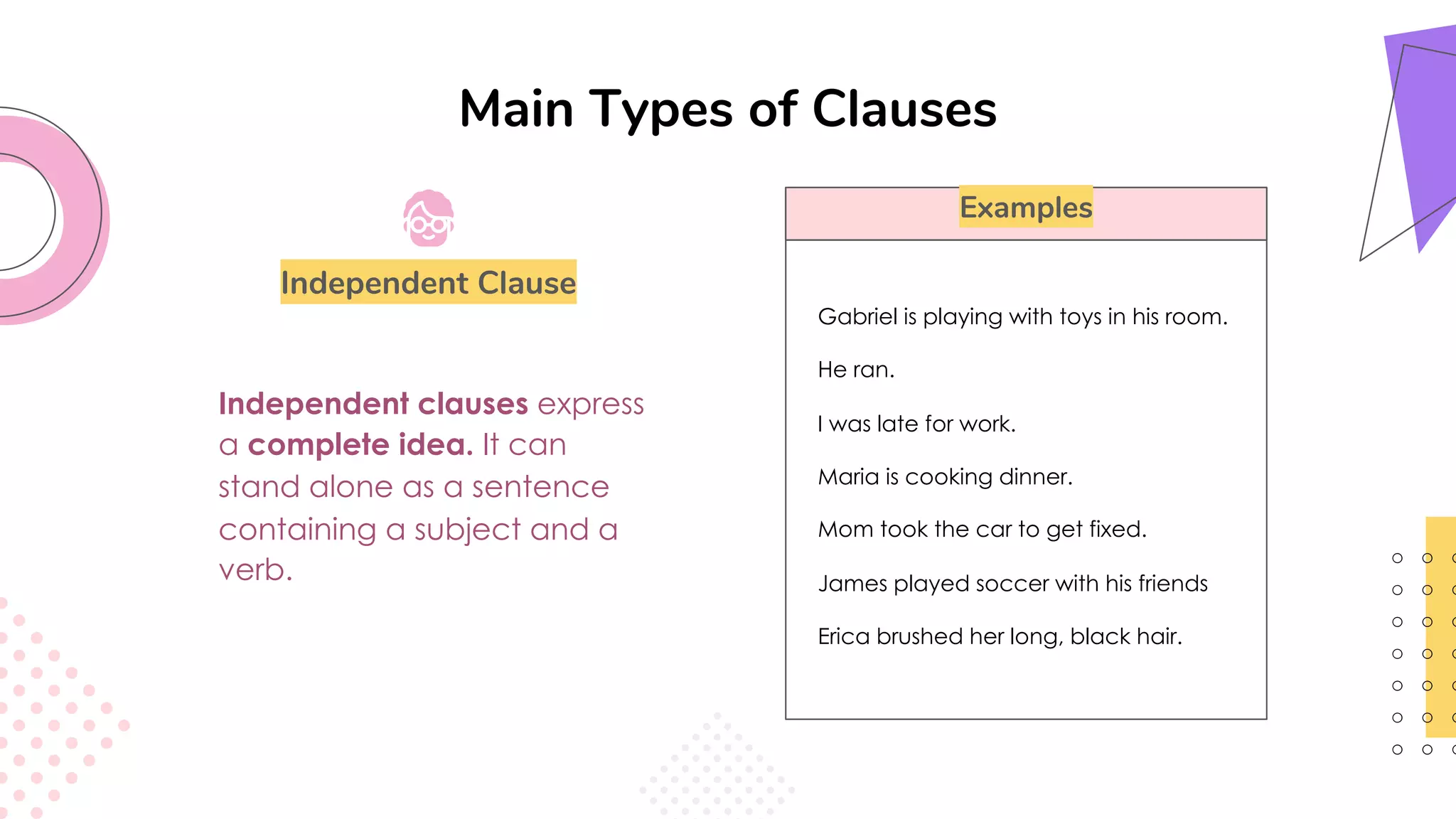
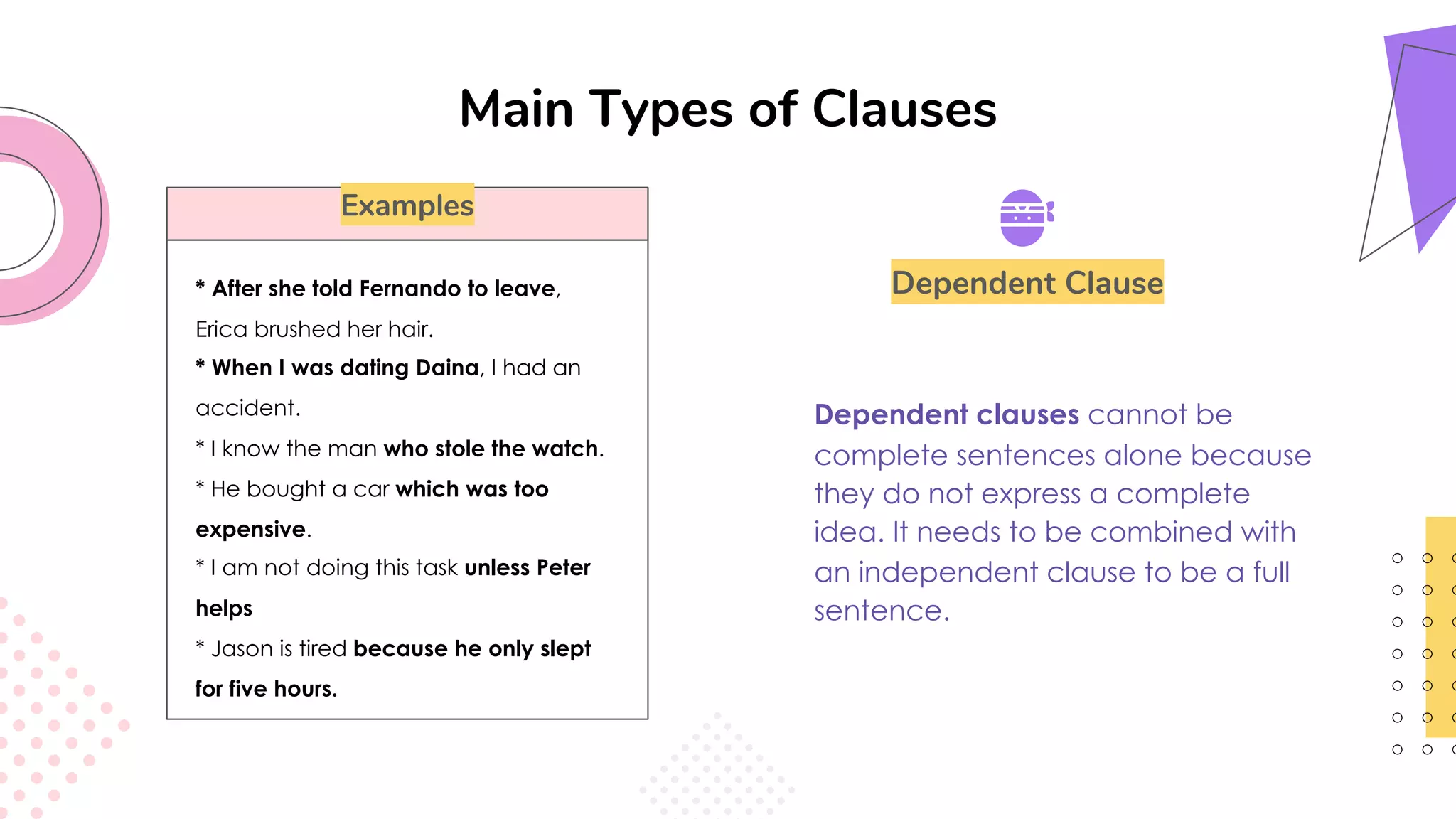
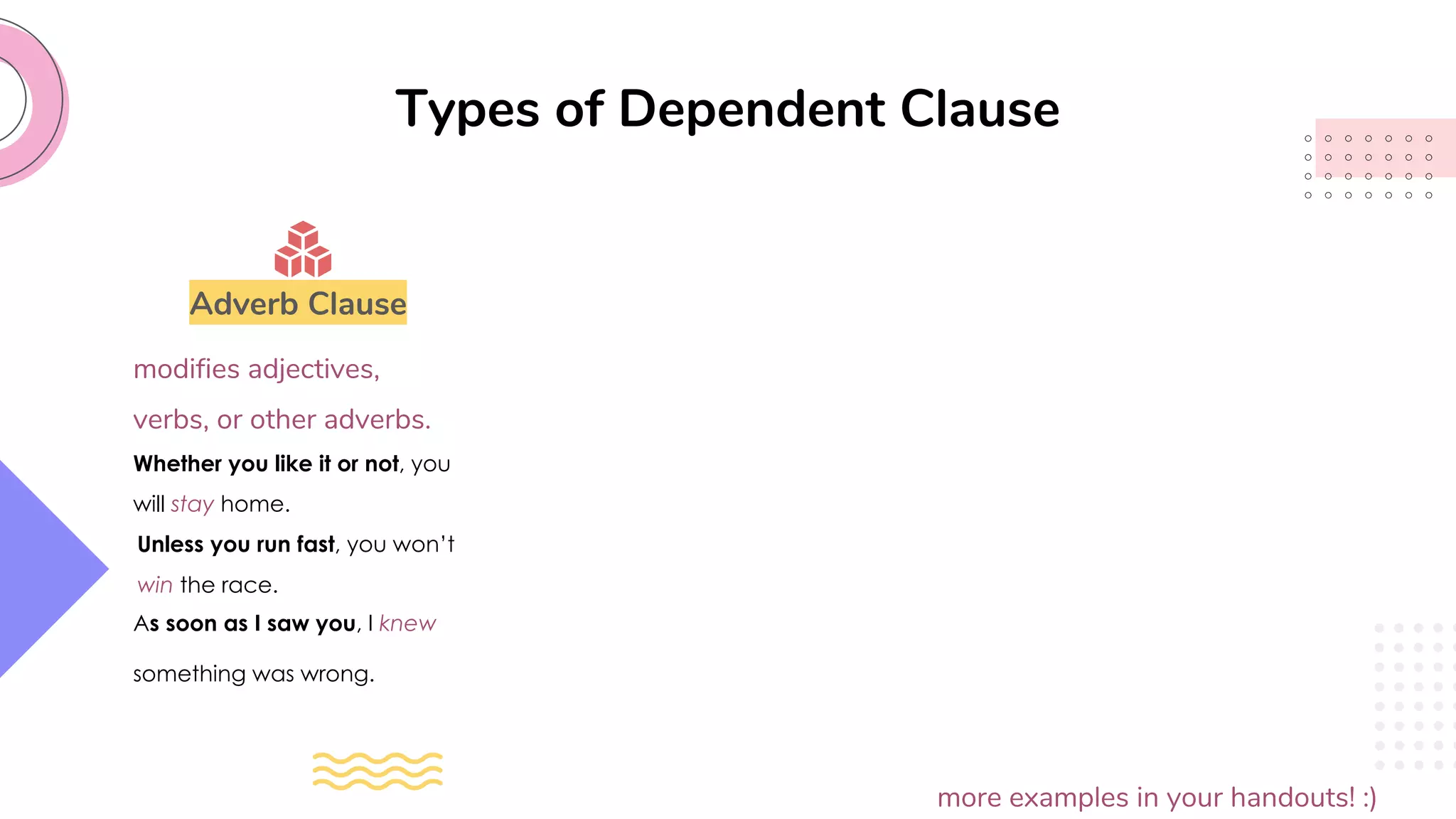
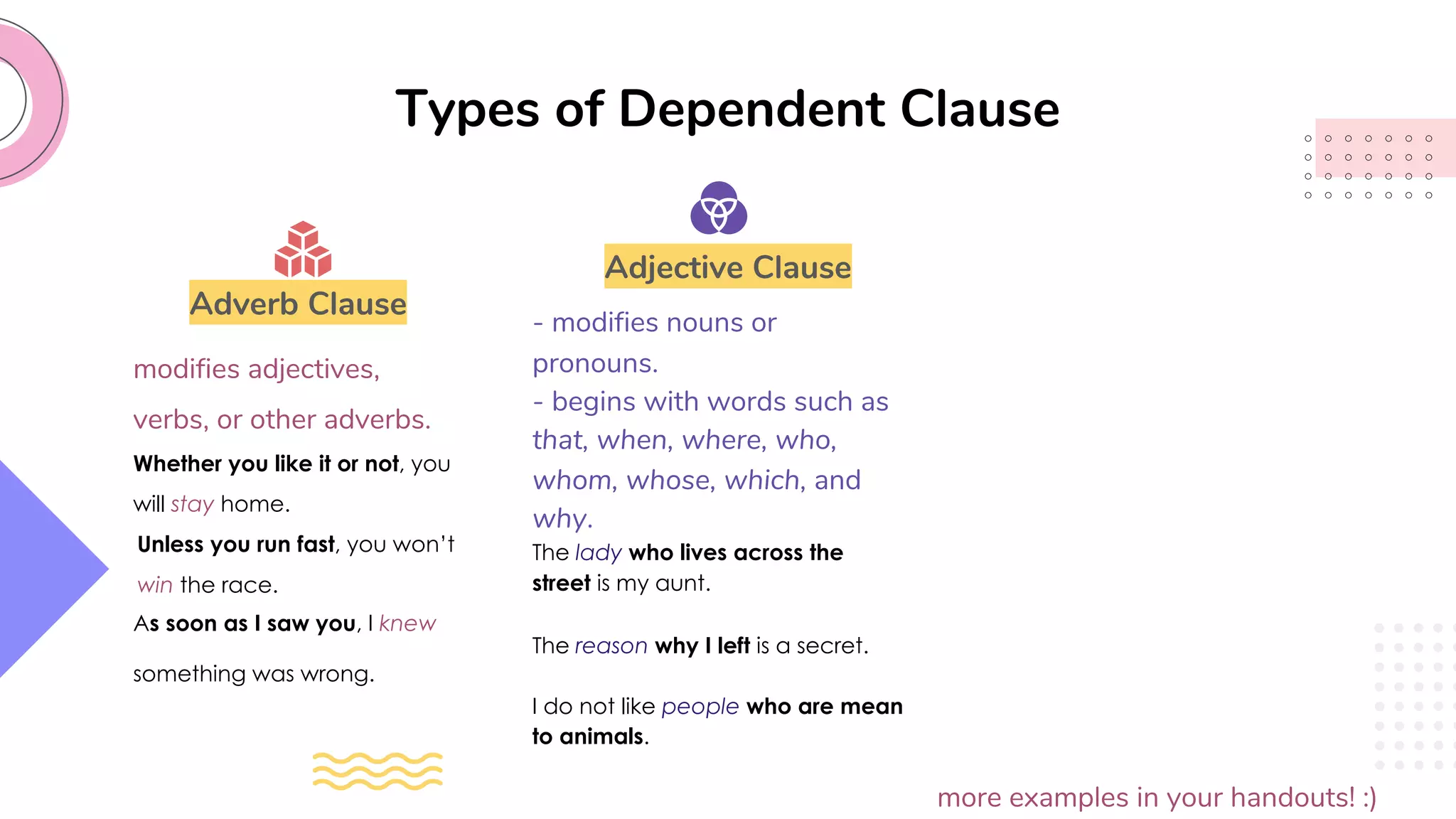
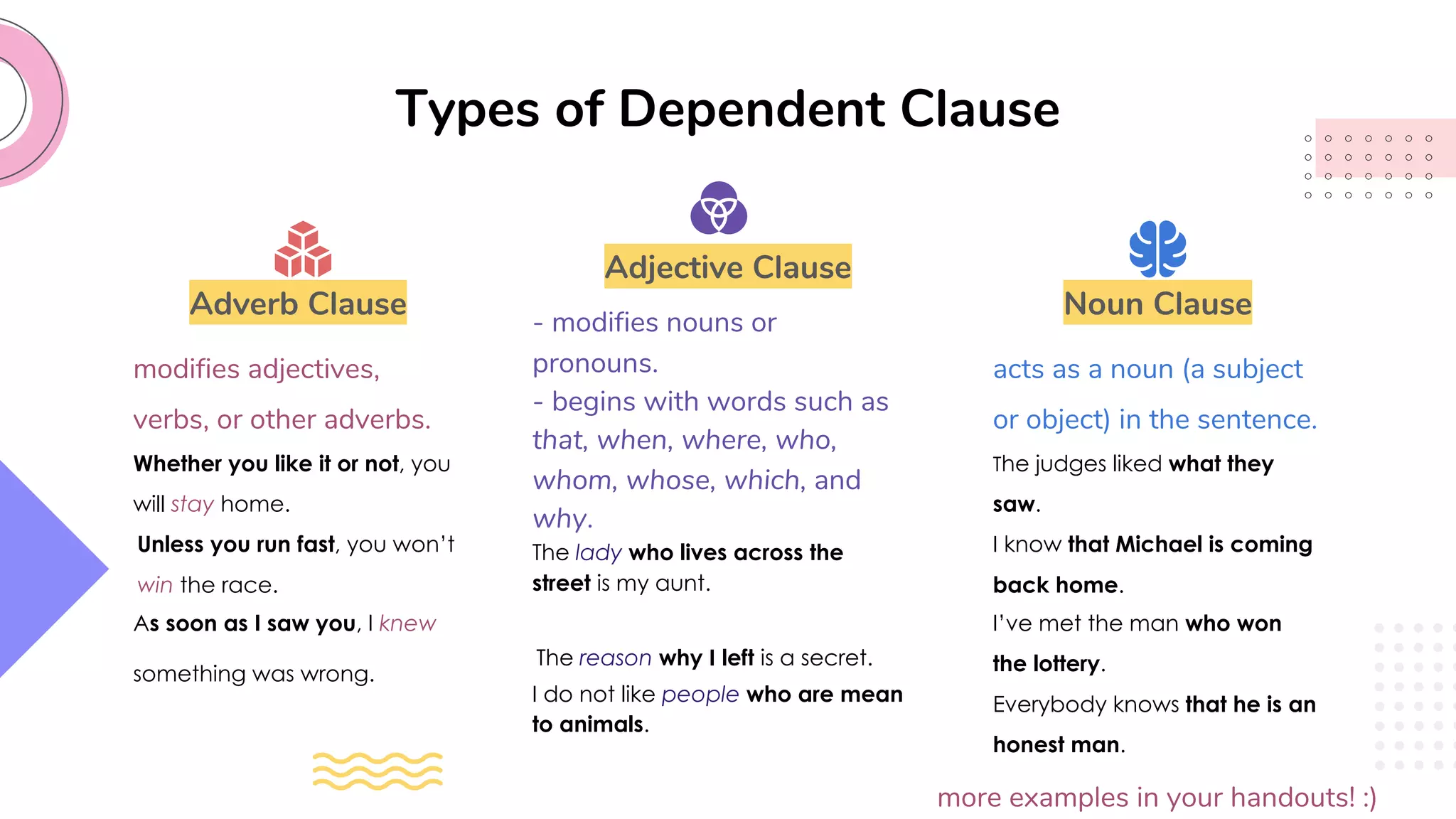
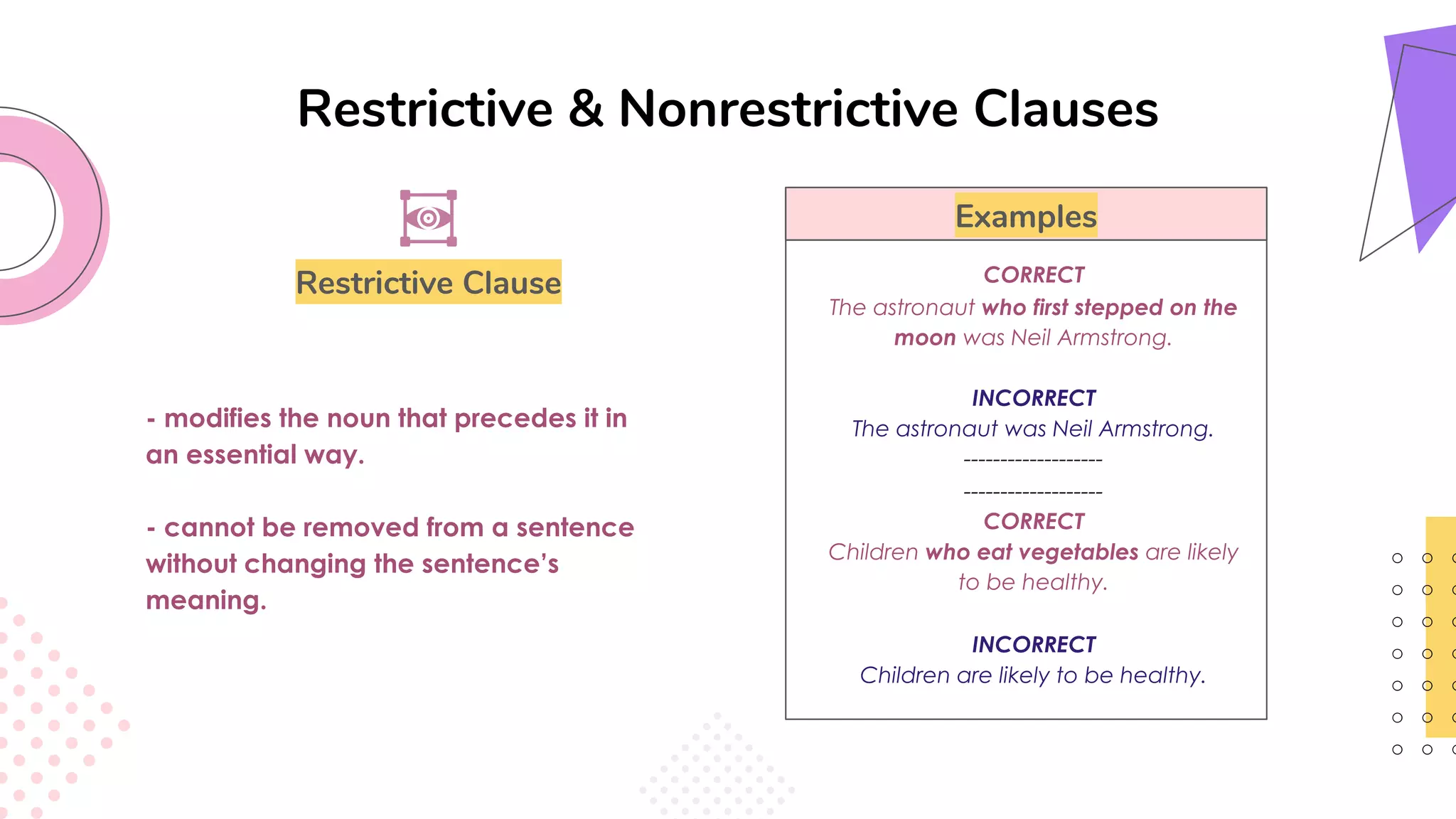
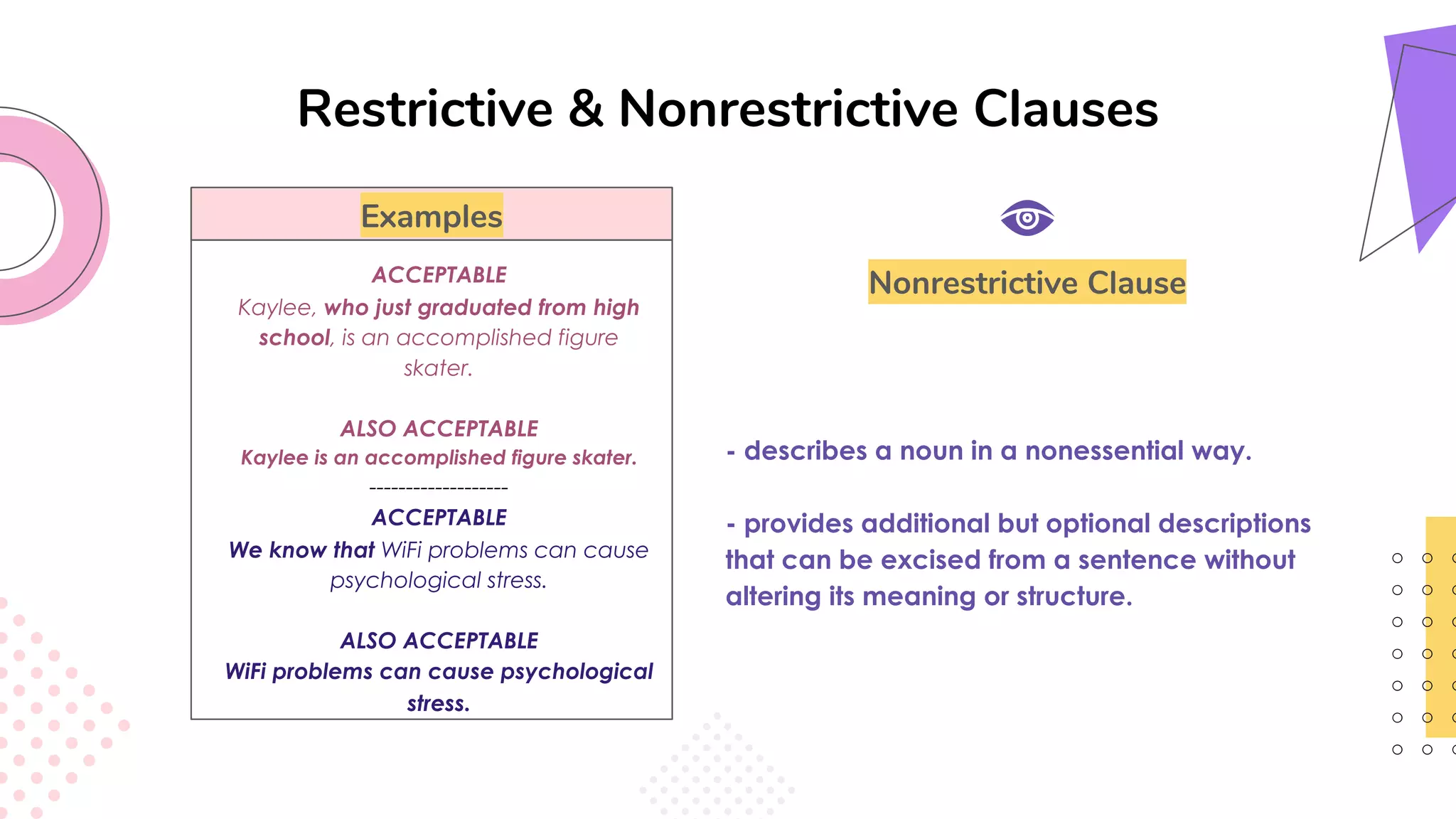
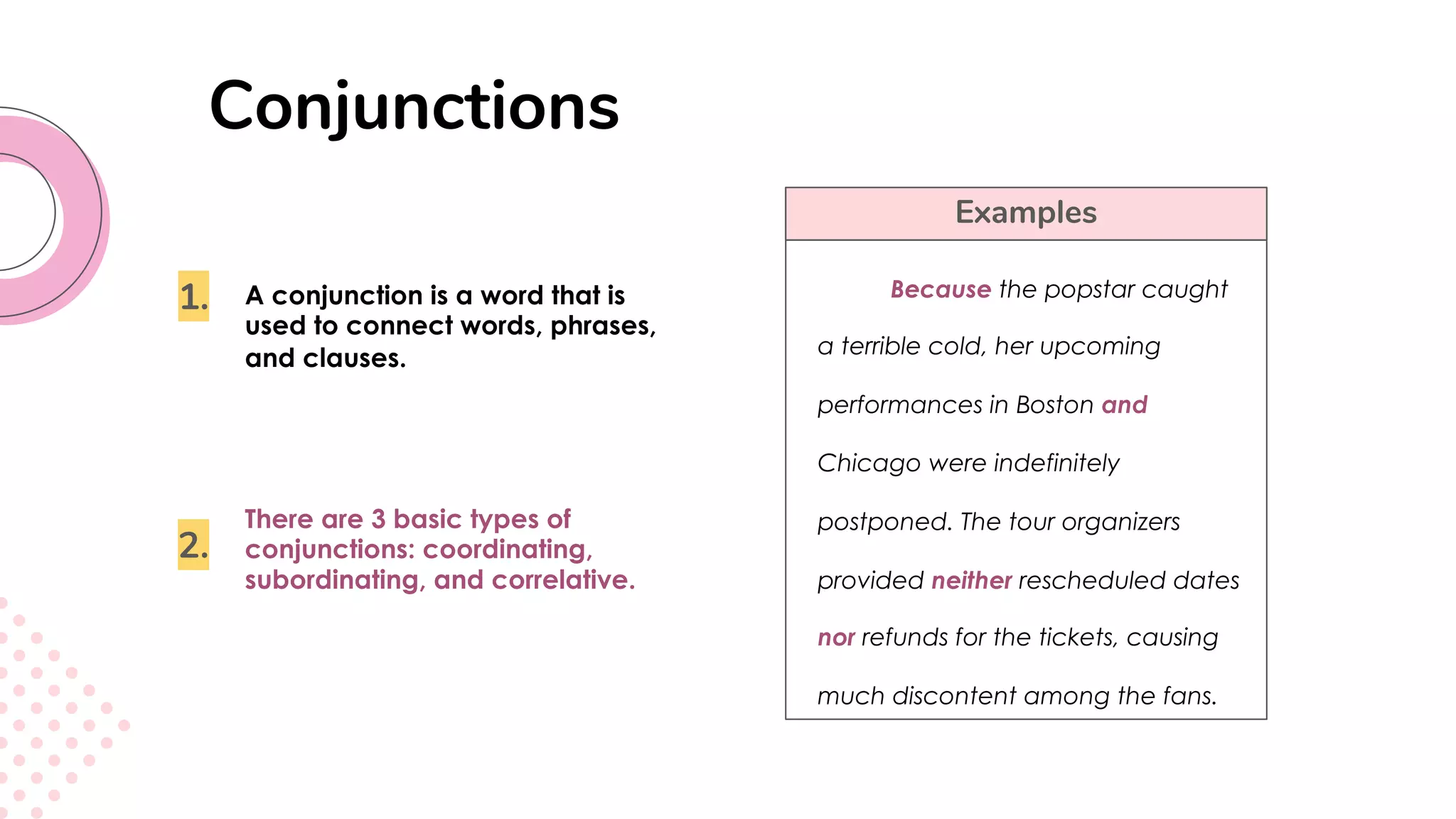
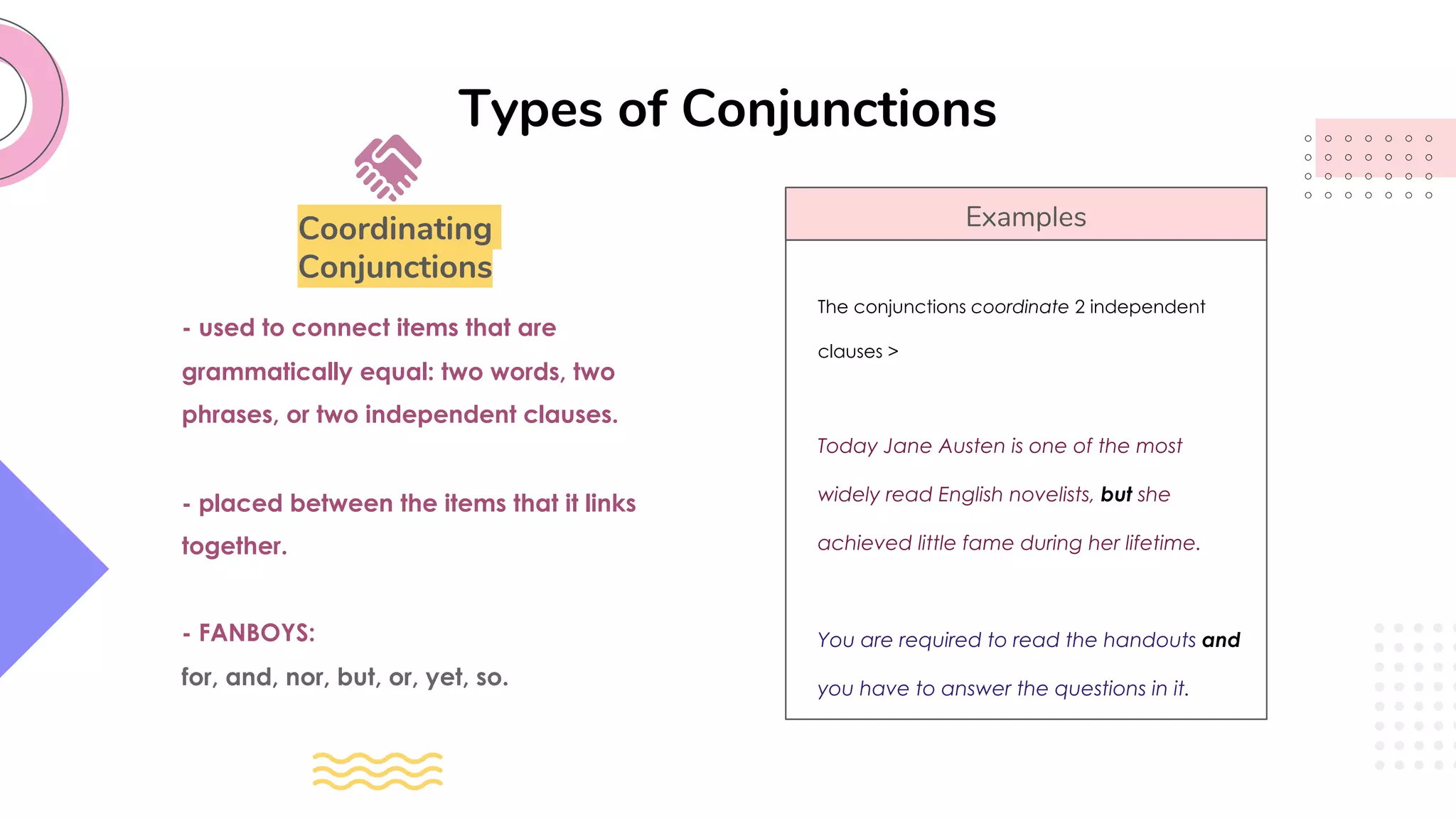
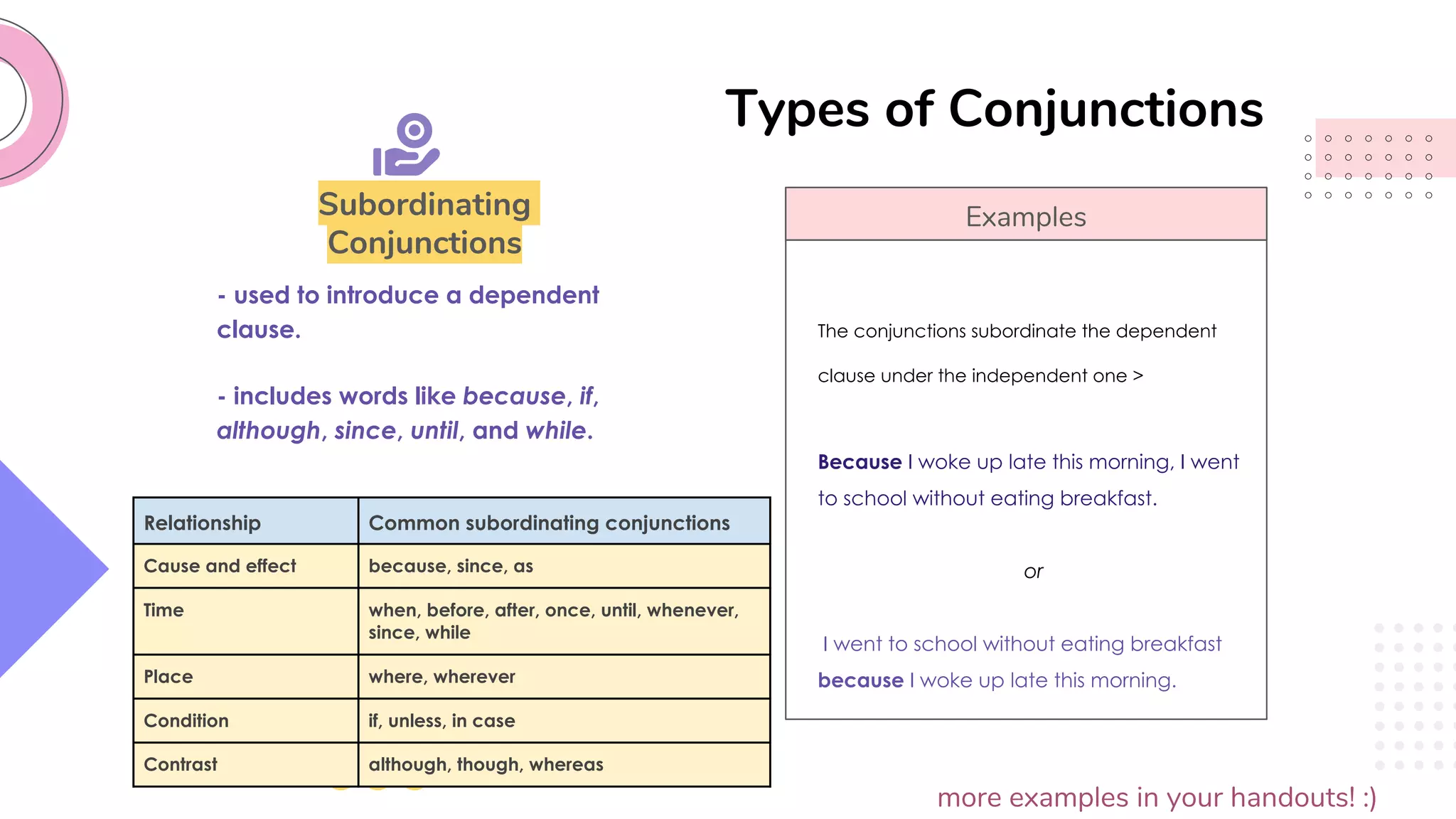
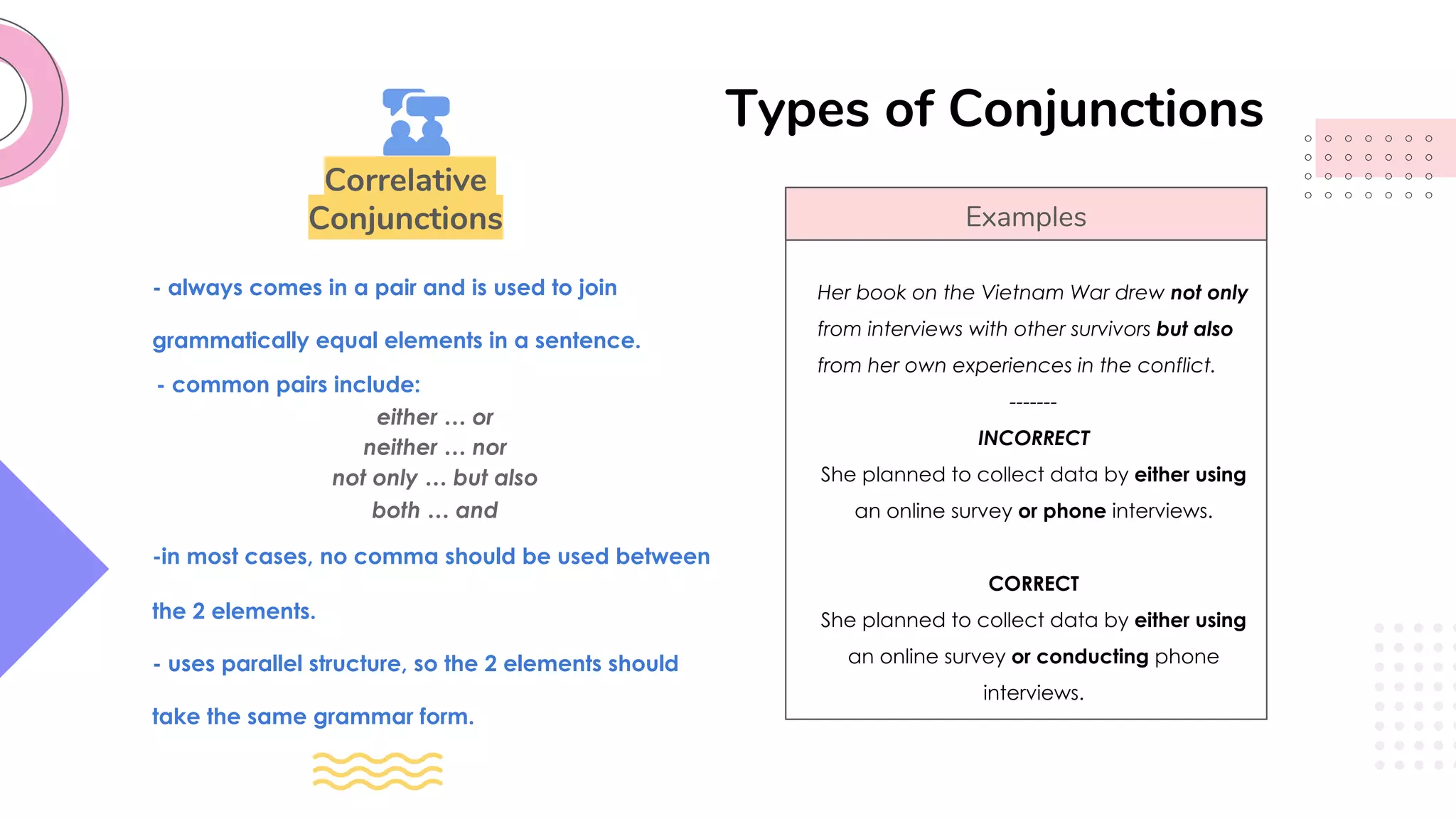
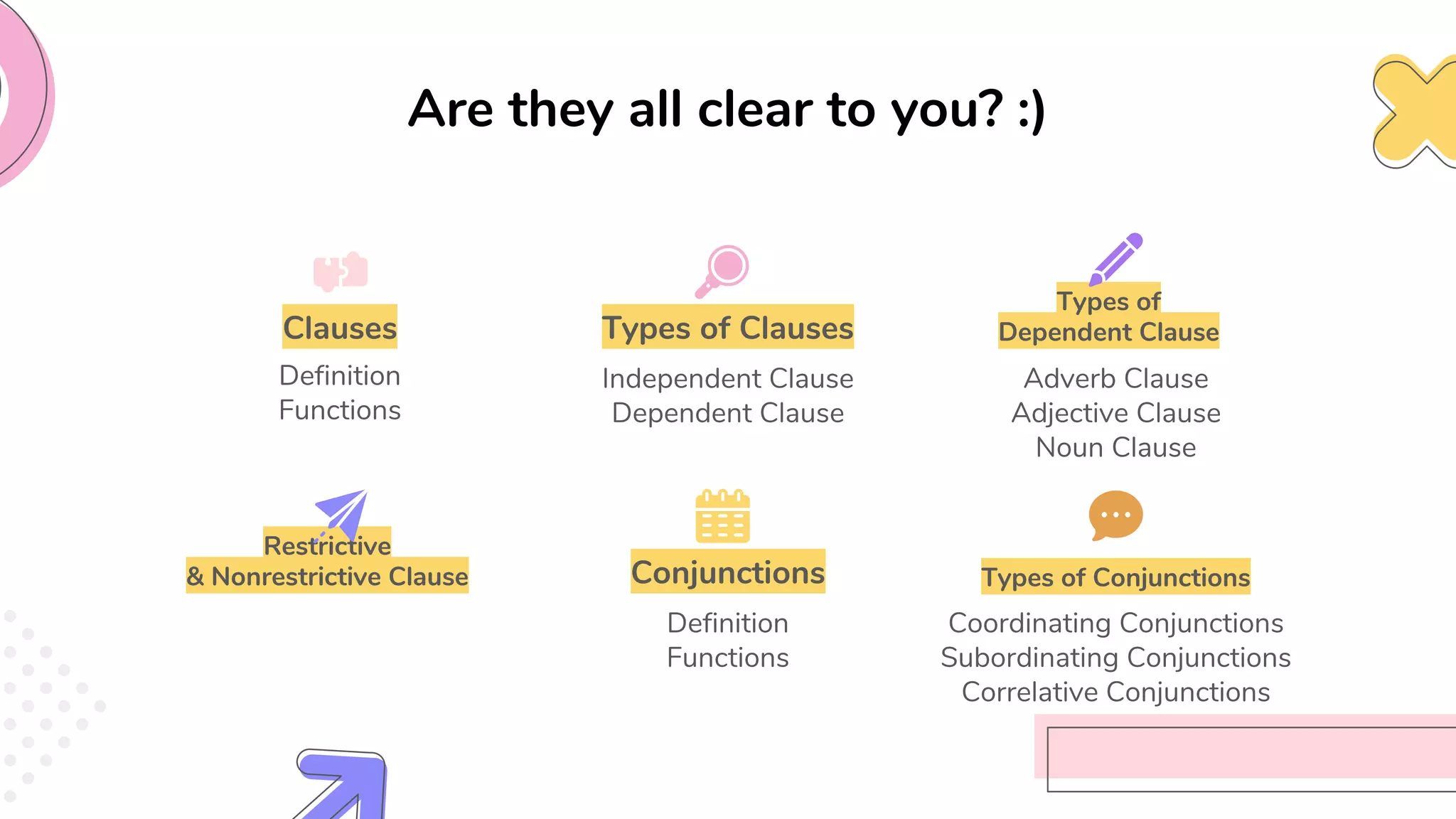
This document provides an overview of clauses and conjunctions in grammar. It defines the different types of clauses, including independent clauses, dependent clauses, and the different types of dependent clauses. It also defines the three main types of conjunctions - coordinating conjunctions, subordinating conjunctions, and correlative conjunctions. Examples are provided to illustrate the different clause and conjunction types. The document concludes by clarifying any questions about clauses and conjunctions.