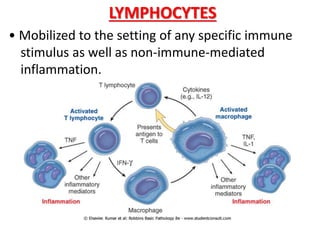
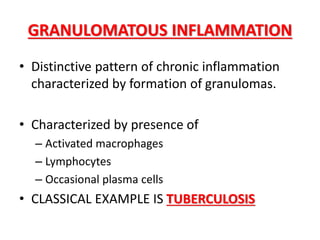
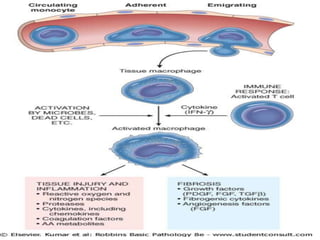
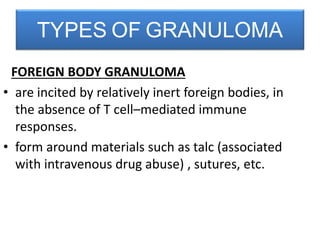
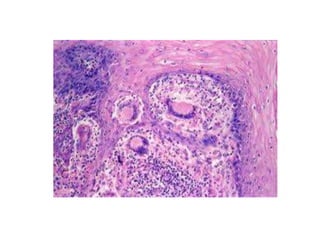
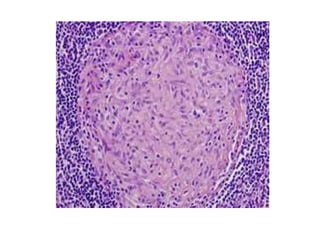
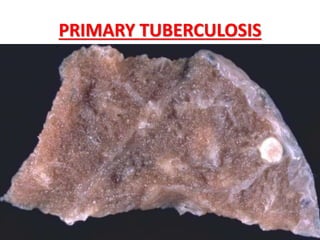
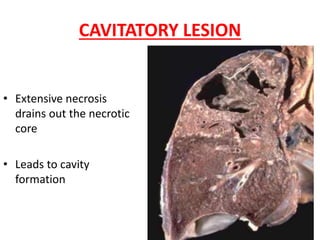
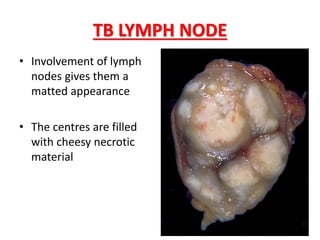
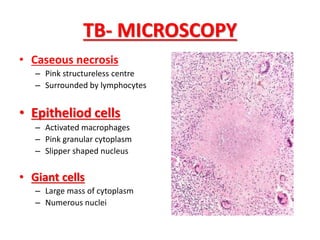
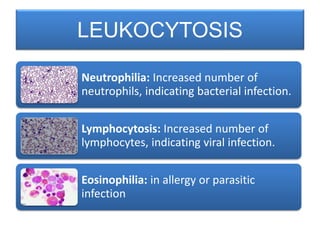
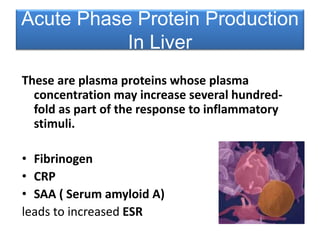
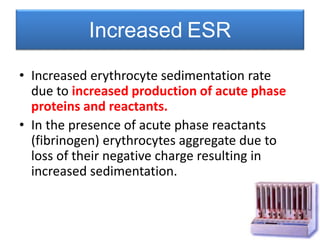
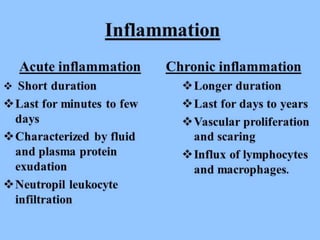
This document discusses chronic inflammation. It defines chronic inflammation as prolonged inflammation lasting weeks or months, where continuing inflammation, tissue destruction, and healing occur simultaneously. Key features of chronic inflammation include infiltration of mononuclear cells like macrophages, T-lymphocytes, and plasma cells, as well as tissue destruction caused by a persistent offending agent or inflammatory cells, and attempts at healing through connective tissue replacement. Granulomas, a hallmark of chronic inflammation, are also described.