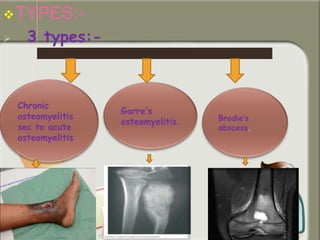
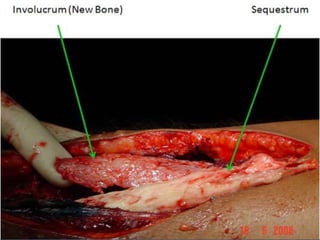
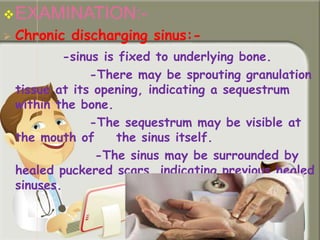
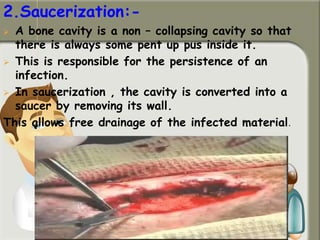
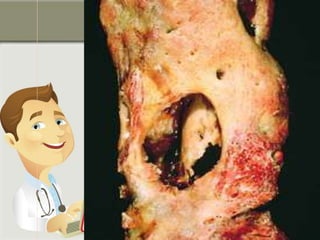
This document provides information on chronic osteomyelitis, including types, pathology, diagnosis, and treatment. It notes that chronic osteomyelitis is usually caused by delayed or inadequate treatment of acute osteomyelitis, which allows spread of infection and bone death. Key features include sequestra (dead bone), involucrum (dense bone overlying sequestra), sinus tracts, and irregular thickened bone visible on x-ray. Treatment involves surgery to remove dead bone and tissue along with antibiotics to eliminate infection. Complications can include exacerbations, growth abnormalities, fractures, or rarely malignant changes in long-standing cases.