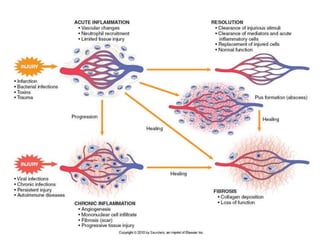
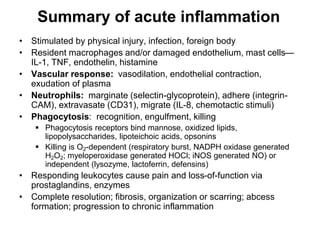
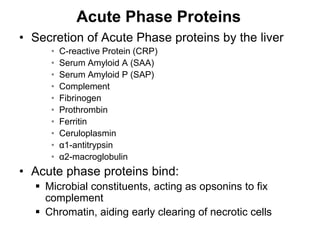
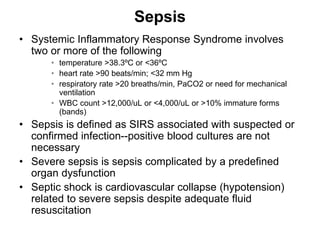
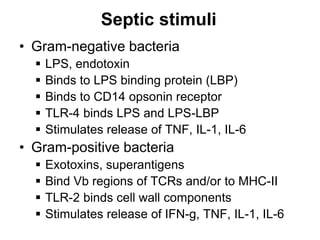
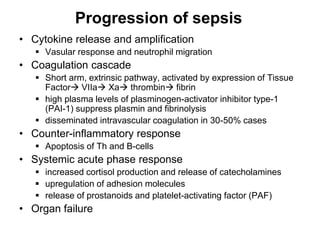
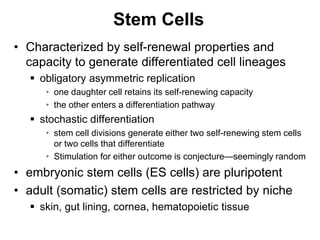
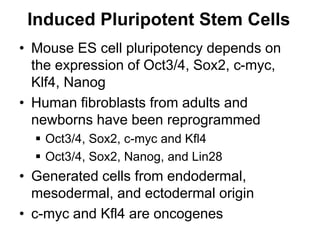
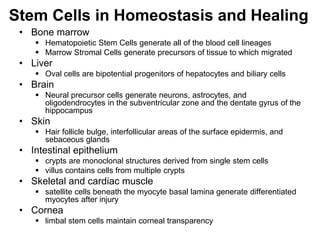
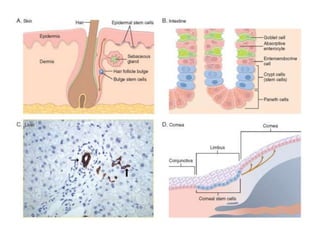
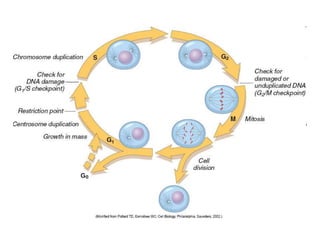
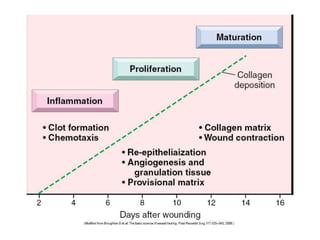
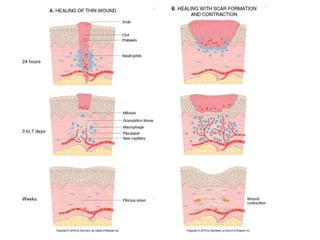
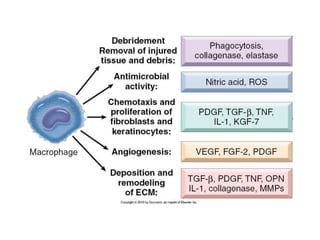
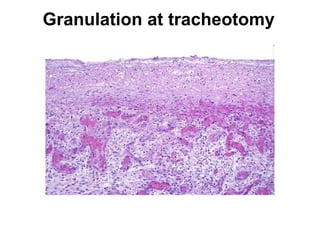
1. Acute inflammation is stimulated by injury or infection and involves vascular changes, neutrophil migration, and phagocytosis to resolve the stimulus and restore tissue structure and function.
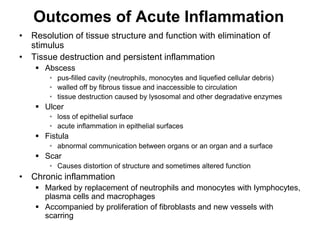
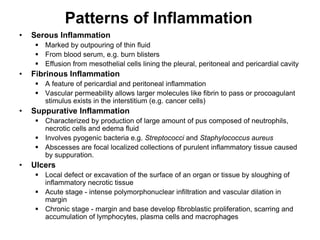
2. Outcomes include resolution, tissue destruction via abscess or ulcer formation, or progression to chronic inflammation.
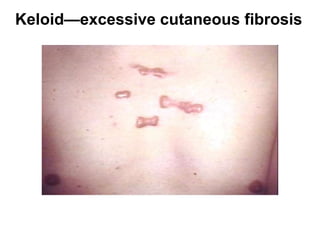
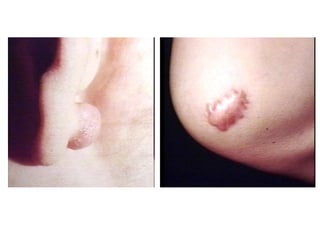
3. Chronic inflammation involves lymphocyte and macrophage infiltration and scarring, and can be caused by persistent infection, prolonged toxic exposure, or autoimmunity.