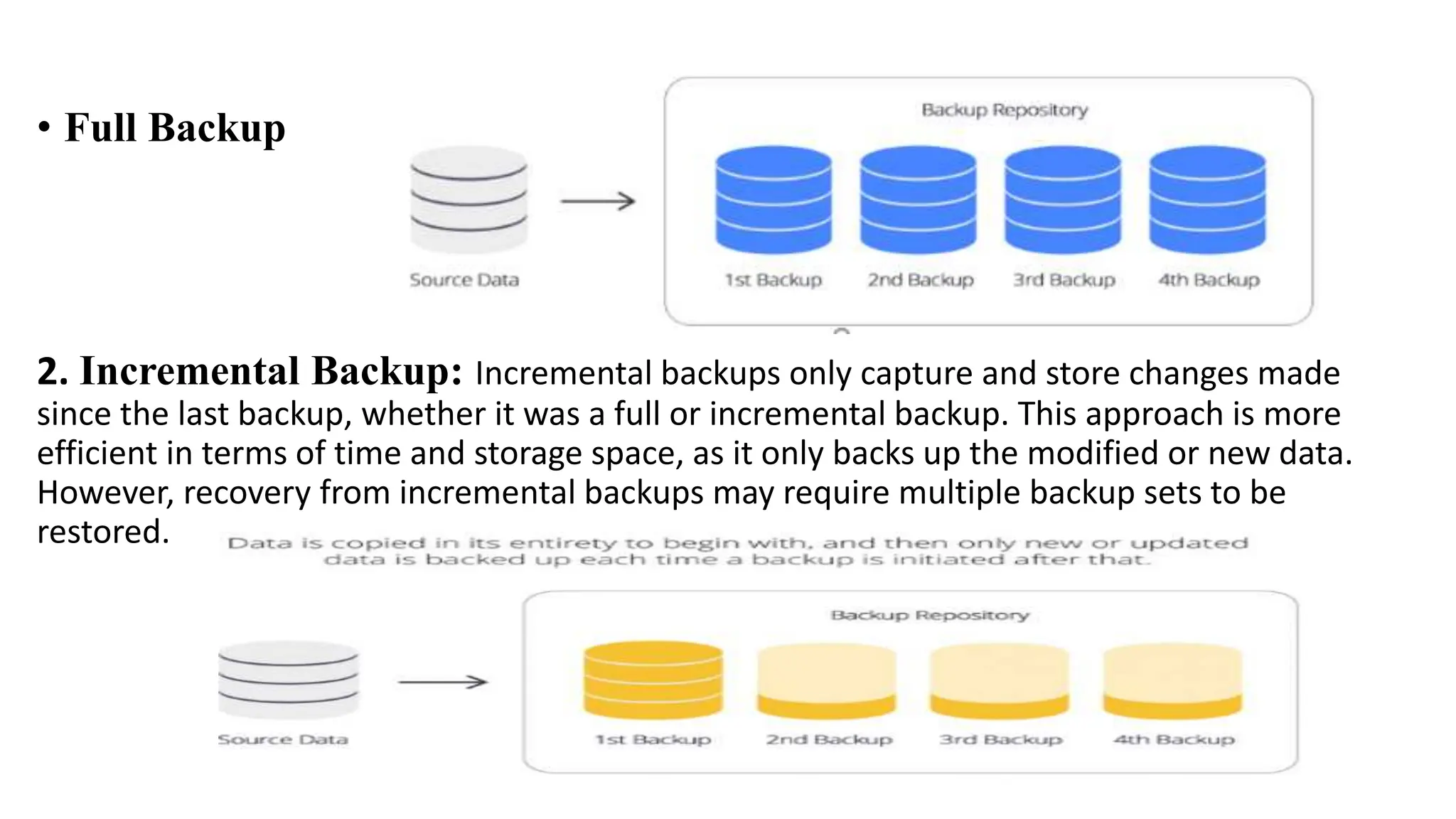
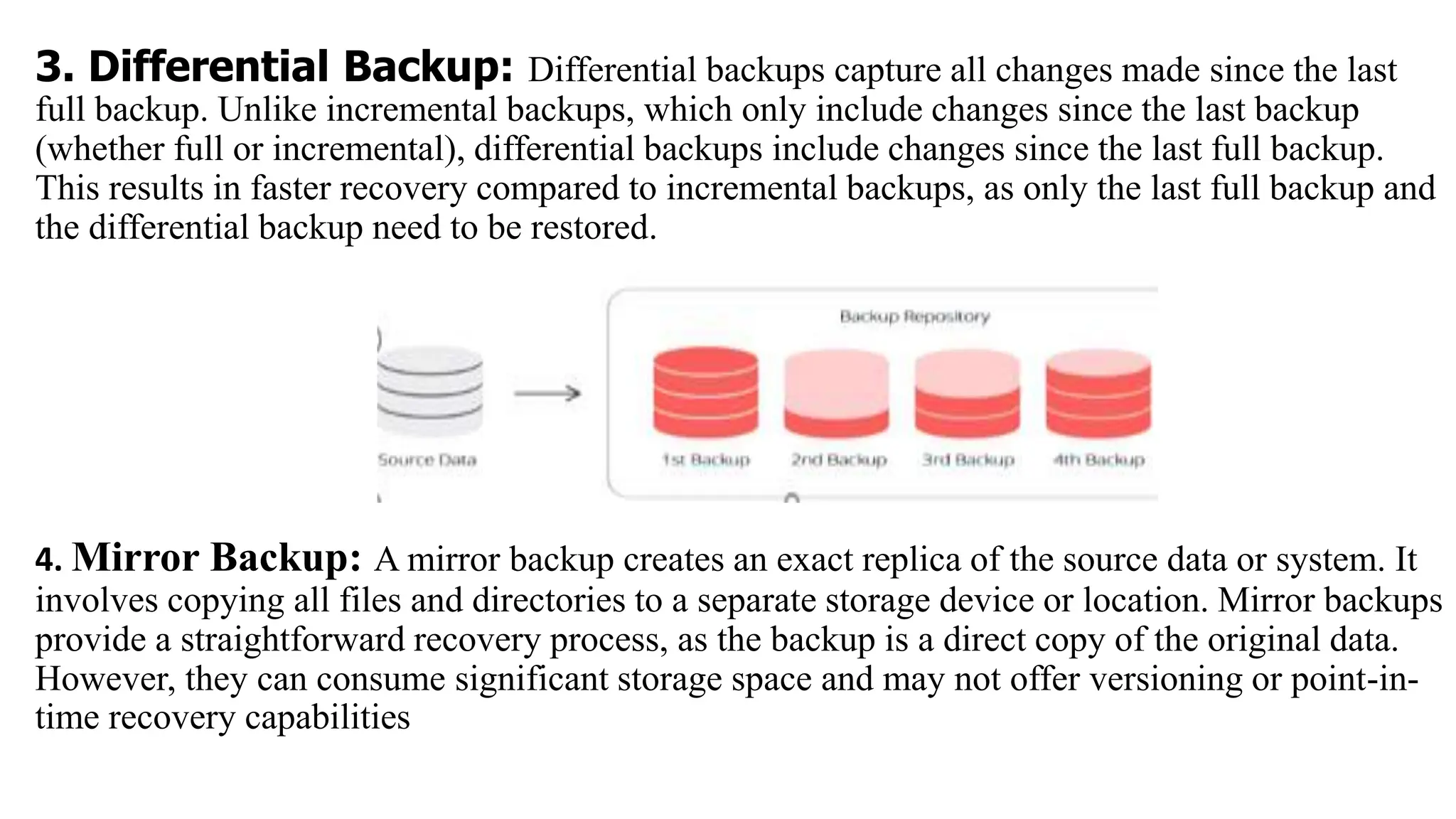
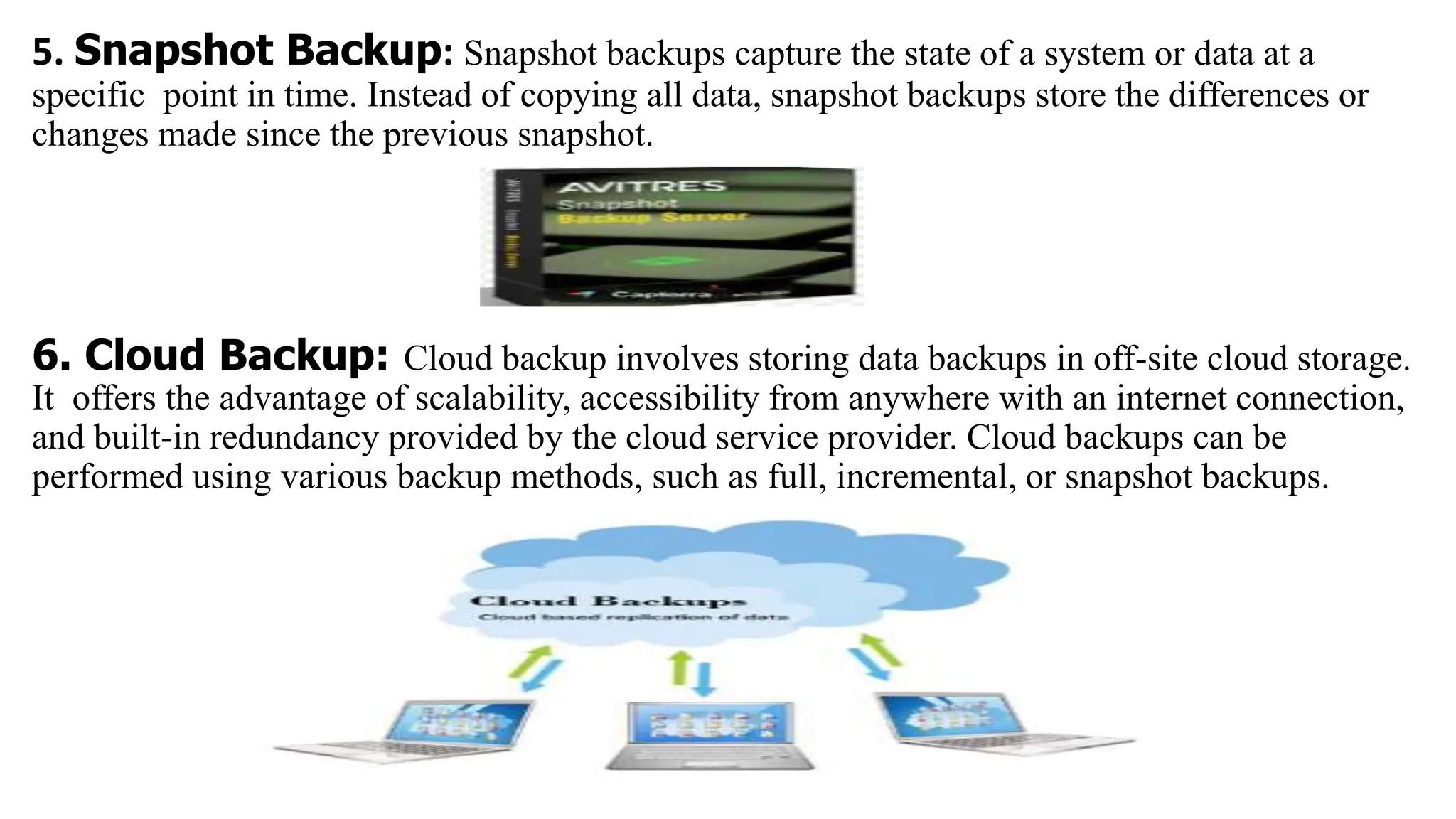
The document outlines the critical aspects of network system administration, focusing on tasks related to managing, monitoring, and securing network infrastructure. It emphasizes key areas such as fault management, configuration management, account management, performance management, and security management, along with the roles and responsibilities of network administrators in maintaining system integrity and security. Additionally, it discusses the importance of disaster recovery planning, outlining various backup methods and procedures to ensure network continuity during disruptions.