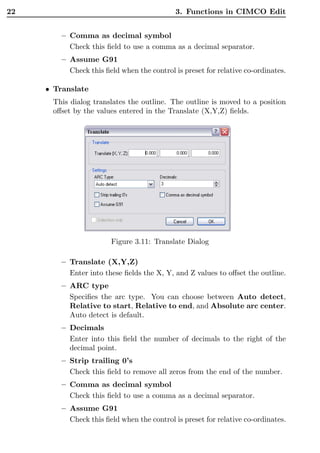
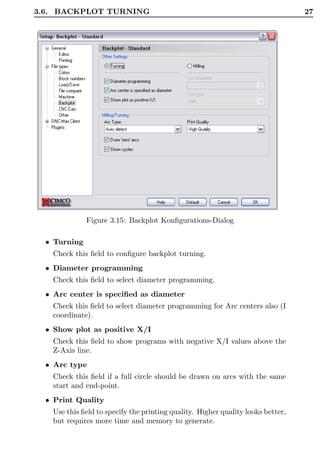
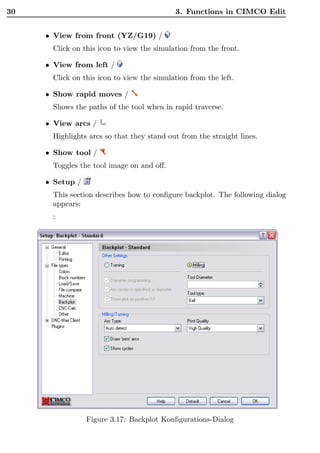
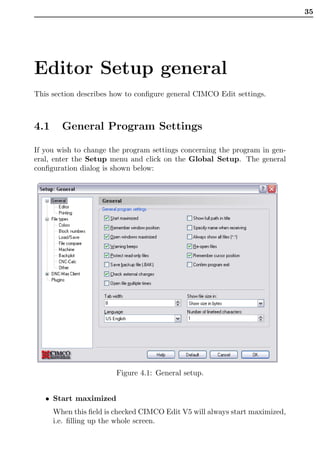
This document is the user guide for CIMCO Edit V5 software. It describes the various functions and menus in the software, including file operations, editing tools, NC functions, transmission functions, file comparison, backplot functions, setup options, and help features. It also covers installation, editor setup options, file type settings, DNC settings, serial communication standards, and using the online help. The guide is intended to help users understand and utilize all of the key capabilities within the CIMCO Edit V5 CAD/CAM software.




























































![Cimco edit 5 user guide[1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cimcoedit5userguide1-110305112440-phpapp01/85/Cimco-edit-5-user-guide-1-81-320.jpg)