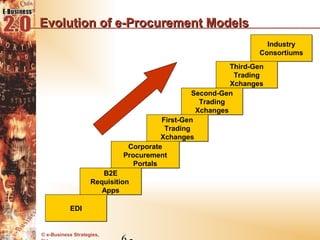
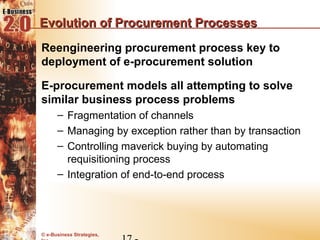
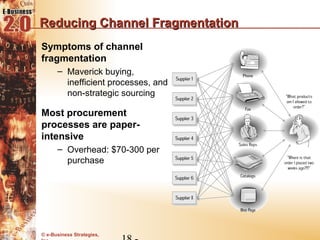
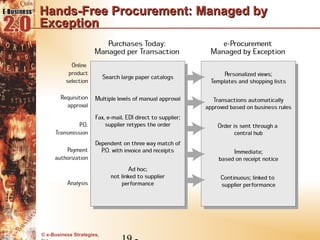
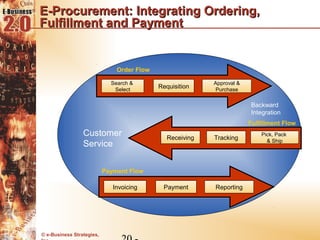
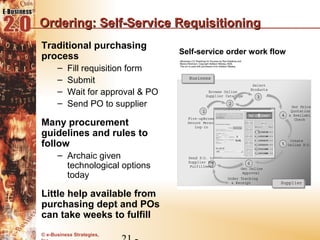
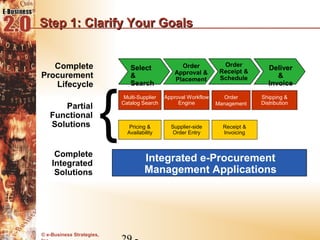
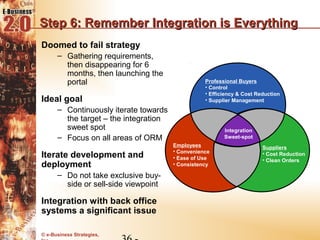
This document discusses the evolution of e-procurement models from early EDI networks and B2E apps to current trading exchanges and industry consortiums. It outlines the key stages in developing an e-procurement strategy including clarifying goals, auditing processes, building a business case, developing supplier integration plans, selecting applications, focusing on integration, and educating stakeholders. The overall evolution aims to streamline procurement, reduce costs, and bring strategic benefits through automation and collaboration.