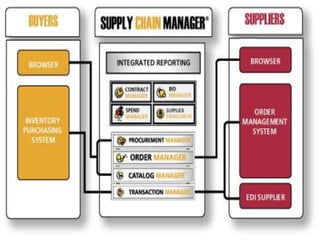
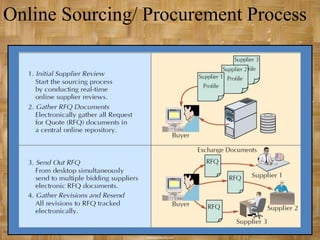
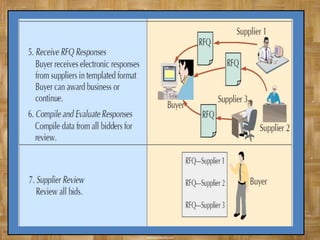
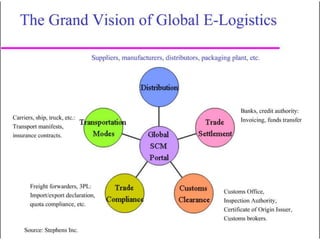
The document discusses the role of information technology in supply chain management. It describes how electronic commerce, e-procurement tools, e-markets, and enterprise resource planning systems can increase efficiency in supply chain operations through improved information sharing and reduced transaction costs. These technologies allow companies to better coordinate activities, improve customer service, and gain a competitive advantage in supply chain management.