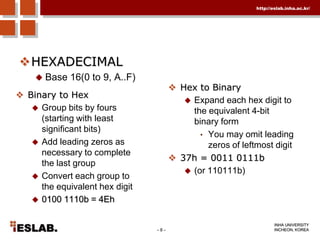
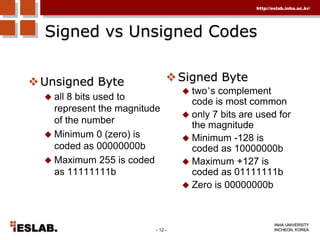
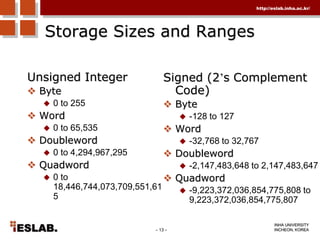
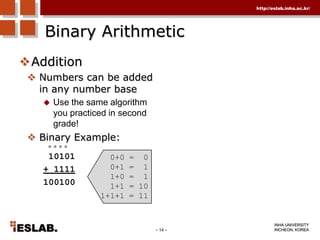
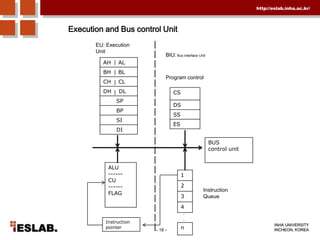
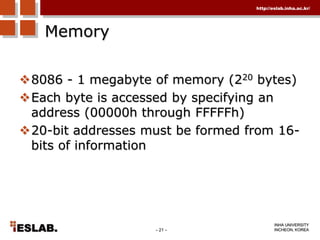
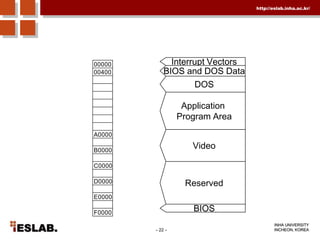
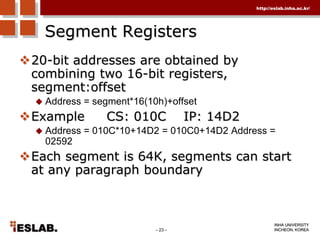
This document discusses the basic hardware features of the PC, including the processor, memory, registers, keyboard, monitor, disk drives, and other external components. It explains bits and bytes as the fundamental units of digital information storage. Various number systems are covered, including binary, decimal, hexadecimal, and how to convert between them. Storage sizes and numeric data representation in computers are also summarized.