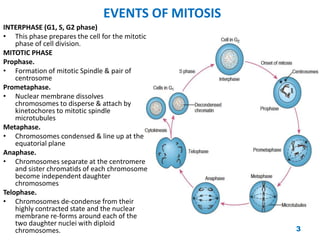
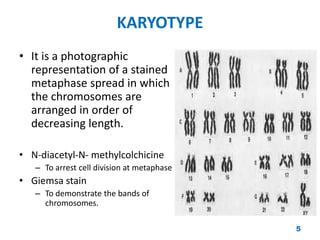
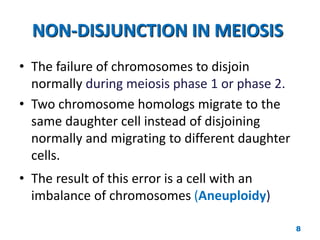
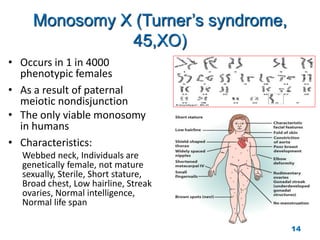
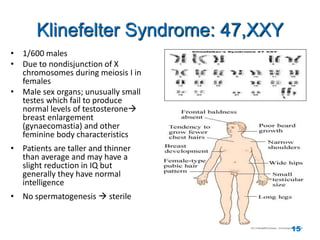
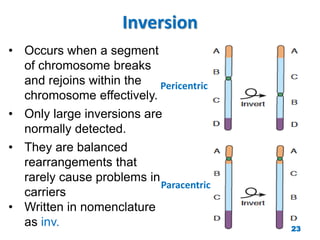
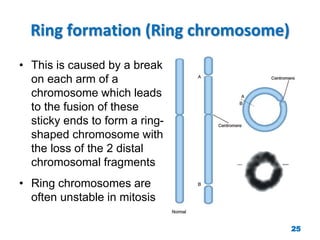
Chromosome disorders can be either numerical or structural. Numerical disorders involve an abnormal number of chromosomes, such as trisomies where there is an extra chromosome, usually arising from non-disjunction during meiosis. Common trisomies are Down syndrome (trisomy 21), Edward's syndrome (trisomy 18), and Patau syndrome (trisomy 13). Structural disorders involve abnormalities in chromosome structure like translocations, inversions, deletions, isochromosomes, and ring chromosomes. Mosaicism can also occur when more than one cell line is present from a single zygote.