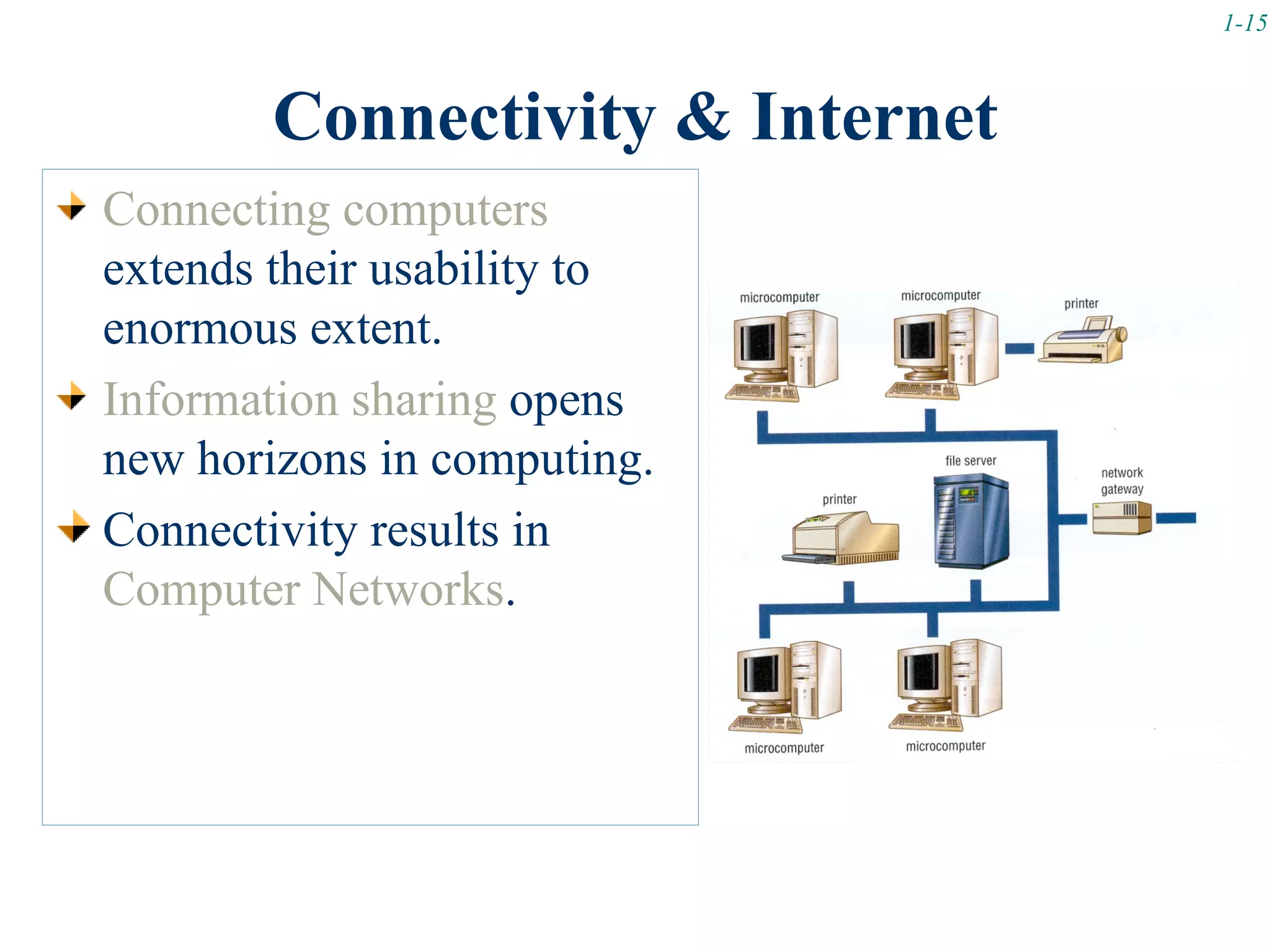
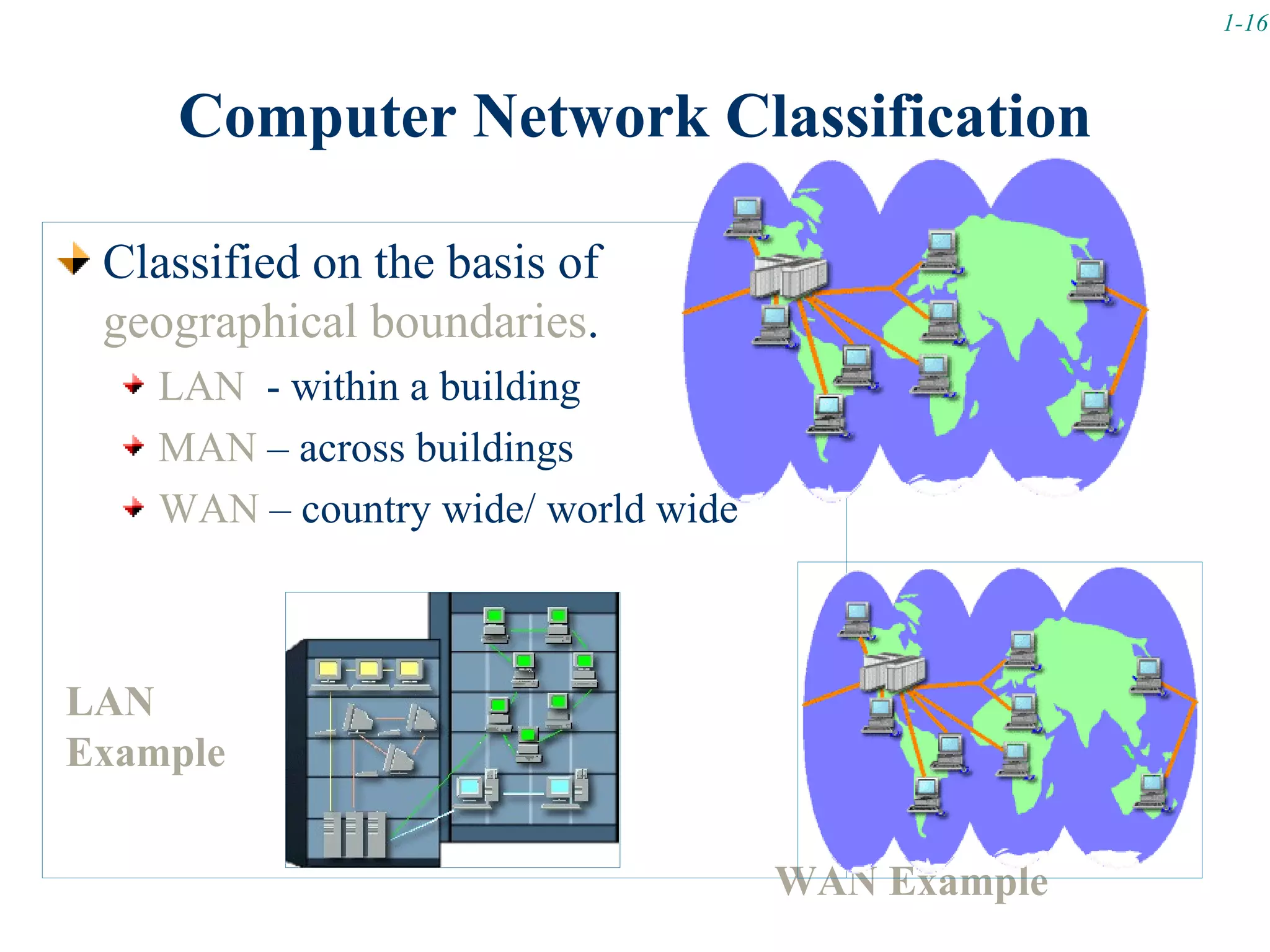
This document discusses computer hardware and classifications. It covers four types of computers: supercomputers, mainframe computers, minicomputers, and microcomputers. It then provides details on microcomputer hardware components including the system unit, input/output devices, secondary storage devices, and communication devices. Finally, it briefly introduces computer networks and their classification based on geographical boundaries as local area networks (LAN), metropolitan area networks (MAN), and wide area networks (WAN).