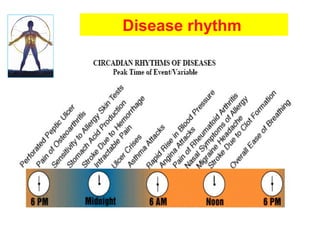
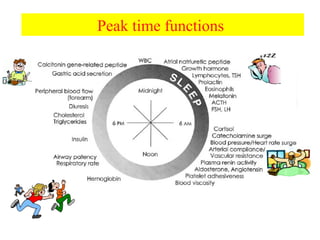
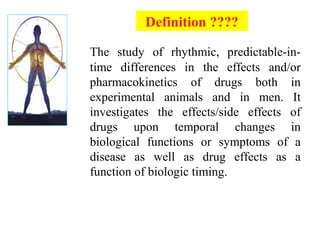
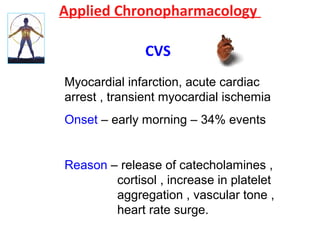
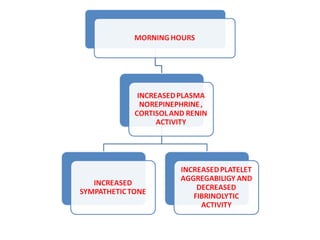
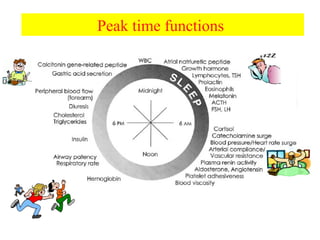
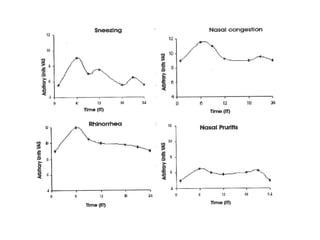
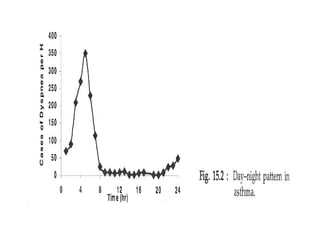
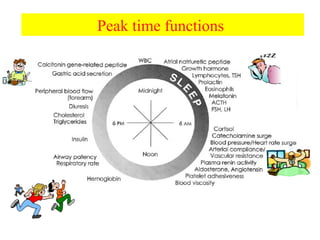
Chronopharmacology is the study of how biological rhythms affect medication. It considers how the effects and pharmacokinetics of drugs vary based on the time of day they are administered. Proper timing of medication can maximize benefits and minimize side effects by matching drug delivery to circadian rhythms in conditions like cardiovascular disease, respiratory disease, and endocrine disorders. For example, inhaled corticosteroids administered in the evening are nearly as effective as multiple daily doses for asthma, and beta blockers taken at night better prevent morning heart attacks. Chronopharmacology aims to deliver medications when the body's need or the disease's symptoms are greatest.
















![Applied Chronopharmacology
RS
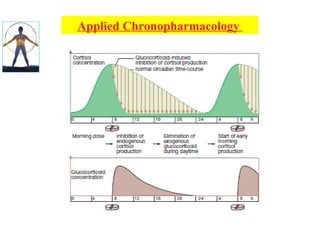
• A single daily dose of inhaled corticosteroids,
when administered at 5:30 pm rather than 8 am, was
nearly as effective as four doses a day.
• Oral prednisone
has been shown to be much more effective in
improving several features of nocturnal asthma
[FEV1]and response to a standard dose of
inhaled beta2 agonist when administered at 3 pm rather
than 8 am](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chronopharmacology-130406002139-phpapp02-201225054807/85/Chronopharmacology-130406002139-phpapp02-36-320.jpg)