CHRONIC OSTEOMYELITIS
- 1. CHRONIC OSTEOMYELITIS DR RITESH JAISWAL M.B.B.S D.Ortho DNB (Ortho) M.N.A.M.S M.Ch (Ortho) Fellowship in Joint Replacement ( Mumbai ) Fellow AO Trauma ( Switzerland )
- 2. INTRODUCTION Severe, persistent & incapacitating infection of bone and bone marrow Characterized by : - Infected dead bone within a compromised soft tissue envelope - Infected foci within bone are surrounded by sclerotic, relatively avascular bone covered by a thickened periosteum and scarred muscle and subcutaneous tissue - This avascular envelope of scar tissue leaves systemic antibiotics esssentially ineffective
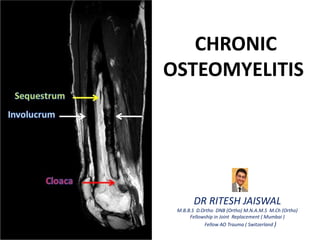
- 3. PATHOGENESIS Due to inadequate treatment of Acute OM or Trauma or Implant/foreign body ↓ Continues inflammatory process with time together with persistent infection ( Commonly with Staph aureus ) ↓ Increase intramedullary pressure due to inflammatory exudate ( Pus ) stripping the periosteum ↓ Vascular thrombosis ↓ Bone Necrosis ( SEQUESTRUM ) ↓ New bone formation ( INVOLUCRUM ) ↓ Discharge of pus, debris & exudates from involucrum through sinuses k/a CLOACAE
- 5. PATHOLOGICAL FEATURES OF CHRONIC OM : - the presence of necrotic bone - the formation of new bone - the exudation of polymorphonuclear leukocytes joined by large numbers of lymphocytes, histiocytes, and occasionally plasma cells. - New bone forms from surviving fragments of periosteum and endosteum in the region of the infection. - It forms an encasing sheath of live bone, known as an involucrum, surrounding the dead bone under the periosteum. - The involucrum is irregular and is often perforated by openings through which pus may track into the surrounding soft tissues and eventually drain to the skin surfaces, forming a chronic sinus.
- 6. - The involucrum may gradually increase in density and thickness to form part or all of a new diaphysis. - New bone increases in amount and density for weeks or months, according to the size of the bone and the extent and duration of the infection. - Endosteal new bone may proliferate and obstruct the medullary canal. - After host defense or operative removal of the sequestrum, the remaining cavity may fill with new bone, especially in children. - However, in adults, the cavity may persist or the space may be filled with fibrous tissue, which may connect with the skin surface by means of a sinus tract
- 7. SEQUESTRUM Term exclusively used in osteomyelitis and is a fragment of necrotic bone ( usually cortical ) found at the nidus of infection within bone. These fragment usually begin as part of the cortex and are surrounded by pus and grannulation tissue. INVOLUCRUM When reactive bone is newly formed at the interface between diseased bone and healthy tissue. Radiologically, it appears as newly formed radiodense bone around the radiolucent sequestrum CLOACA Opening in involucrum through which pus and sequestra make there way out
- 9. GROSS CHARACTERISTICS OF SEQUESTRUM - White, brittle bone piece with smooth pus facing and rough grannulation facing surface lying free from parent bone - No punctate bleeding - Sinks in water - Dull note on percussion - Closed haversian canal
- 11. TYPES OF SEQUESTRUM 1) TUBULAR – Pyogenic sequestrum in children 2 ) FEATHERY - Pyogenic infection 3 ) COARSE SANDY - Tuberculosis 4) DENSE IVORY - Syphilis 5) RING - Pin tract infection 6) BOMBAY SEQUESTRUM ( Black ) - Calcaneum OM 7) KISSING SEQUESTRUM - TB Spine 8) CONICAL SEQUESTRUM - Amputation Stump
- 12. BIOFILM - Aggregates of microorganisms in which cells adhere to each other on a surface. - These adherent cells are frequently embedded within a self - produced matrix of extracellular polymeric substance composed of extracellular DNA, proteins and polysaccharides . - It protects bacteria from phagocytosis , recognition & helps to cling to inert implant material and form numerus colonies. - It inhibits T lymphocyte proliferation , B Lymphocyte blastogenesis , immunoglobulin production , interferes with cell chemotaxis , and white cell degranulation
- 13. Biofilm bacteria exists in 2 forms : 1) Planktonic state 2) Stationary state
- 14. CLASSIFICATION
- 15. CIERNY & MADER CLASSIFICATION
- 18. CLINICAL PRESENTATION A) SILENT PHASE ( PERIOD OF INACTIVITY ) - Usually no symptoms - Overlying skin thin, scarred , poorly nourished - Poor healing Ulcerations of skin - Scarring of muscles with contractures of surrounding joints
- 19. B) ACTIVE PHASE ( PERIOD OF ACTIVITY ) - Local inflammatory signs present ( swelling, reddness, warmth, tender ) - Fever mostly lowgrade - Aching mainly on wt bearing - Discharging sinus ( draining pus with or without small pieces of bone )
- 20. - Disease showing flare ups with intervals of months to week - Due to poor general condition & low resistance - Recurrent toxemia cause debilitary sometimes fatal amyloidosis
- 21. - Patient usually have H/O acute OM - Chronic OM usual presenting Features are : - long standing discharging sinus - Bone pain - Pathological #
- 22. O/E - Drainage of pus - Small pieces of sequestra through sinus ( hallmark of Chronic OM ) - Protruding grannulation tissue through sinus - Sinus often adherent to underlying tissue - Deformity of limb - Muscle contracture - LLD
- 24. DIAGNOSIS PHYSICAL EXAMINATION - Check for - Integrity of skin & soft tissue - Bone Stability - Neurovascular status
- 25. LAB : - Nonspecific - ESR, CRP Elevated in most patients - WBC Elevated only in 35 %
- 26. RADIOGRAPH - Osteolytic area - Bone Resorption - Thickening & Sclerosis of surrounding bone - Sequestrum ( Denser than normal bone ) can be seen inside cavity - Sinogram is useful in planning surgery
- 28. CT SCAN - Provides excellent definition of cortical bone - Evaluation of the surrounding soft tissues - useful in identifying sequestra.
- 29. MRI - Provides extent of the pathological involvement by showing the margins of bone and soft-tissue edema. - May reveal a well-defined rim of high signal intensity surrounding the focus of active disease (rim sign). - Sinus tracks and cellulitis appear as areas of increased signal intensity on T2-weighted imaging.
- 30. BONE SCAN Technetium-99m bone scans – - ↑ uptake in areas of increased blood flow or osteoblastic activity. - Lacks sensitivity - High negative predictive value Gallium scans – - ↑ uptake in areas where leukocytes or bacteria accumulate. - A normal gallium scan virtually excludes the presence of osteomyelitis and can be useful as a follow-up examination after surgery. Indium-111–labeled leukocyte scans - more sensitive than technetium or gallium scans - useful in differentiating chronic osteomyelitis from neuropathic arthropathy in the diabetic foot.
- 31. DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS - Tuberculous OM - Soft tissue Infection - Ewing’s sarcoma
- 32. TREATMENT - Chronic OM cannot be eradicated without surgical treatment. - Challenges to eradicate the infection only with Antibiotic - Adherence of bacteria to orthopaedic implants & bone - can hide intracellularly. - slimy coat protecting from phagocytic cells and antibiotics. - Goal of surgery is eradication of the infection by achieving a viable and vascular environment.
- 33. Debridement : - Radical débridement may be required to achieve this goal. - Inadequate débridement main reason of high recurrence rate - Adequate débridement often leaves a large dead space that must be managed to prevent recurrence and significant bone loss that may result in bony instability. Appropriate reconstruction of the bone and soft-tissue defects may be needed after proper identification of the infecting organism and appropriate antibiotic therapy.
- 34. Reconstruction should be undertaken only after careful planning and identification of sequestra and intraosseous abscesses by plain radiographs, sinography, CT, and MRI. For the reconstructive phases, a plastic surgeon skilled in coverage techniques, such as skin grafts, muscle and myocutaneous flaps, and occasionally free flaps should be consulted. The duration of postoperative antibiotics is controversial – practice is to place the patient on 6 weeks of antibiotics, typically intravenous, under the direction of an infectious disease specialist, followed by clinical and laboratory examinations
- 35. AIMS 1) Adequate debridement 2) Appropriate reconstruction of bone and soft tissue defect 3) Appropriate antibiotic therapy
- 36. Sequestrectomy and Curettage - Sinus tracks can be injected with methylene blue 24 hours before surgery to make them easier to locate and excise - Appropriate preparation should be made before surgery as more time to perform and result in considerably more blood loss. - Expose the infected area of bone, and excise all sinus tracks completely & indurated periosteum. - Use a drill to outline a cortical window at the appropriate site, and remove it with an osteotome. - Remove all sequestra, purulent material, and scarred and necrotic tissue - After removing all suspicious matter, carefully excise the overhanging edges of bone, and avoid leaving a cavity or dead space.
- 39. - If a cavity cannot be filled by the surrounding soft tissue, a local muscle flap or a free tissue transfer can be used to obliterate the dead space. - If there is a nonunion present with any bony instability, the bone must be stabilized, preferably with an Ilizarov-type external frame. - If possible, close the skin loosely over drains, and ensure that no excessive skin tension is present. - If closure is impossible, pack the wound open loosely or apply an antibiotic bead pouch, and plan for delayed closure or skin grafting at a later time - Appropriate antibiotics should be used before, during, and after the operation.
- 40. - The limb is splinted until the wound has healed, and then it is protected to prevent pathological fracture. - Bony and soft-tissue defects must be filled to reduce the chance of continued infection and loss of function. - Several techniques have been described for the management of such defects - Methods described to eliminate this dead space are (1) bone grafting with primary or secondary closure (2) use of antibiotic polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) beads as a temporary filler of the dead space before reconstruction (3) local muscle flaps and skin grafting with or without bone grafting (4) microvascular transfer of muscle, myocutaneous, osseous, and osteocutaneous flaps (5) the use of bone transport ( Ilizarov technique )
- 41. Open Bone Grafting Papineau technique This procedure is based on the following principles: (1) granulation tissue markedly resists infection (2) autogenous cancellous bone grafts are rapidly revascularized and are resistant to infection (3) the infected area is completely excised (4) adequate drainage is provided (5) adequate immobilization is provided (6) antibiotics are used for prolonged periods
- 42. The operation is divided into three stages: (1) EXCISION OF INFECTED TISSUE WITHOUT OR WITH STABILIZATION USING AN EXTERNAL FIXATOR OR AN INTRAMEDULLARY ROD (2) In this stage, completely excise the sinus tracks and sequestra, and saucerize the areas of devitalized bone. (3) It sometimes may be necessary to resect the diaphysis in segments, such as in cases of infected nonunion (4) If the demarcation between healthy and infected tissues is difficult to recognize, repeat this stage at intervals of 5 to 7 days. (5) Between the operations, pack the wound open with dressings soaked in antibiotic, or use an antibiotic pouch technique
- 43. (6) If stabilization is required, an external fixator is applied at this time (7) Papineau et al. recommended an intramedullary nail for stabilization. (8) Delay the next stage until signs of infection are absent, and healthy-appearing granulation tissue is present throughout.
- 44. (2) CANCELLOUS AUTOGRAFTING - This stage consists of autogenous cancellous bone grafting & fill the cavity completely - If indicated, use local muscle pedicle grafts to enhance the blood supply to the grafts, and leave the overlying skin and subcutaneous tissue open - Especially in subcutaneous bones such as the tibia, excise the lips of the wound if the skin tends to cover the granulation tissue before it completely covers the graft
- 45. (3) WOUND COVERAGE In some cases, spontaneous epithelialization results in adequate wound coverage otherwise, in stage III use one of several techniques - skin grafts - myocutaneous flaps - muscle pedicle flaps - free flaps requiring microvascular anastomosis
- 47. Polymethylmethacrylate Antibiotic Bead Chains - The use of antibiotic-impregnated PMMA beads in the treatment of chronic osteomyelitis is common practice. - The rationale for this treatment is to deliver levels of antibiotics locally in concentrations that exceed the minimal inhibitory concentrations. - This has the advantage of obtaining very high local antibiotic concentrations (200 times), while maintaining low serum levels and low systemic toxicity. - The antibiotic is leached from the PMMA beads into the postoperative wound hematoma and secretion, which act as a transport medium. - High concentrations of the antibiotic can be achieved only with primary wound closure; if such closure cannot be performed, the wound can be covered with a water-impermeable dressing (bead pouch technique). - Before the beads are implanted, all infected and necrotic tissue should be adequately débrided surgically, and all foreign material should be removed.
- 48. - Suction drains are not recommended because the concentration level of the antibiotic is diminished when they are used. - Aminoglycosides are the most commonly employed antibiotics for use with PMMA beads. - Penicillins, cephalosporins, and clindamycin are eluted well from PMMA beads; vancomycin elutes much less effectively. - Antibiotics such as the fluoroquinolones, tetracycline, and polymyxin B are broken down during the exothermic process of cement hardening and cannot be used with PMMA beads. - Porous, high-viscosity cements, by providing greater surface area, may allow antibiotics to elute more readily than less porous cements. - Currently, most commercially available bone cements have a prepackaged form available with gentamicin (500 mg per 40 g pack). - Add 2 to 4 g of vancomycin to each pack because methacillin-resistant S. aureus is the most common bacterium that can be seen in this setting.
- 49. - Short-term, long-term, or even permanent implantation of PMMA antibiotic beads is possible. - In short-term implantation, the beads are removed within 10 days, and in long-term implantation, they may be left for 80 days. - We recommend removal of PMMA beads at about 6 weeks. - The rationale for removal of PMMA beads is based on numerous factors. - Local bactericidal antibiotic levels last only 2 to 4 weeks after placement, and when all the antibiotic has leached out of the bead, a foreign body remains that may be colonized by glycocalyx forming bacteria. - PMMA also has been shown to inhibit local immune response by impairing various phagocytic immune cells. -
- 50. - The antibiotic bead pouch technique, described subsequently, has been used with encouraging results for preventing infection in open fractures. - It also can be used in the treatment of osteomyelitis if soft- tissue coverage is impossible after initial débridement. - The bead pouch must be changed frequently, and repeat débridement should be performed until the wound is ready for a soft-tissue coverage procedure.
- 51. TECHNIQUE - Thoroughly débride all necrotic tissue & Irrigate the wound using a pulsatile lavage system with 9 L of saline solution containing bacitracin. - Prepare antibiotic PMMA beads by mixing high- viscosity bone cement powder with a powder form of the antibiotic in a bowl. - Add the activating solution, and stir the mixture until the cement is workable. - Form several beads by rolling them into small spheres. - Place the beads on an 18-gauge or 20-gauge wire to form a bead chain.
- 52. - Allow the cement to harden. Place the PMMA antibiotic bead chains into the bony defect filling the dead space. - Close all wound extensions with interrupted nylon sutures. - Apply an adhesive porous polyethylene wound film (Op Site) to cover the wound. - The limb should be appropriately immobilized. - The bead pouch should be changed at 72-hour intervals with repeat débridement and irrigation until the wound is ready for a soft-tissue coverage procedure
- 55. Ilizarov Technique - The Ilizarov technique has been helpful in the treatment of chronic osteomyelitis and infected nonunions. - This technique allows radical resection of the infected bone. - A corticotomy is performed through normal bone proximal and distal to the area of disease. - The bone is transported until union is achieved. - Disadvantages of this technique include the time required to achieve a solid union and the high incidence of associated complications.
- 56. Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy - Hyperbaric oxygen therapy is another method for treating chronic osteomyelitis, but has not proved to be reliably effective. - The use of hyperbaric oxygen can be recommended only as an adjuvant to more traditional methods of treatment
- 62. COMPLICATIONS 1) Pathological Fracture 2) Deformity 3) Limb Length Discrepancy 4) Muscle Fibrosis 5) Malignant Changes - Squamous cell carcinoma of sinus tract - Osteosarcoma 6) Amyloidosis