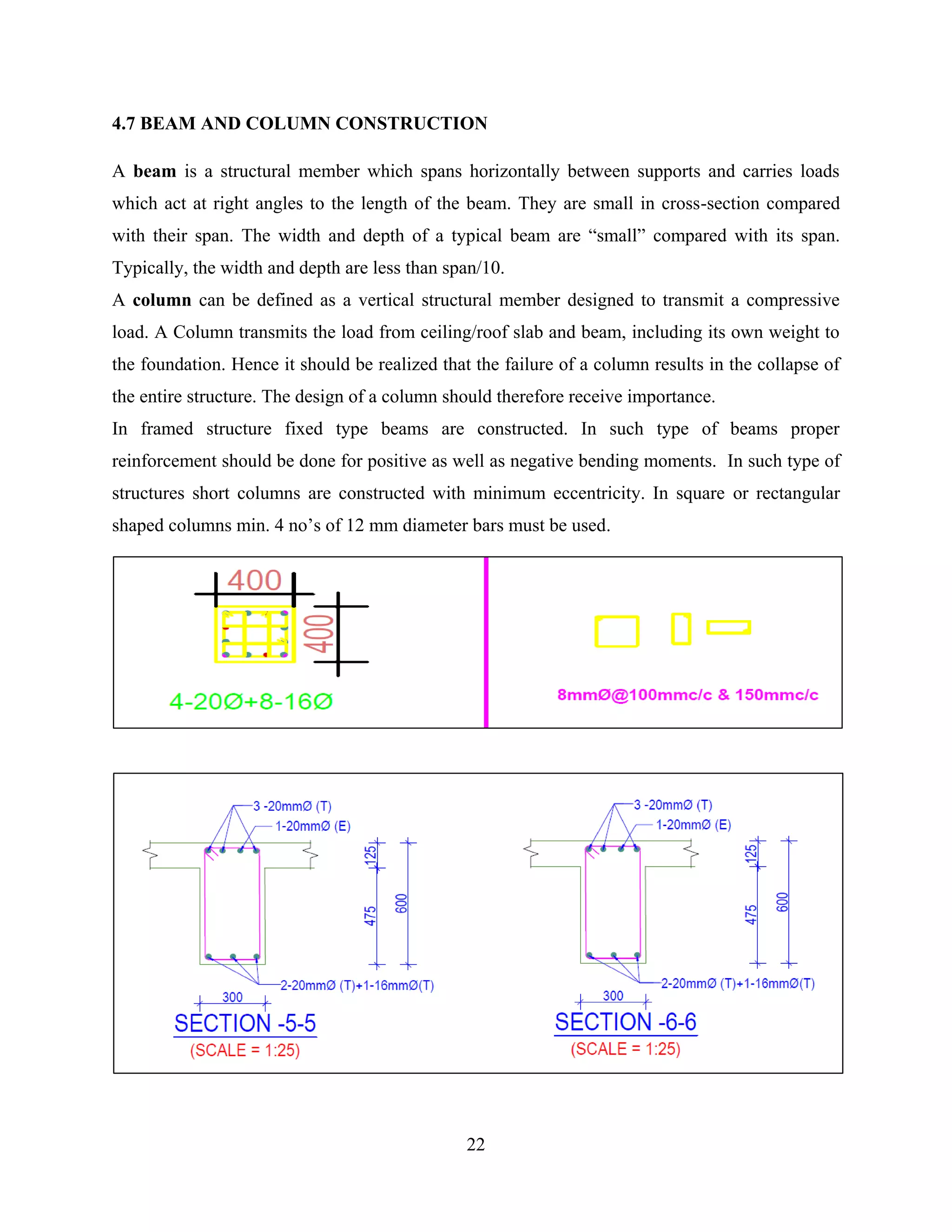
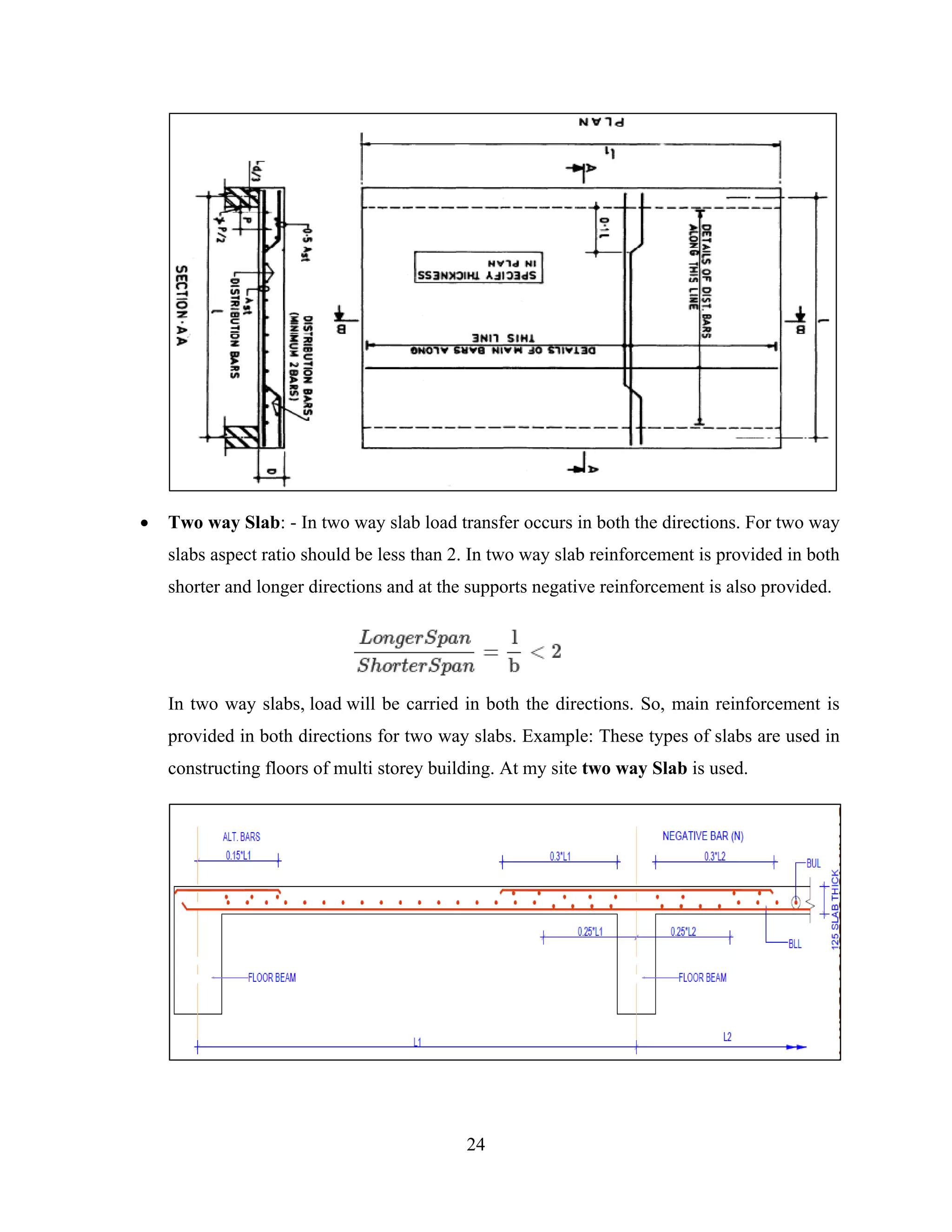
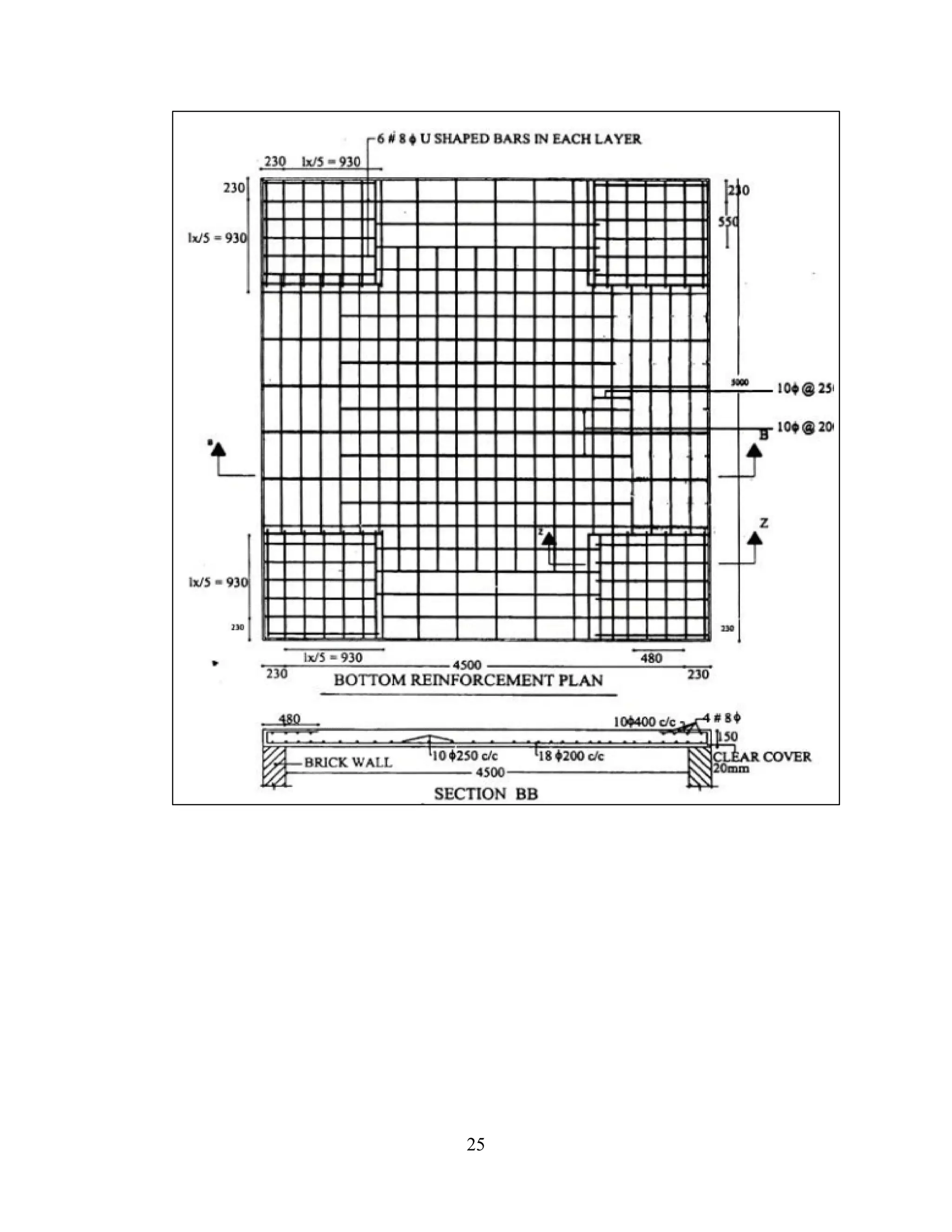
This document is a training report submitted by Masud Alam Ansari from January 1st to May 2nd, 2020 for their internship constructing a 5-storey building at Ram Raja Campus in Kalaiya Sub-Metropolitan City. It discusses the construction company, materials and equipment used, and steps taken in constructing the building, including site clearance, surveying, excavation, foundation, and concrete works. Quality control measures are also outlined.










![8
Coarse aggregate:-The aggregate, which pass through 75 mm I.S. sieve and entirely
retain on 4.75 mm I.S. sieve is known as coarse aggregates. Coarse aggregate acts as inert
filler material for concrete. The functions are almost same as that of fine aggregate.
[Note: - At construction site aggregate used are coarse aggregate of 20mm size. Coarse aggregate
of 12.5 mm size (As per concrete mix design). And River bank Fine aggregate.]
iii. REINFORCEMENT
The material that develops a good bond with concrete in order to increase its strength is called
reinforcement. Steel bars are highly strong in tension, shear, bending moment, torsion and
compression.
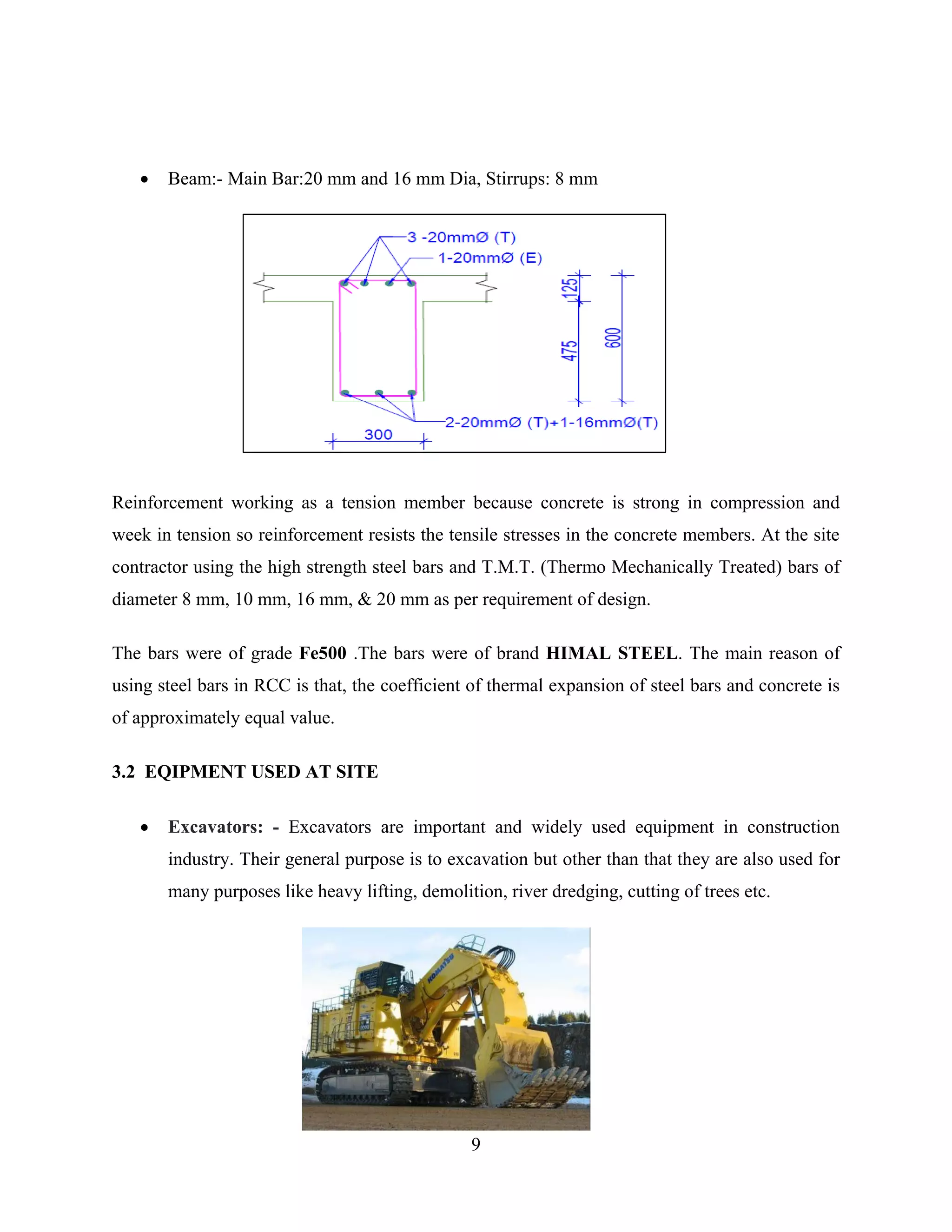
Foundation Mess (Footing):- 12 mm Dia. Both Direction
Column: - Corner Bar: 20 mm Dia, Inner Bar: 16 mm Dia, Stirrups: 8 mm Dia.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/report-200625111535/75/CIvil-Engineering-Training-Report-13-2048.jpg)







![21
Ability to receive various finish materials Cost and ability to provide openings such as
doors and window.
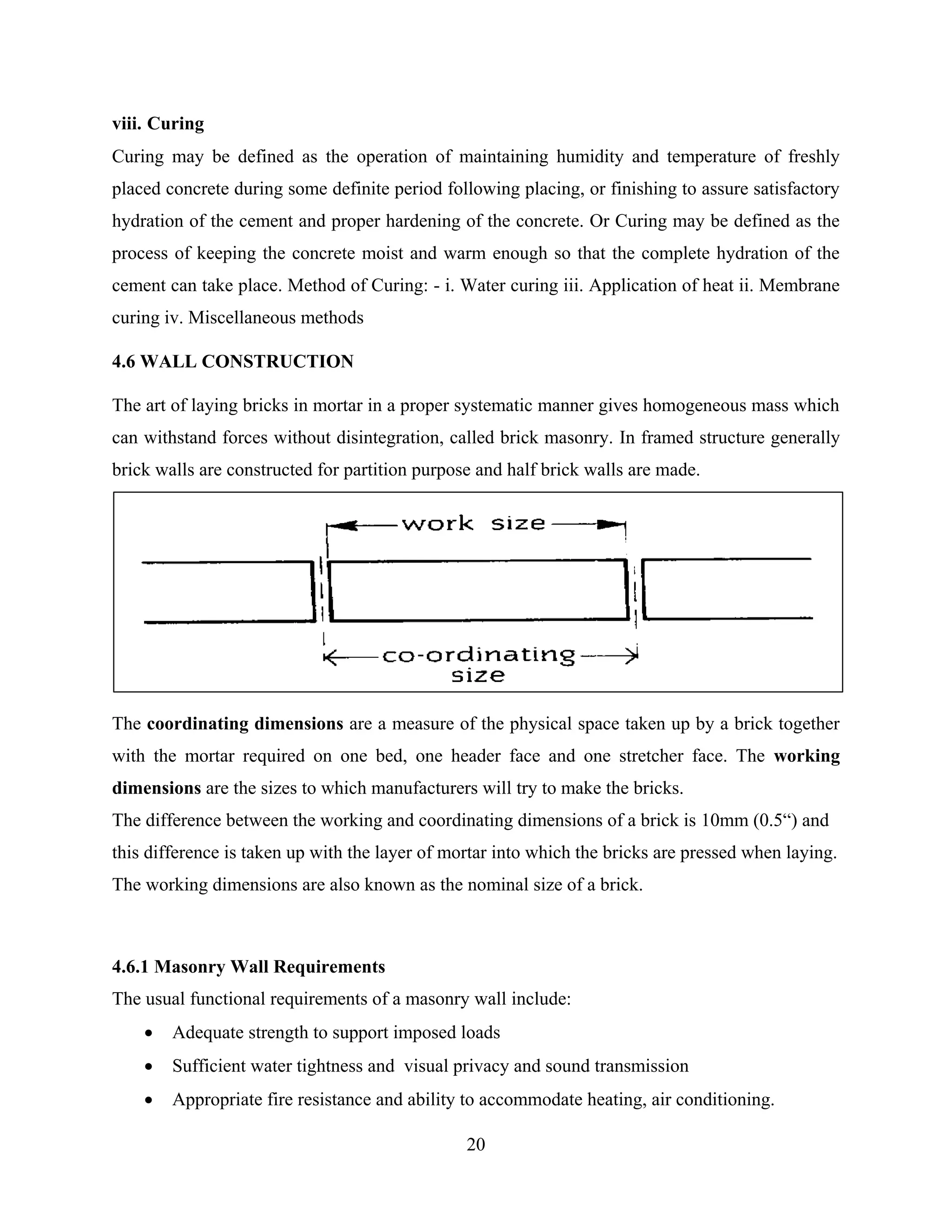
4.6.2 Bonds in Bricks
The arrangement of bricks in brick works so that the vertical joints don’t come over each other.
Bonds in brick work are provided to achieve a united mass as soon as practicable to suit the
length, height and thickness of brick work and stresses to which it is subjected. To break the
continuity of vertical joints and to provide proper bond in brick masonry portion of bricks are
provided in alternative courses.
[Note: At my Construction site 1st
class brick work is used and the ratio of mortar for brickwork
is 1:6 (Cement: sand)]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/report-200625111535/75/CIvil-Engineering-Training-Report-26-2048.jpg)