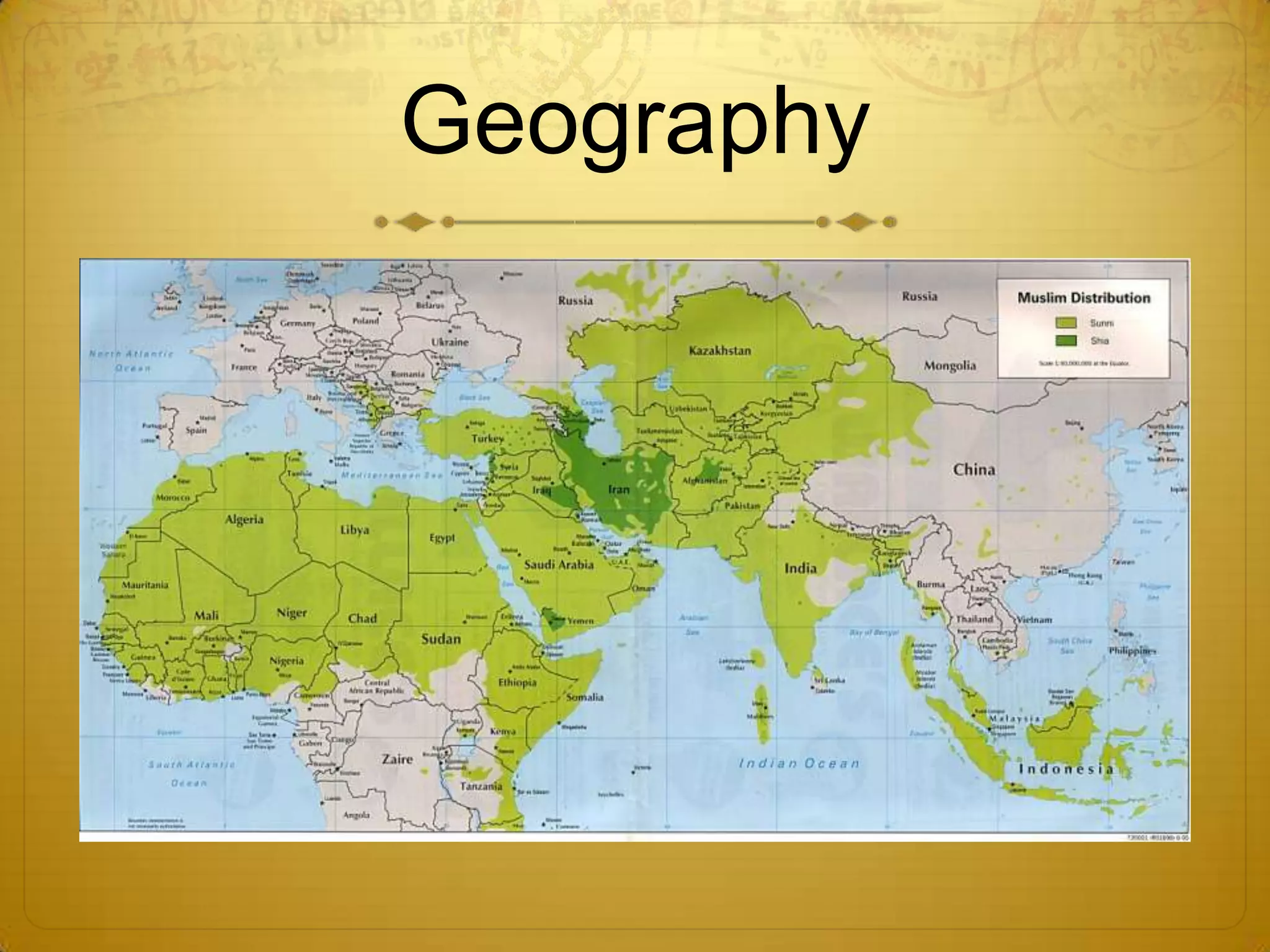
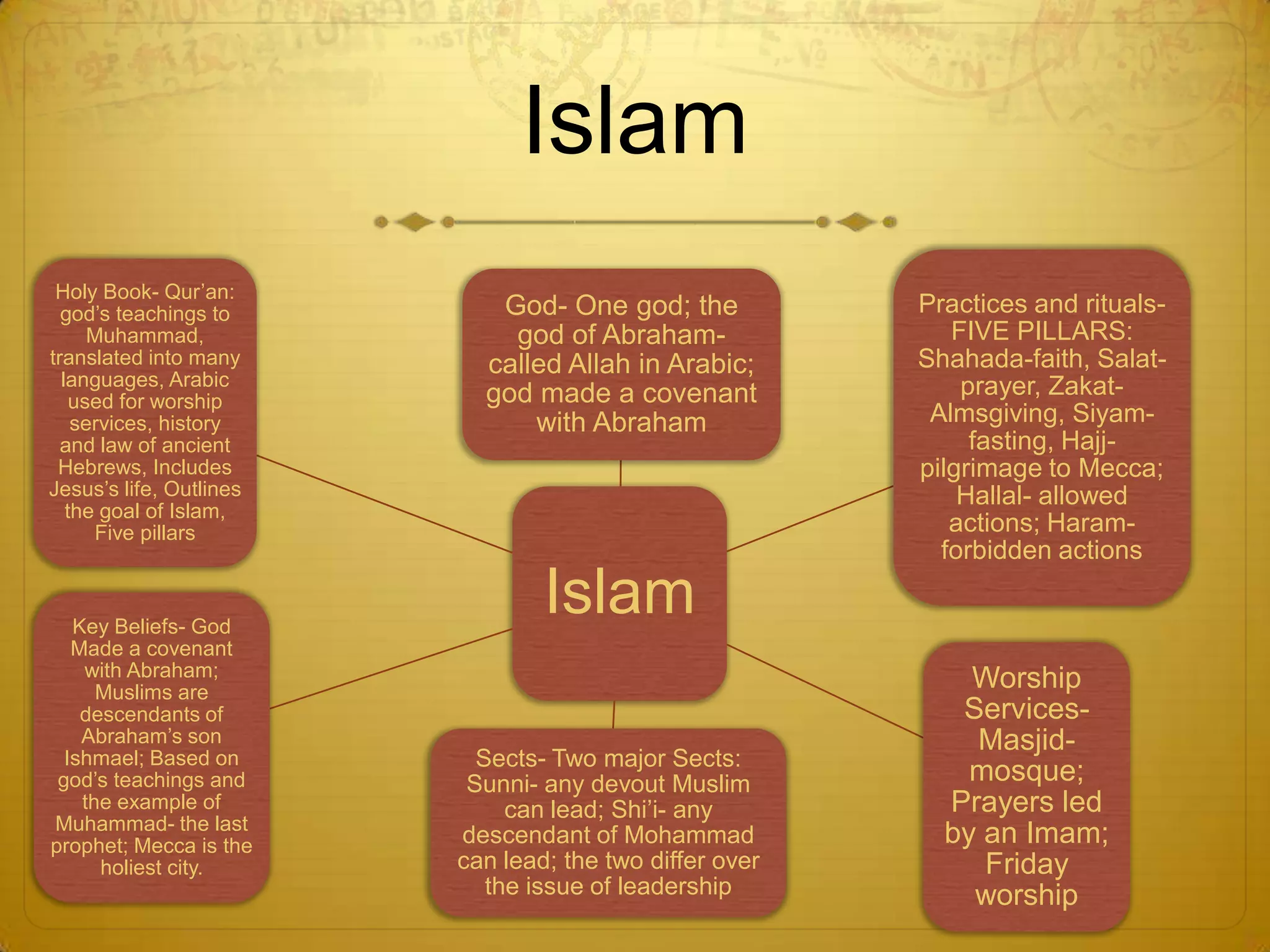
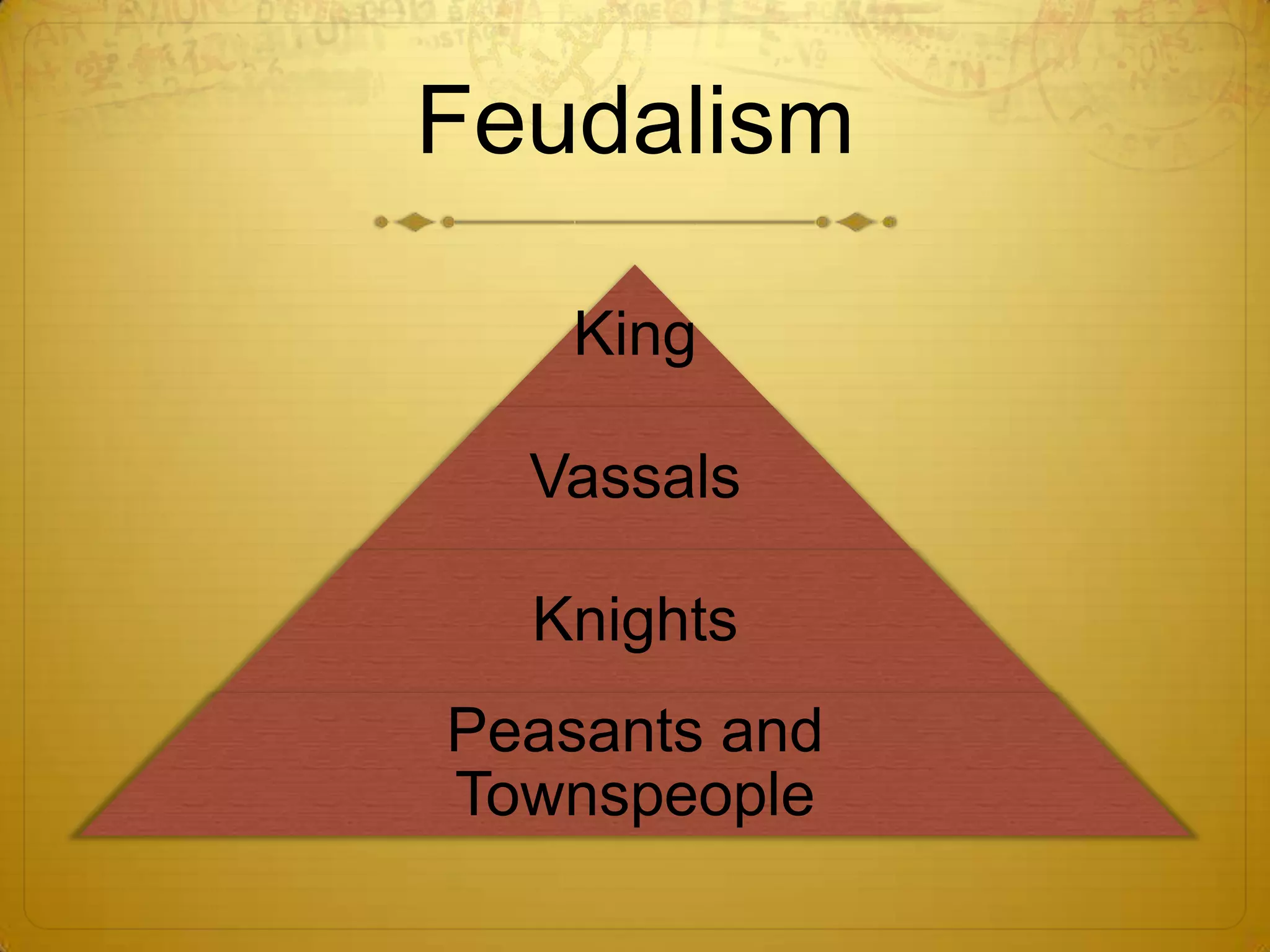
This document provides information about the geography, government, and history of ancient Greece and Rome.
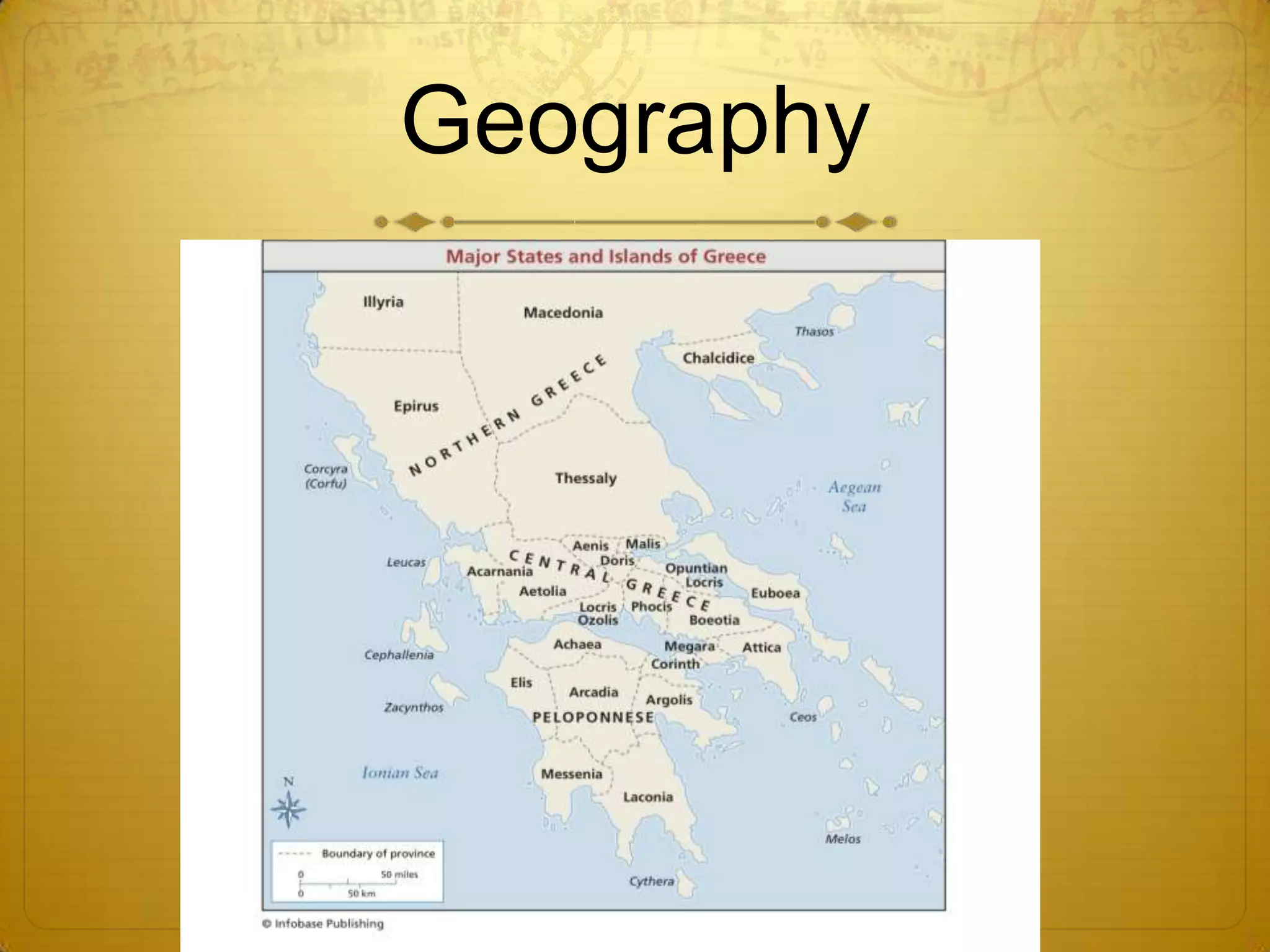
It discusses how the mountainous geography of Greece led to the development of independent city-states. It also summarizes Athens' golden age under Pericles and key differences between Athens and Sparta. The spread of Greek culture through Alexander the Great and the blending of cultures in his empire to form Hellenism is noted.
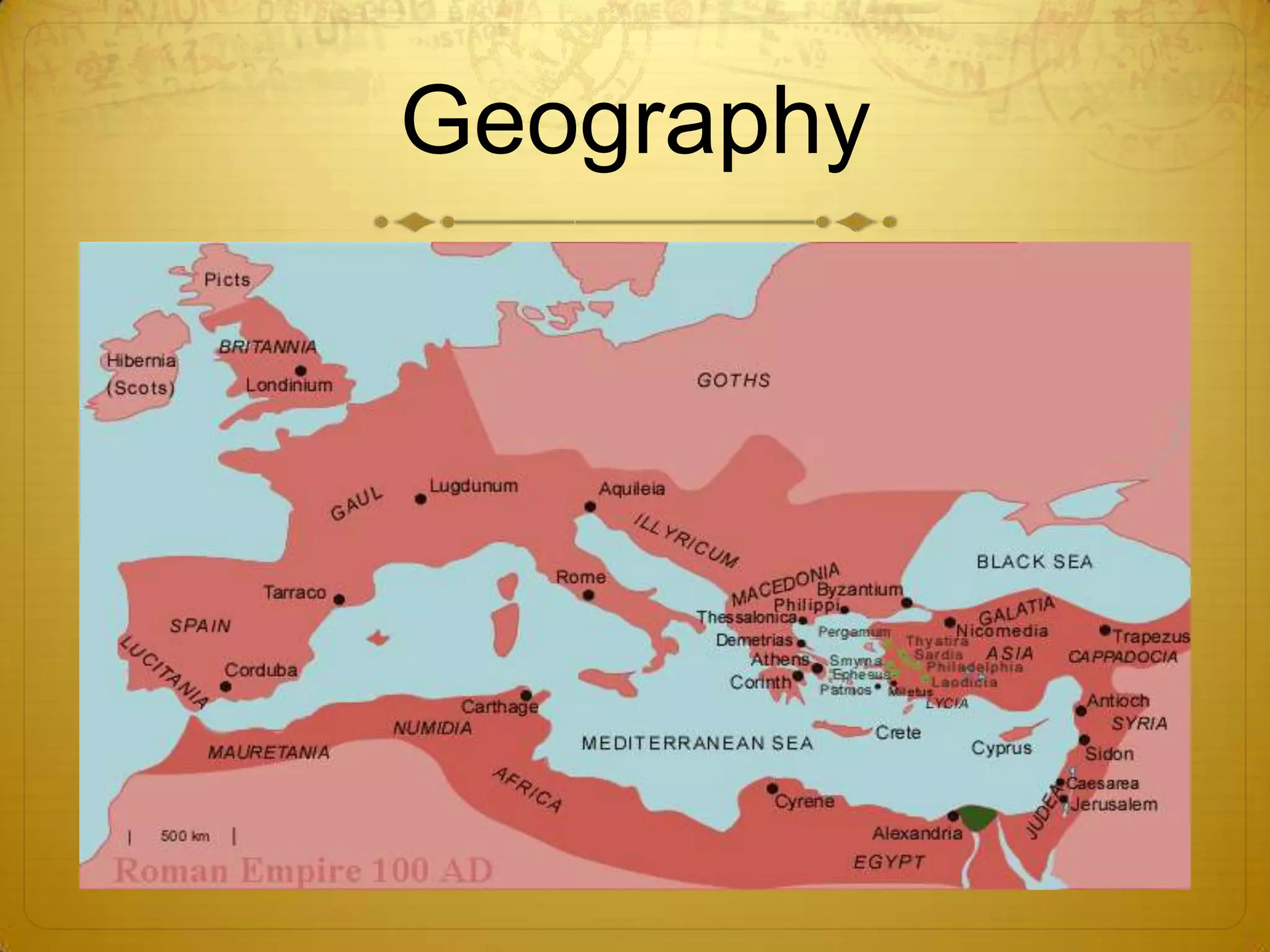
For Rome, the document outlines how its geography along the Mediterranean influenced its growth and notes the development of the Roman Republic and its laws like the Twelve Tables.