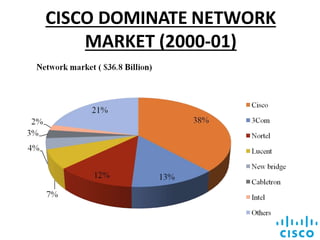
Cisco Systems, founded in 1984 in San Jose, California, is a leader in internet protocol-based networking technologies and has a diverse global supply chain with over 300 product families. The company shifted towards online orders in the late 1990s but faced significant losses due to a market downturn in 2001, leading to inventory write-offs and challenges in managing demand and supply imbalances. Cisco's supply chain relies heavily on contract manufacturers and has been impacted by issues such as inflated demand projections and collusive behaviors among suppliers.