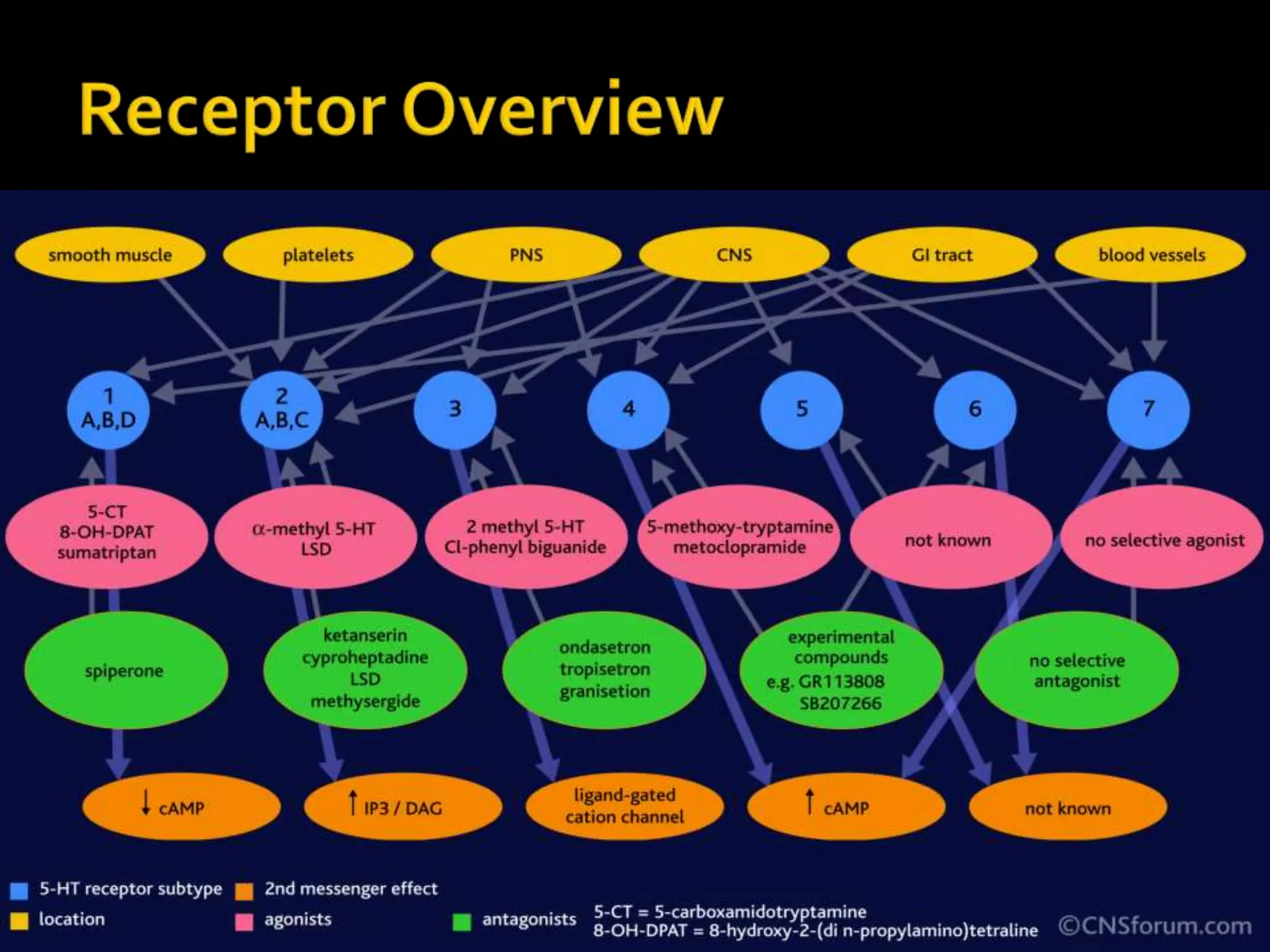
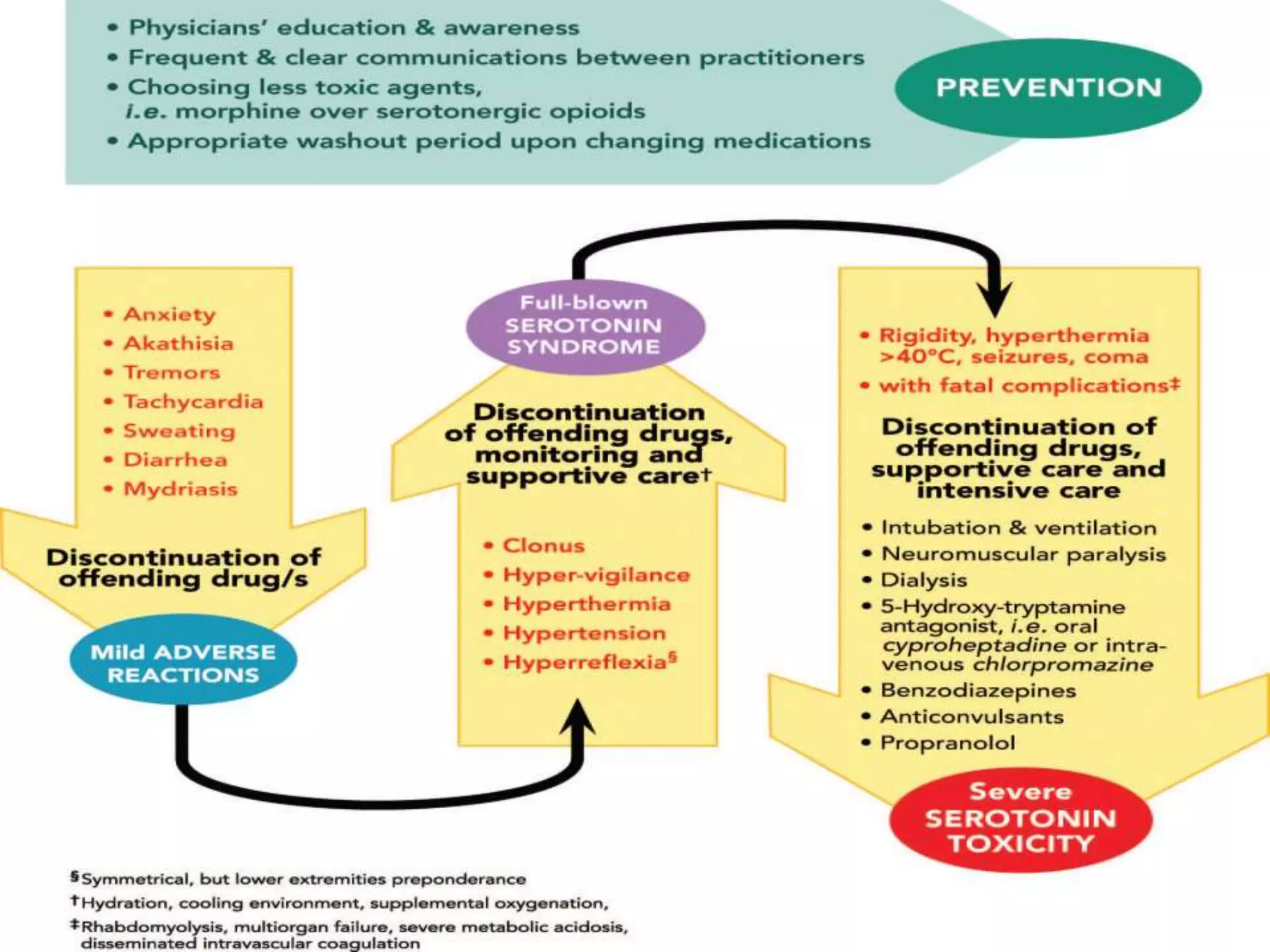
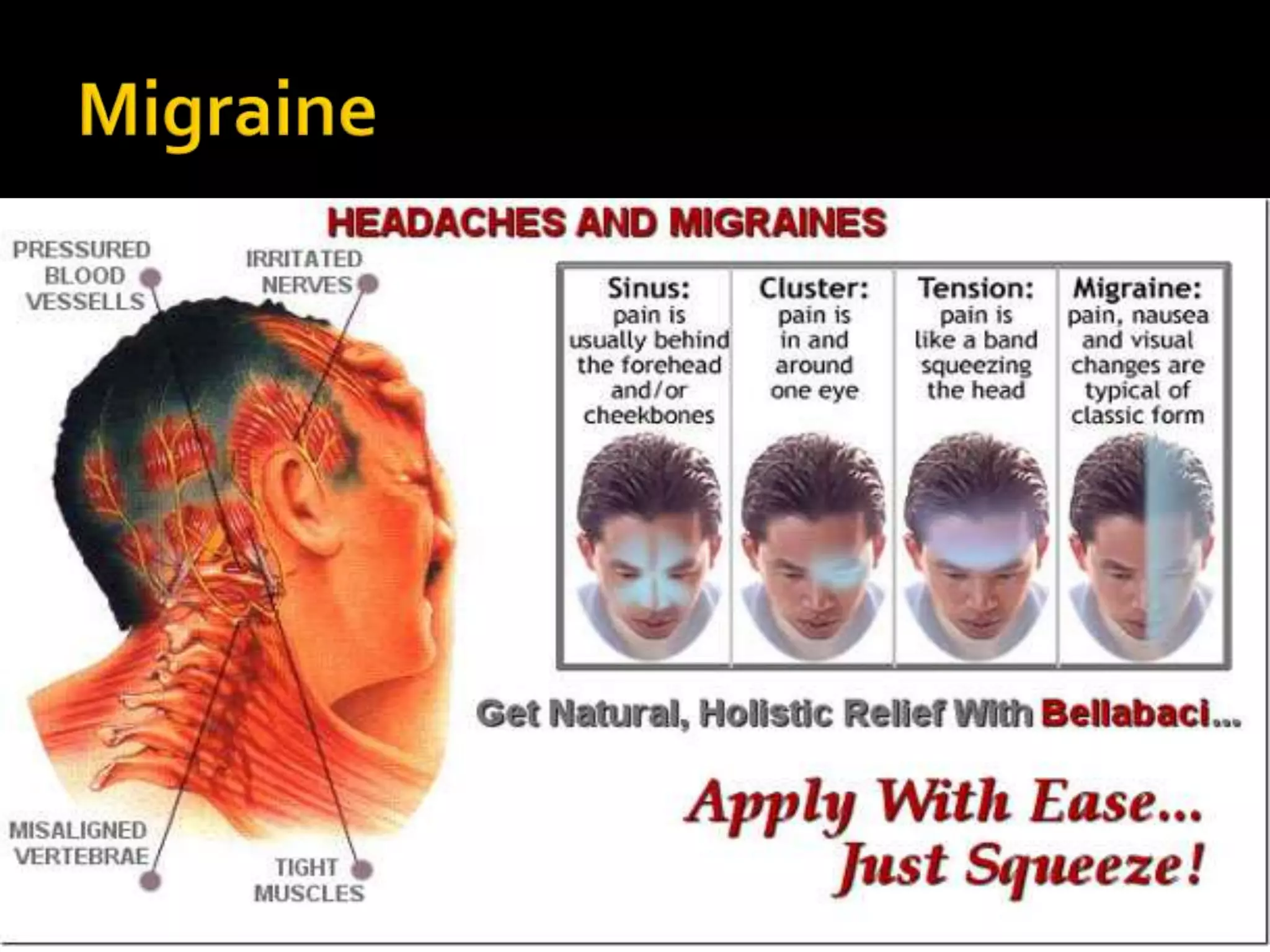
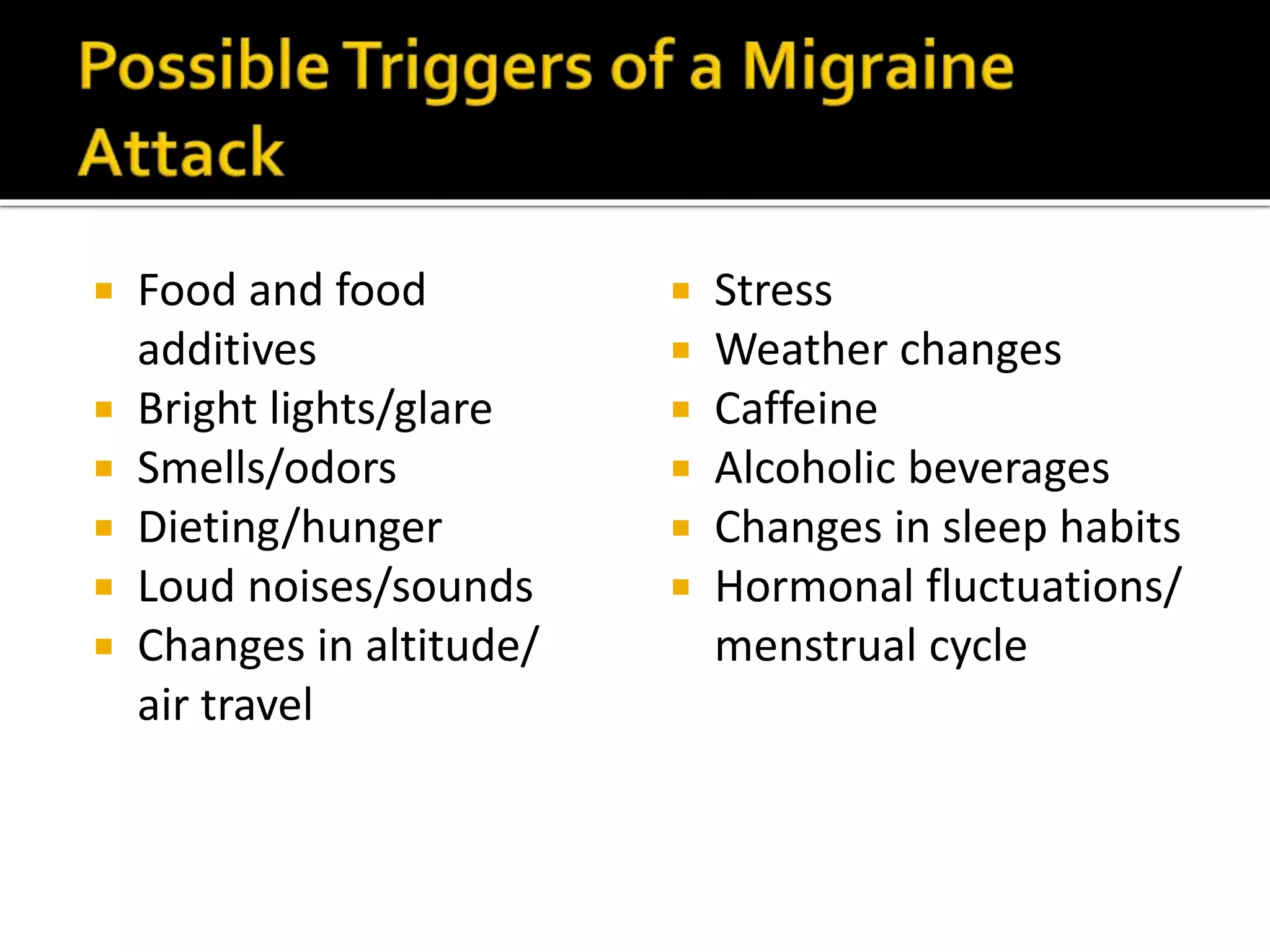
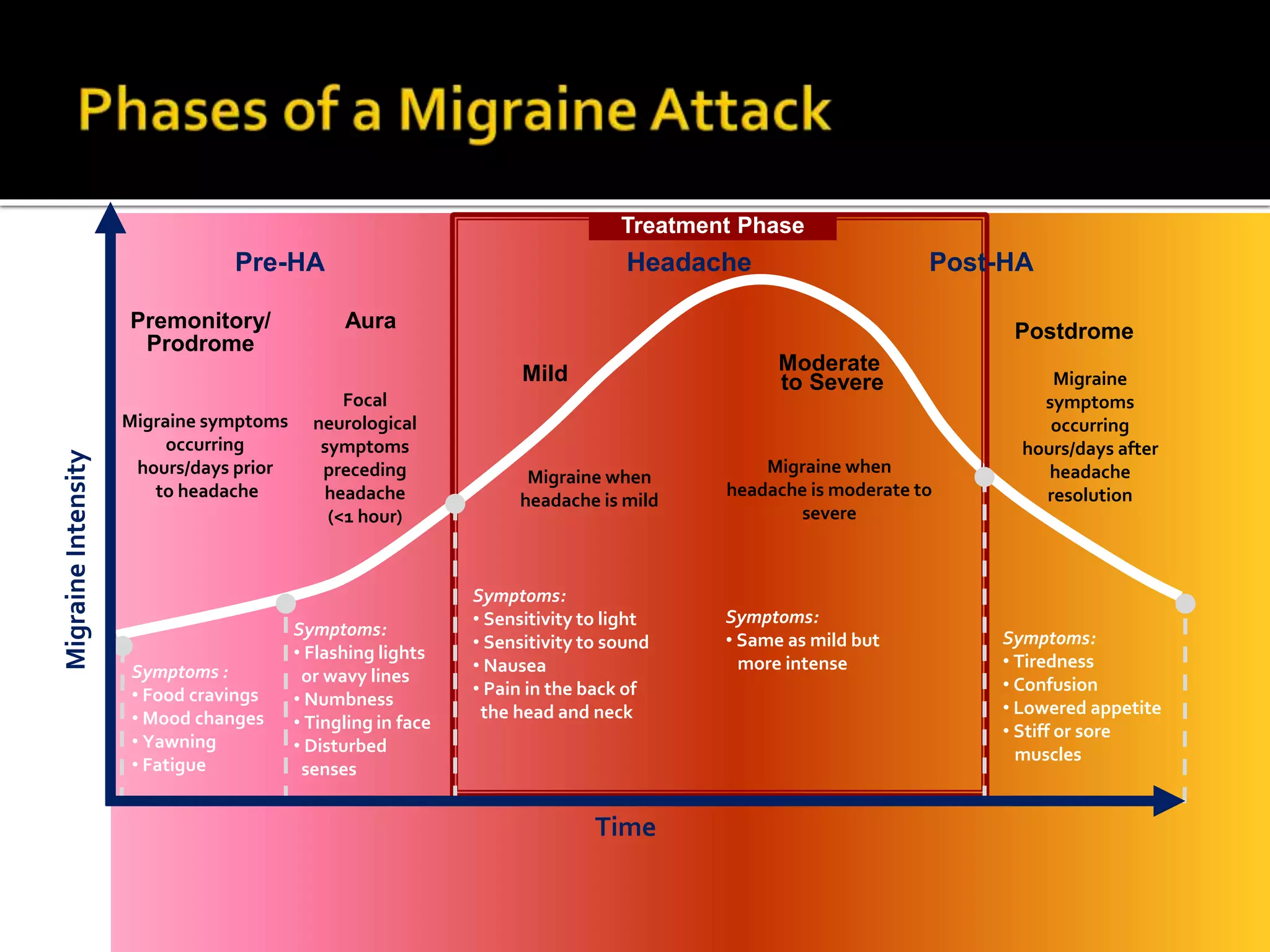
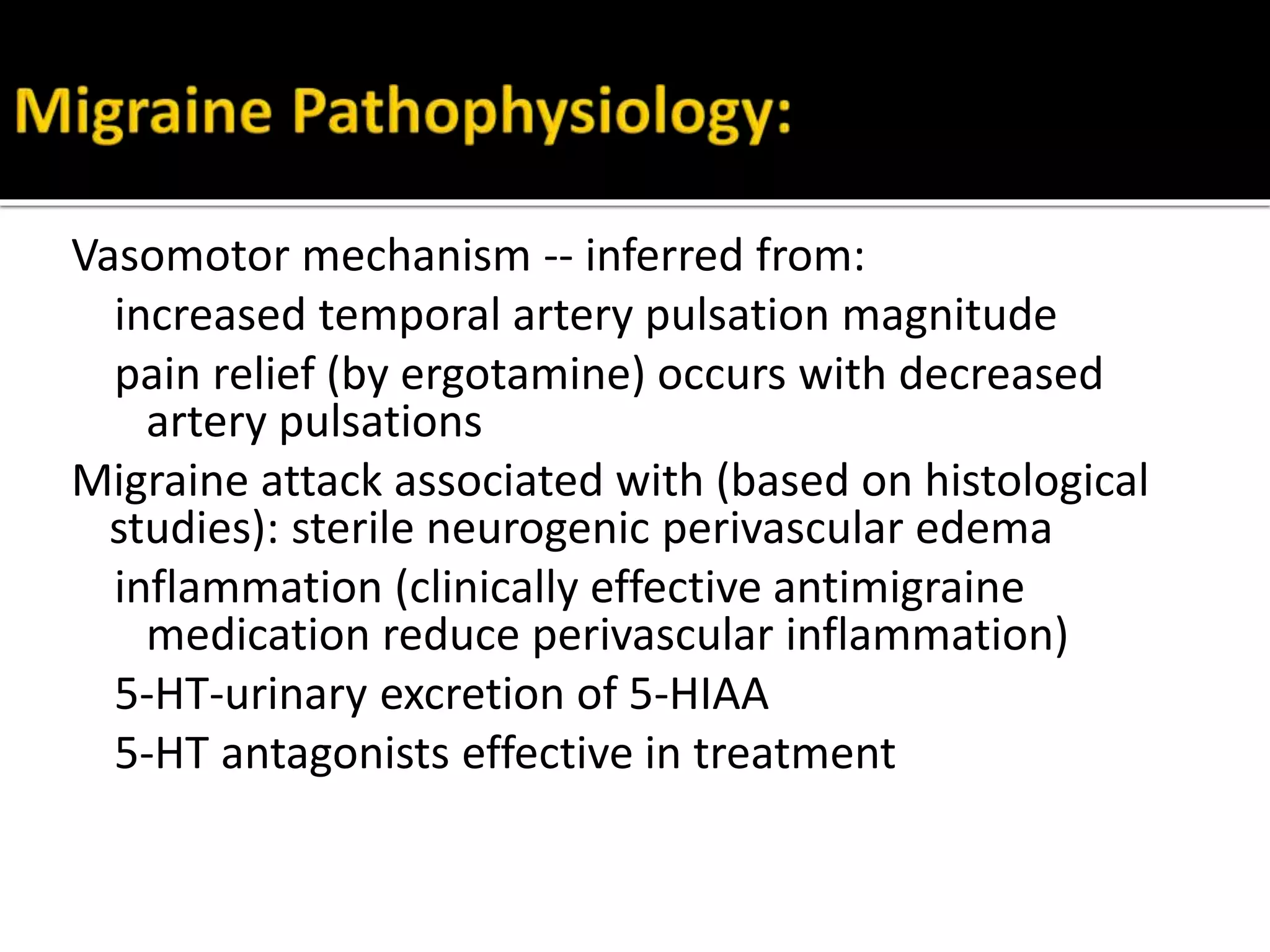
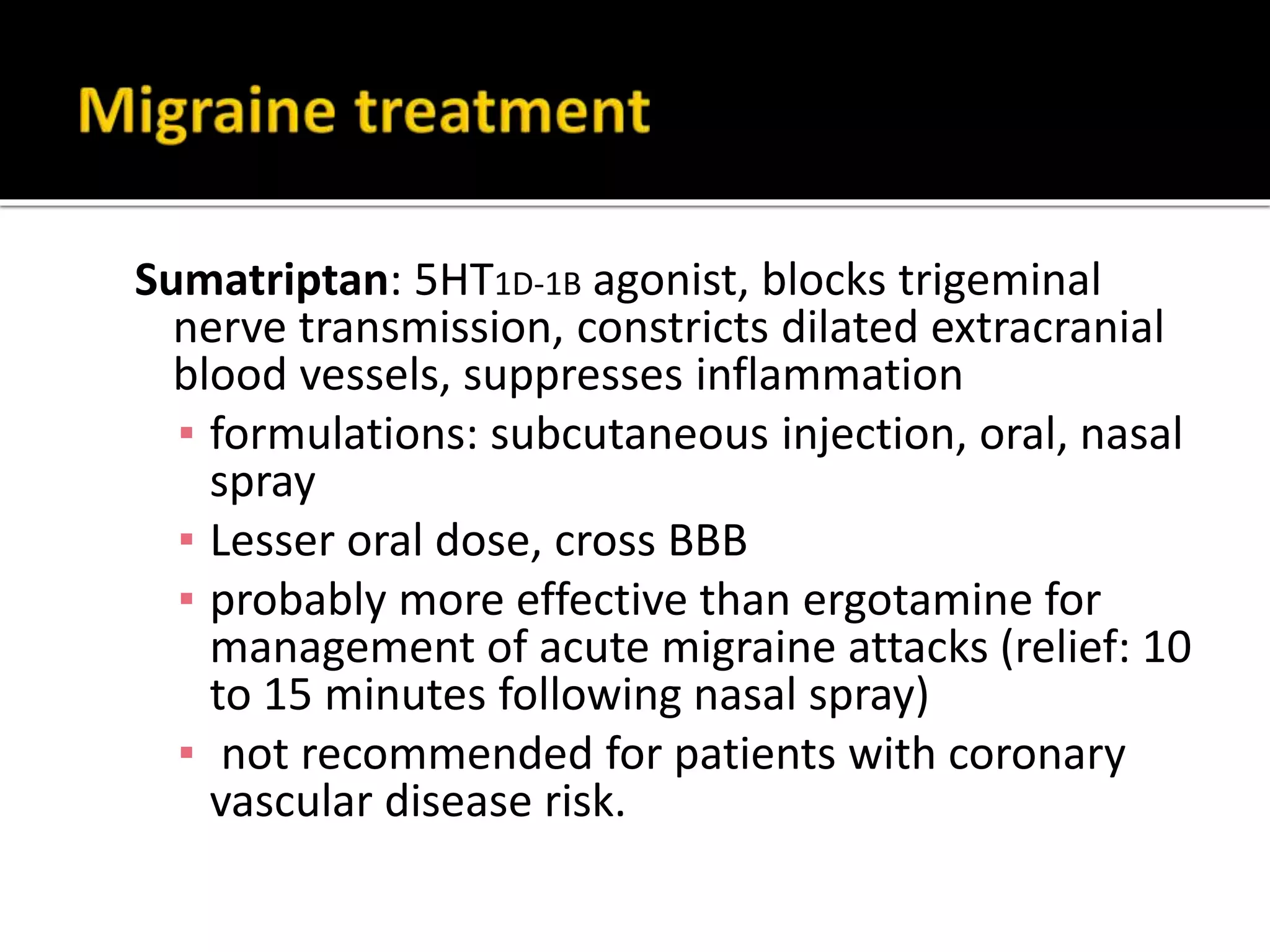
Serotonin plays an important role in migraine pathogenesis. It is involved in pain perception, sleep, mood, and vasoconstriction/dilation. Serotonin is synthesized in neurons and enterochromaffin cells, stored in granules, and acts on receptors throughout the body. During a migraine attack, activation of trigeminal nerve terminals and serotonin receptors leads to neurogenic inflammation and pain. Common migraine treatments target serotonin pathways or inhibit inflammation. These include triptans, ergotamine, NSAIDs, and preventive medications like beta-blockers.