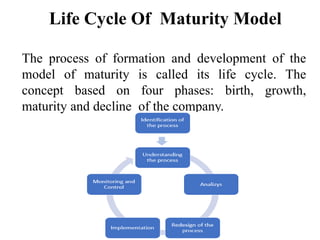
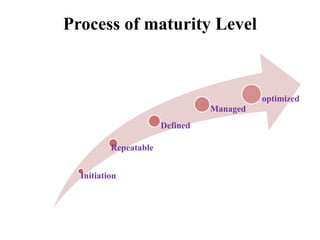
Maturity models provide a framework for evolving improvements in processes. They can be used descriptively to assess current processes or prescriptively to determine areas for improvement. Greater process maturity should lead to benefits like reduced costs and risks. Maturity models can be applied to areas like project management, quality management, and risk management. They involve assessing the current level based on phases from initiation to optimization and provide a reference for connecting strategy to processes.