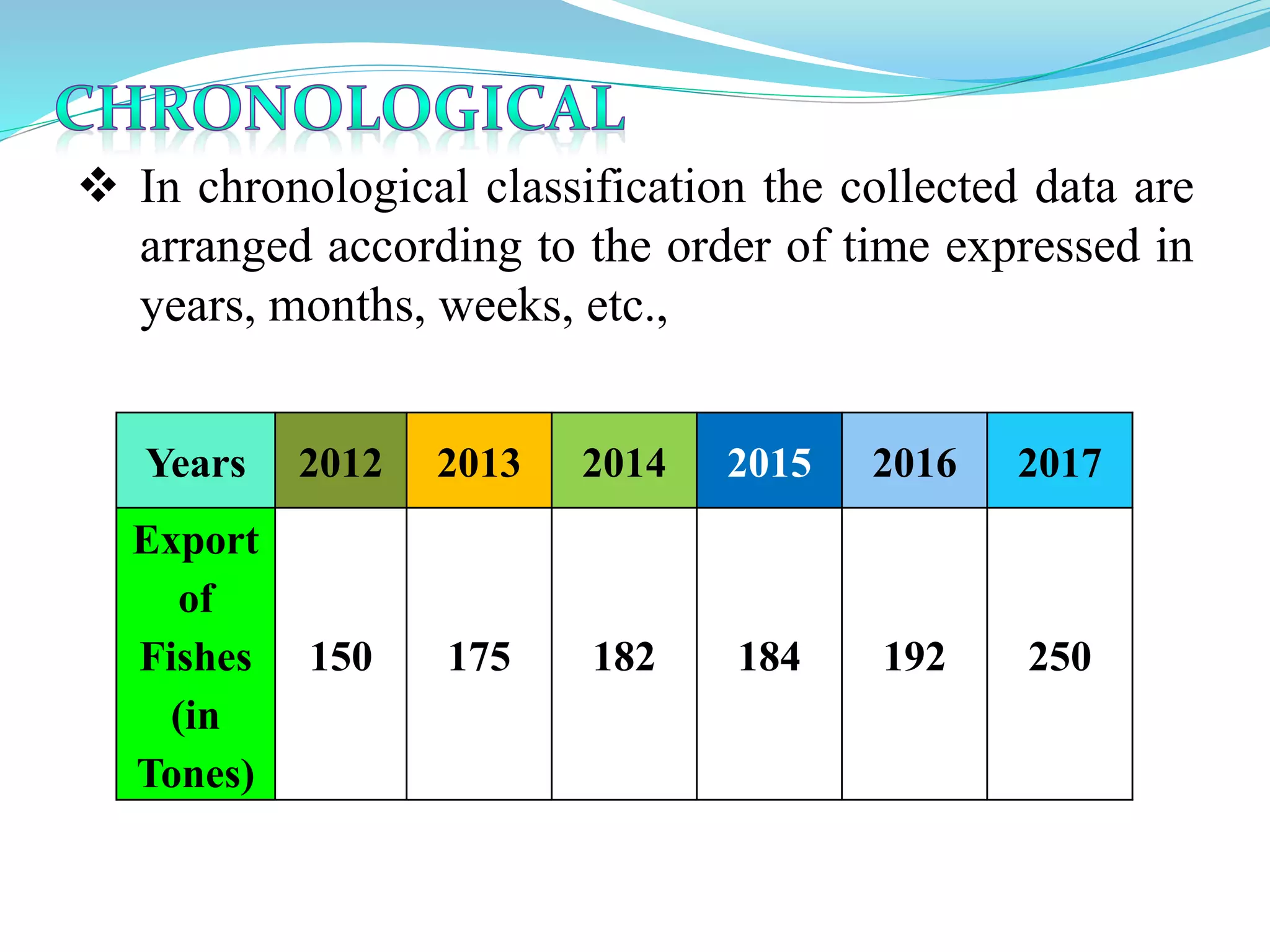
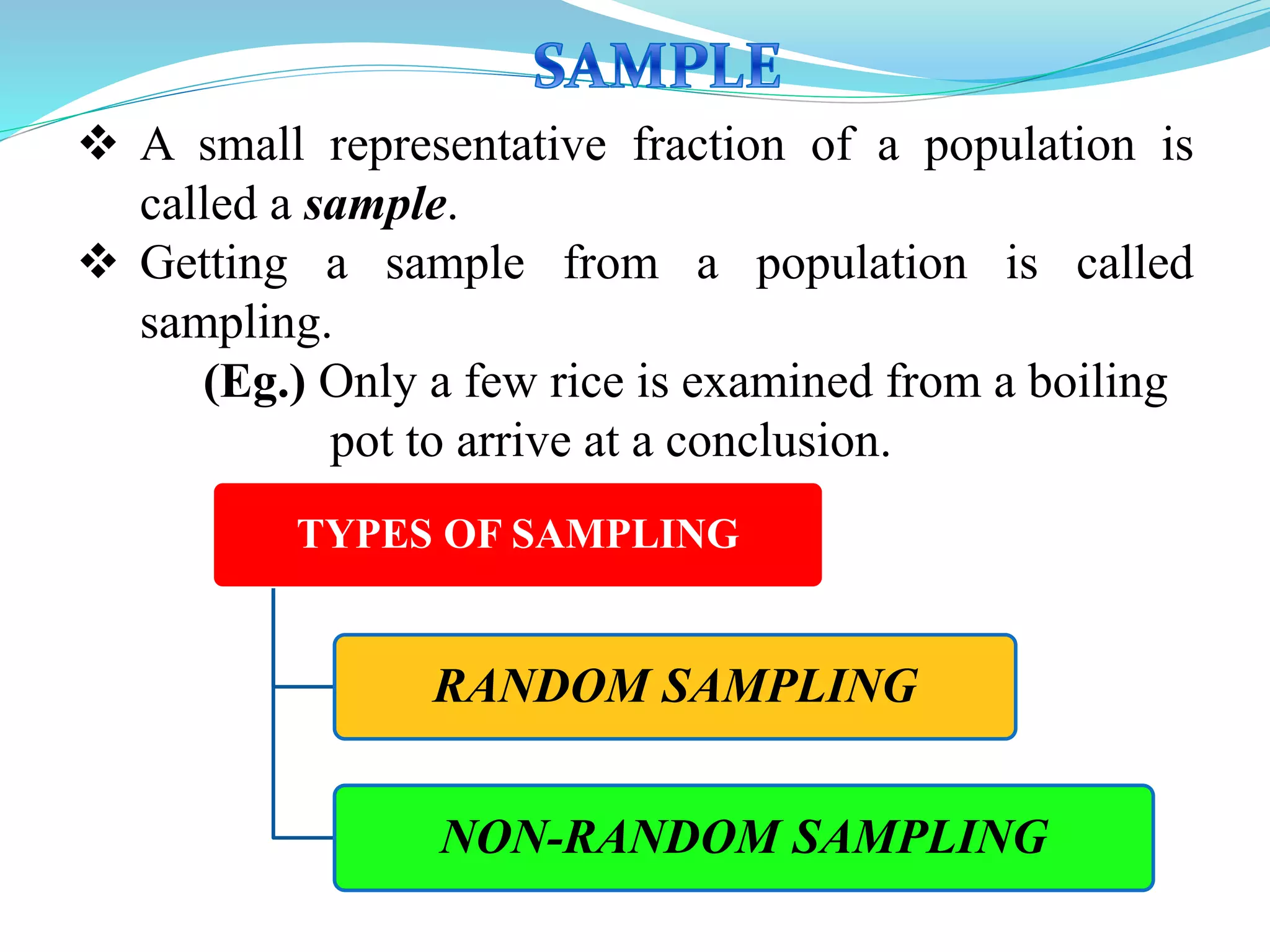
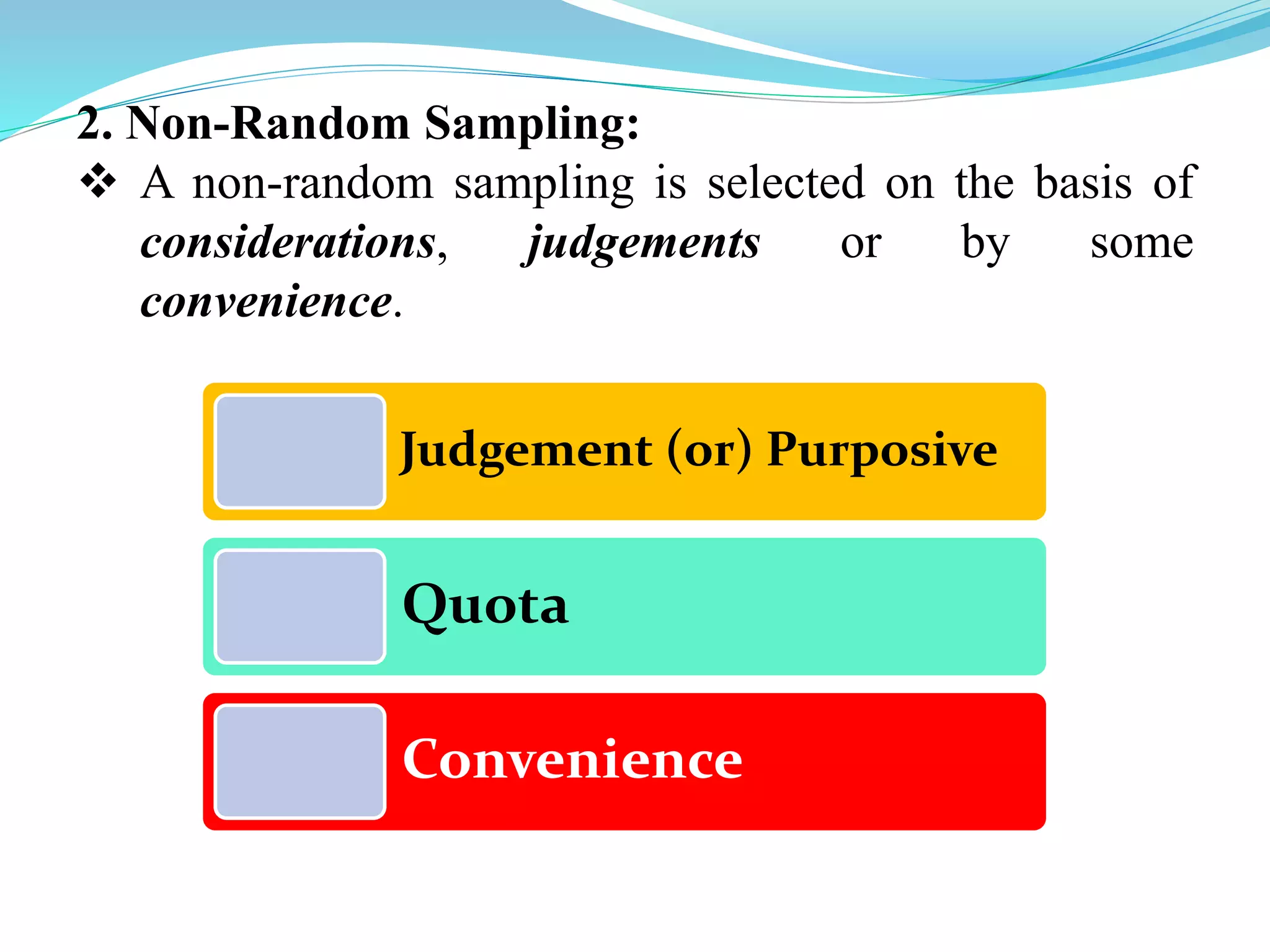
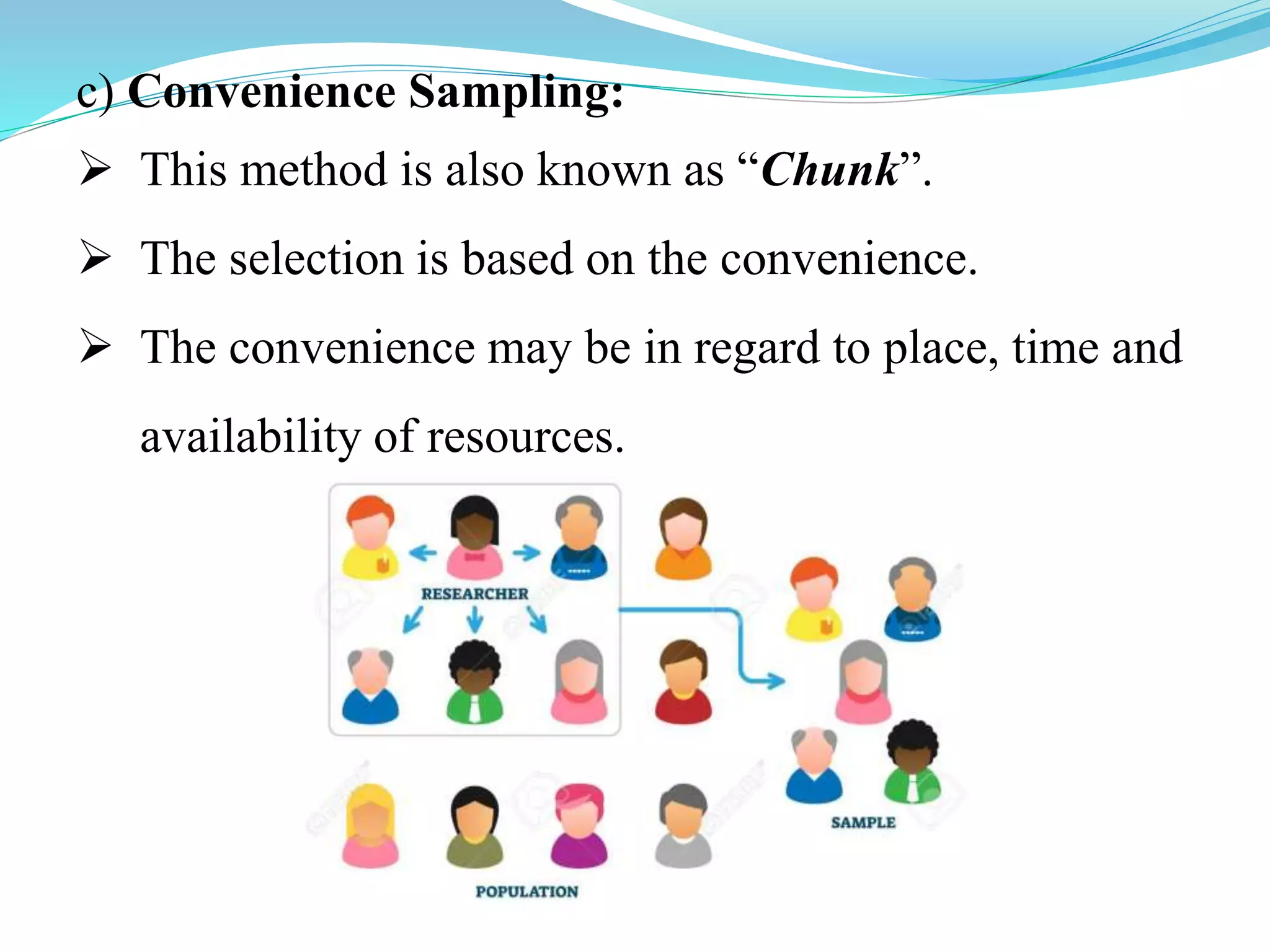
This document discusses different types of classification and sampling methods used to organize data. It describes classification based on time, geography, attributes, and quantities. Random sampling methods like simple random sampling, stratified random sampling, and systematic random sampling are explained where every item has an equal chance of selection. Non-random sampling techniques include judgment sampling, quota sampling, and convenience sampling where selection is not completely random. The document provides examples to illustrate each classification and sampling technique.