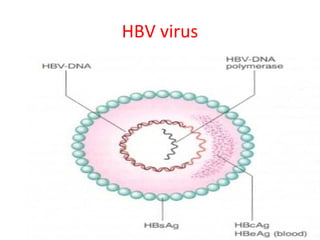
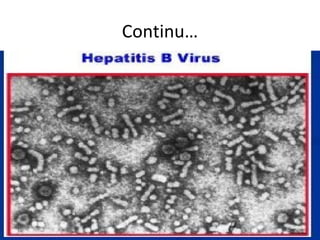
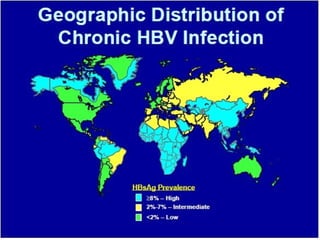
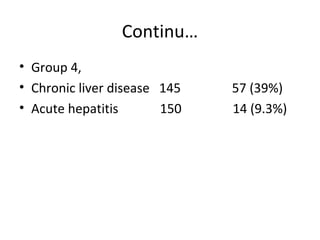1. Hepatitis B virus (HBV) is a serious disease that can cause lifelong infection, liver cirrhosis, liver cancer, liver failure, and death. It is 100 times more infectious than HIV.
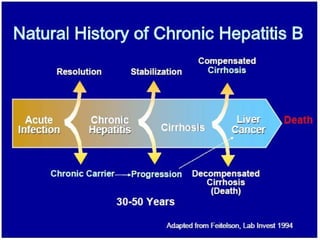
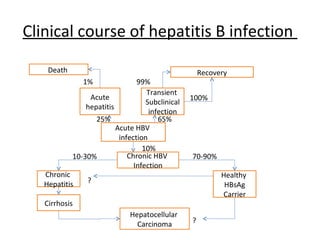
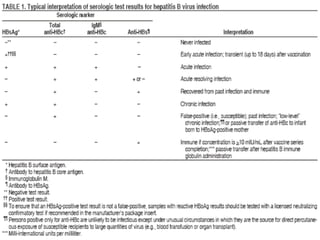
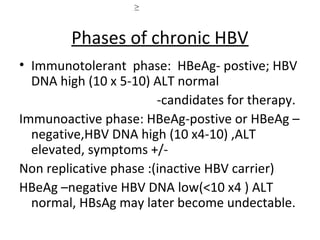
2. HBV is transmitted through contact with infectious blood or body fluids and can lead to either an acute or chronic infection. Chronic infections may progress to complications like cirrhosis or liver cancer.
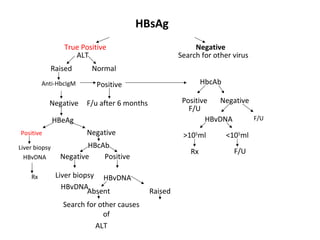
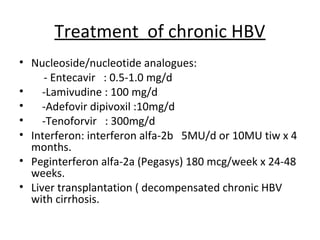
3. Treatment options for chronic HBV infection include nucleoside/nucleotide analogues like entecavir and tenofovir, as well as interferon-alpha. Vaccination and immunoglobulin can prevent HBV infection in high-risk groups or following exposure.