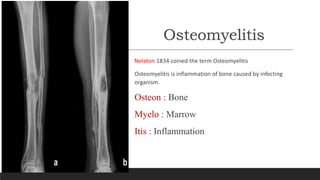
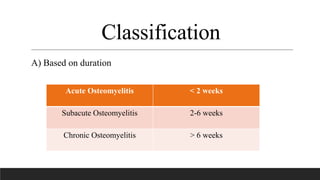
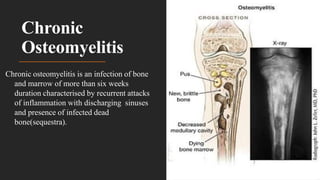
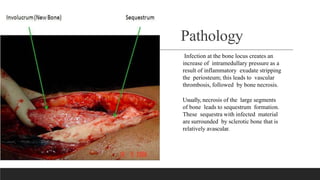
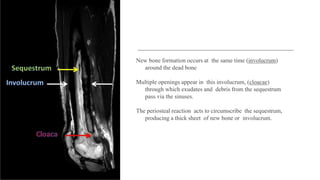
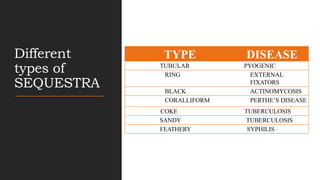
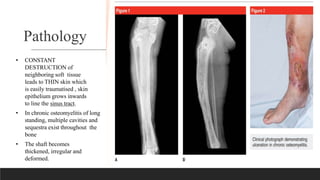
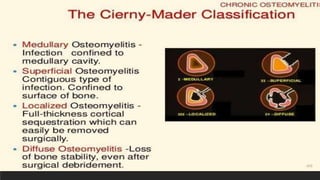
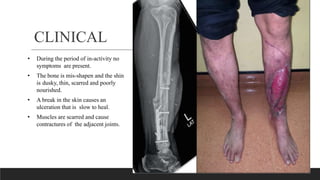
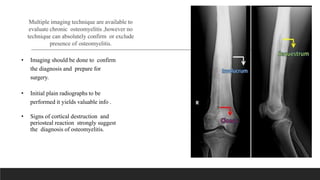
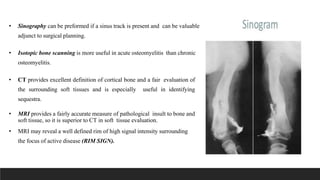
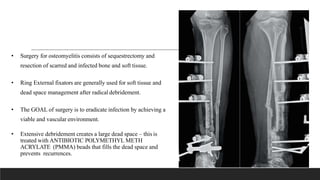
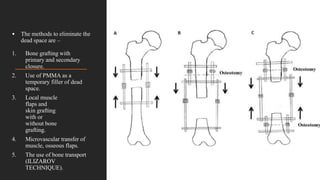
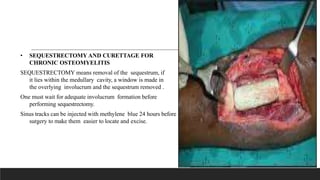
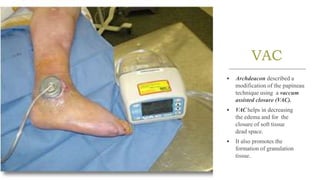
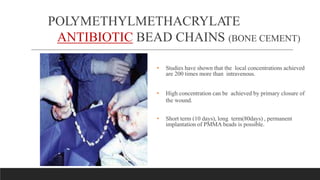
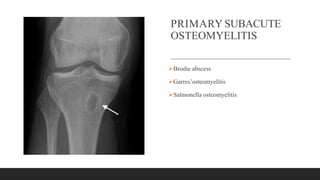
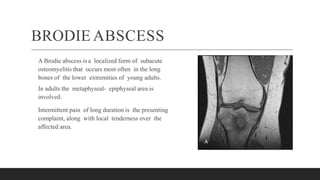
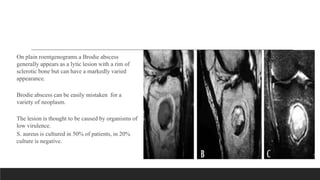
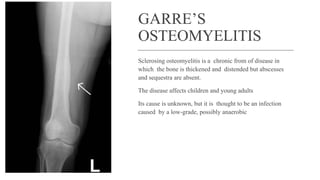
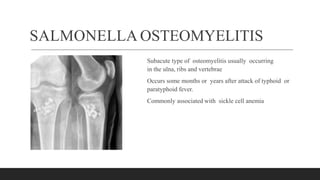
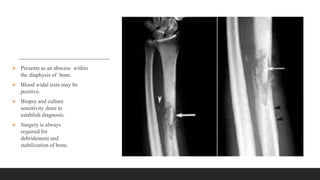
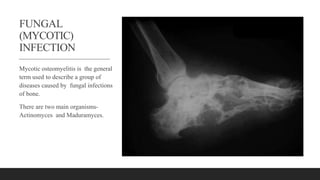
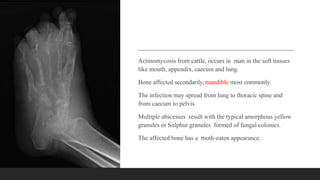
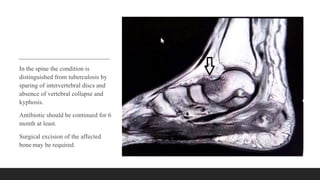
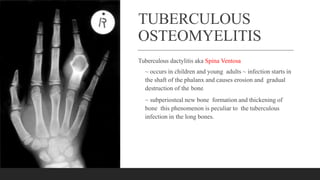
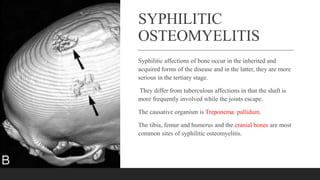
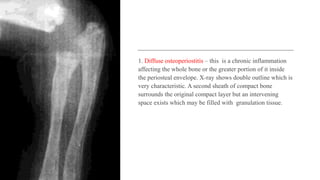
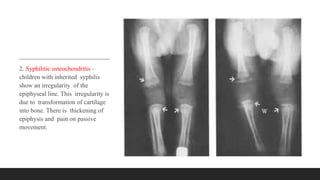
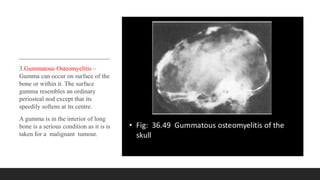
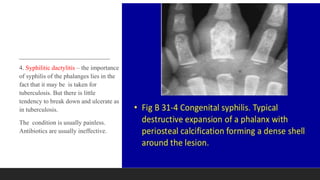
Chronic osteomyelitis is a bone infection lasting over 6 weeks characterized by recurrent inflammation, discharging sinuses, and dead bone. Staphylococcus aureus is the most common cause. Risk factors include inadequate treatment of acute osteomyelitis allowing it to become chronic. On imaging, dead bone (sequestra) is surrounded by sclerotic bone. Treatment involves surgical debridement of infected bone and tissue, followed by long-term antibiotics, bone grafts, or antibiotic beads to eliminate dead space and prevent recurrence. Complications can include exacerbation of infection, bone deformities, fractures, or joint stiffness.