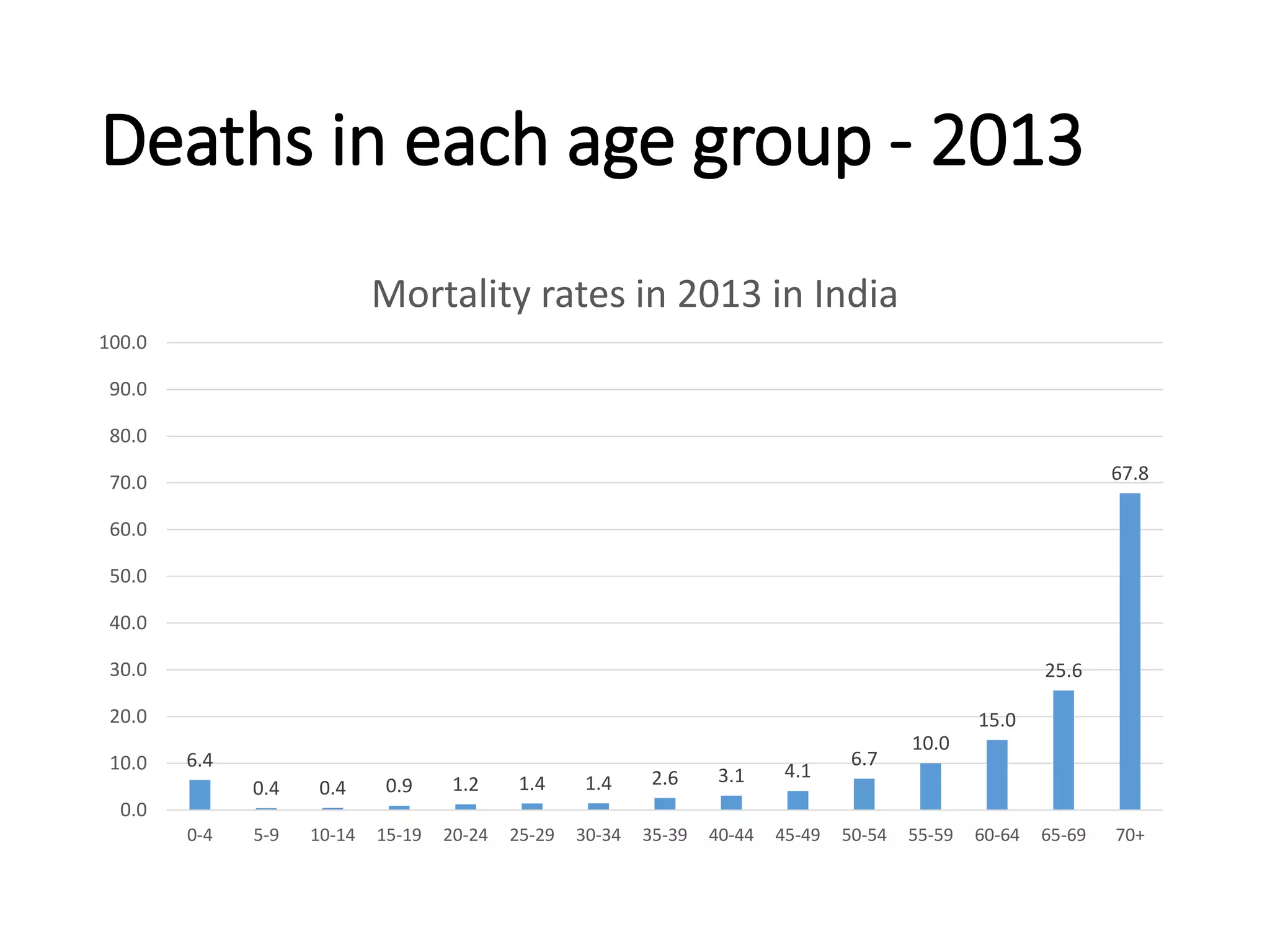
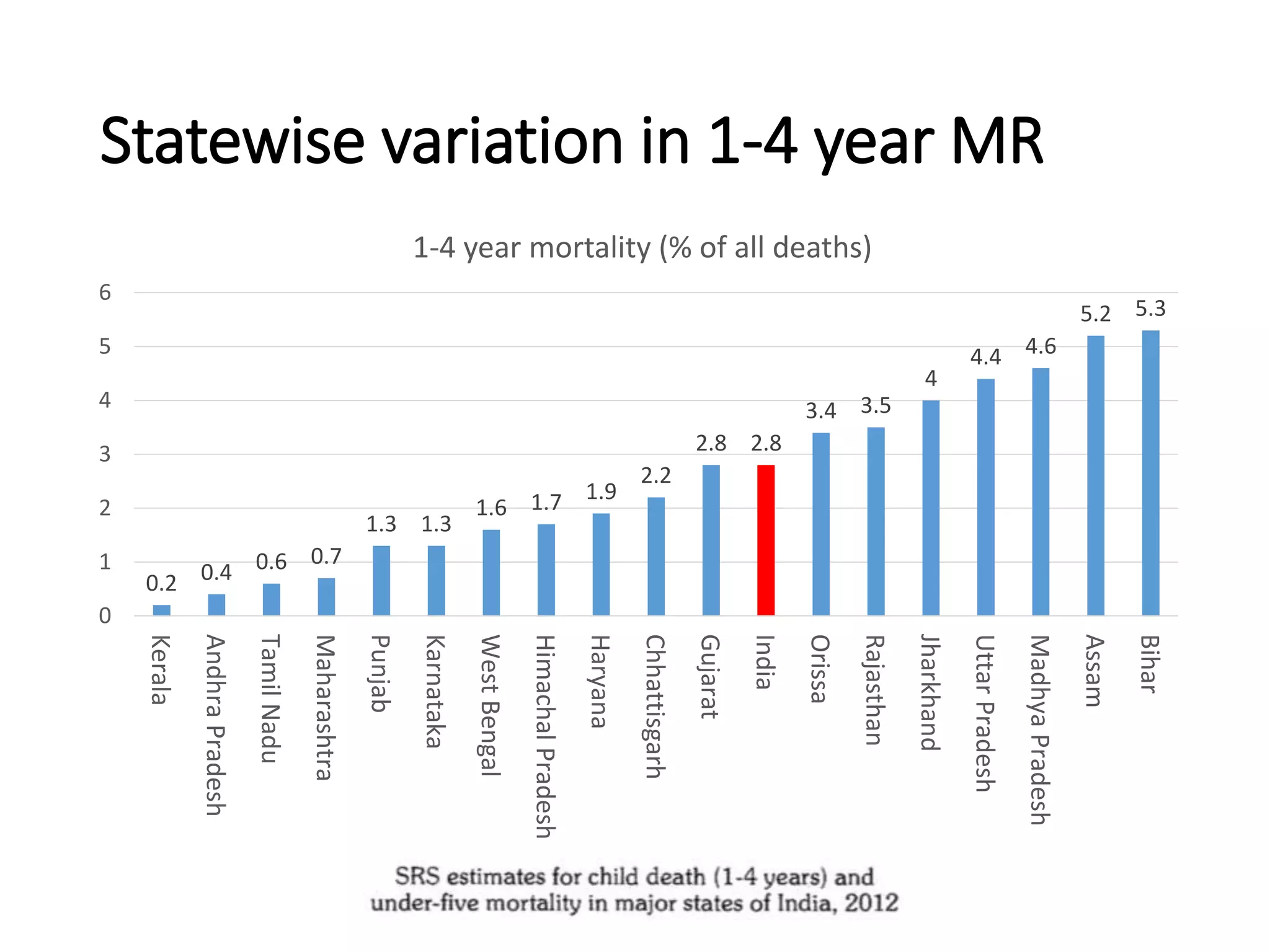
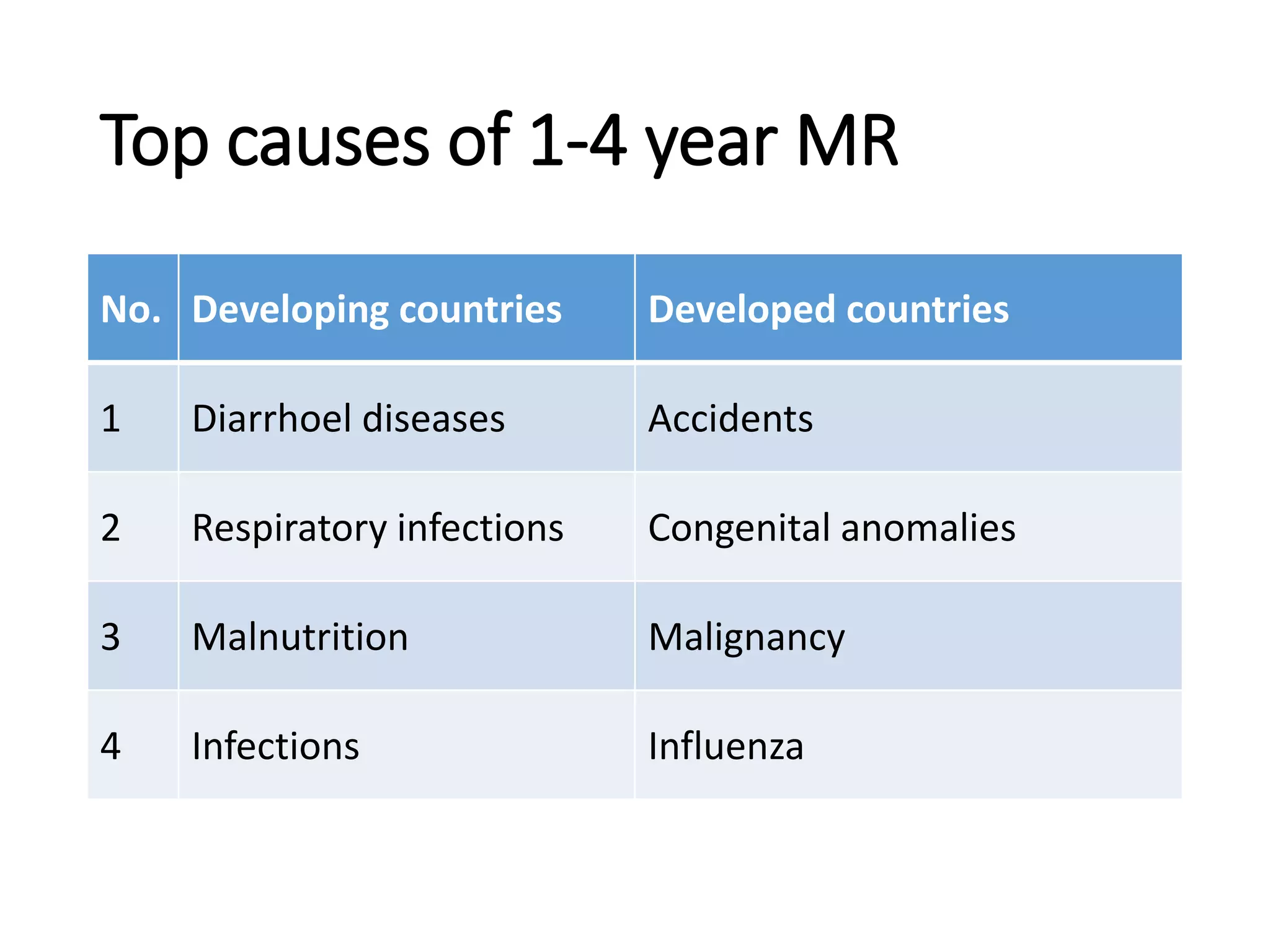
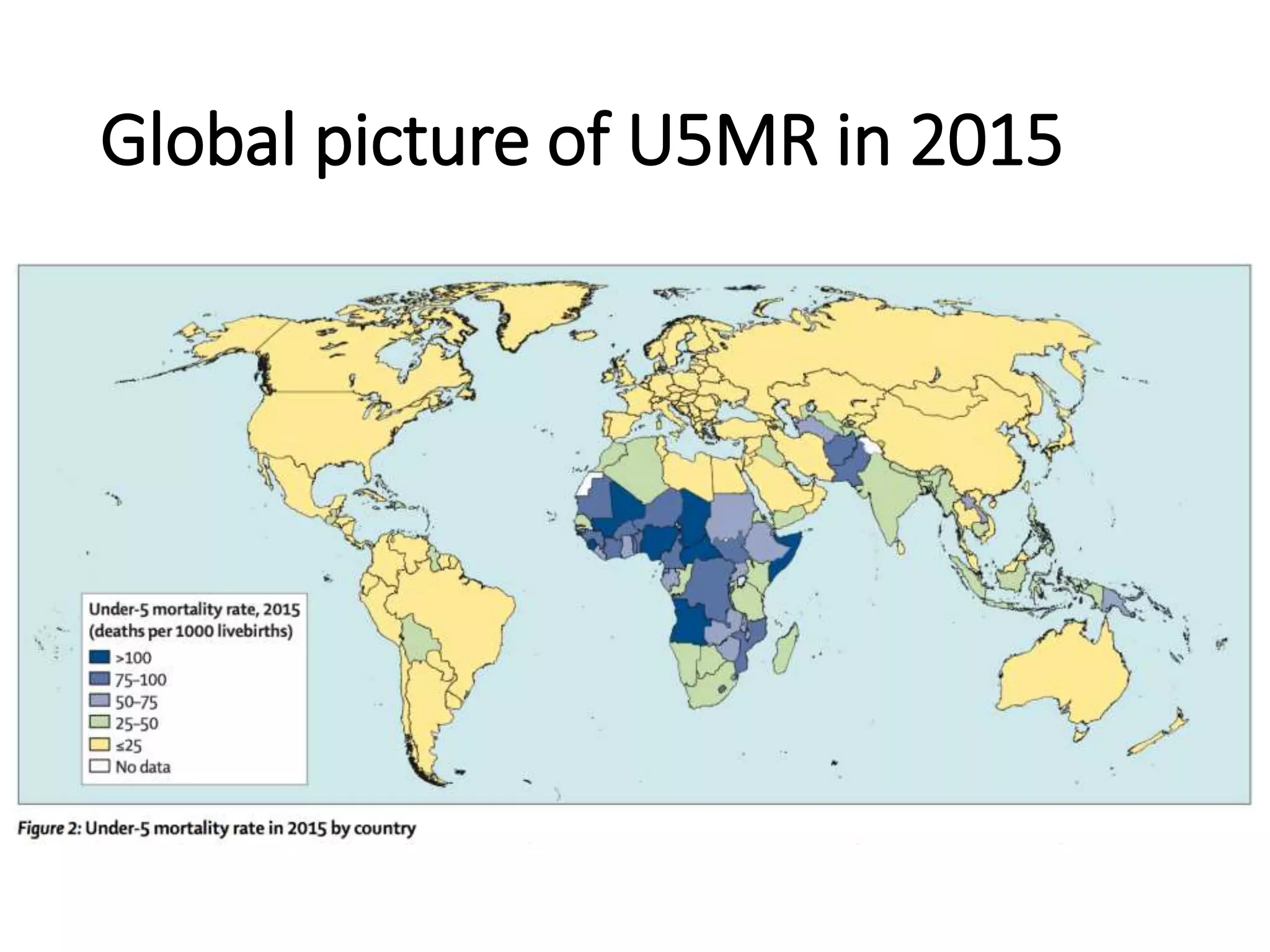
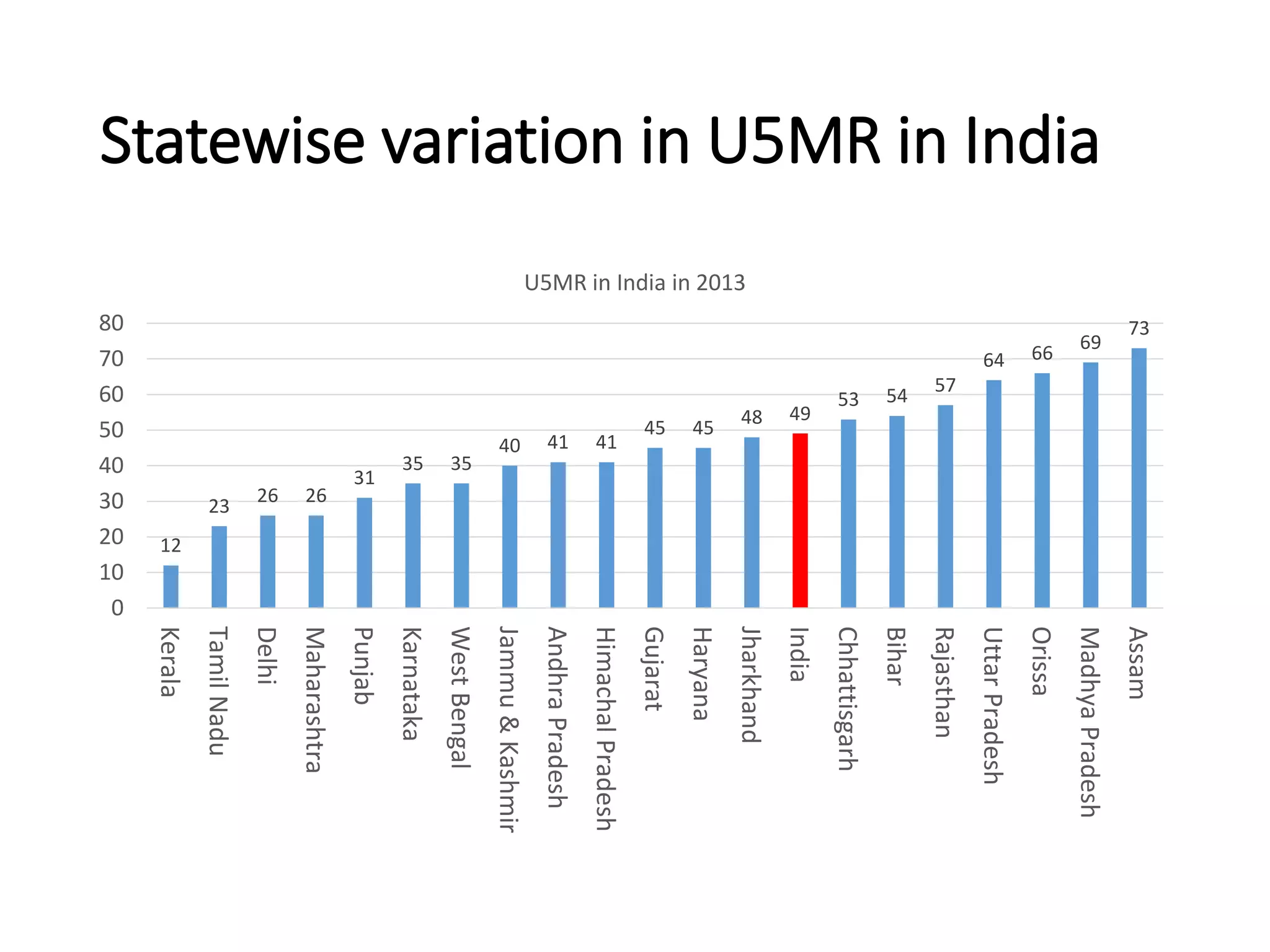
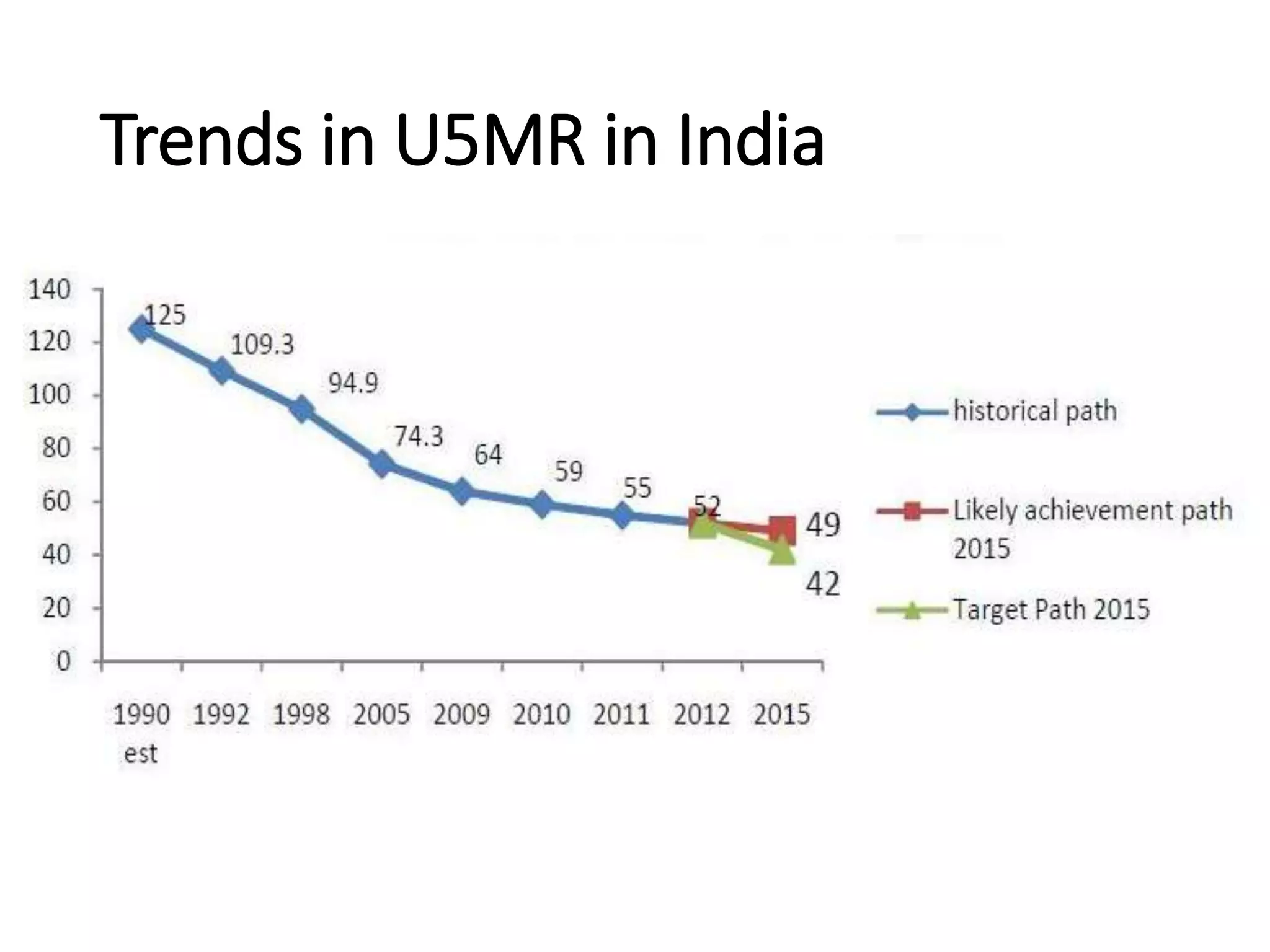
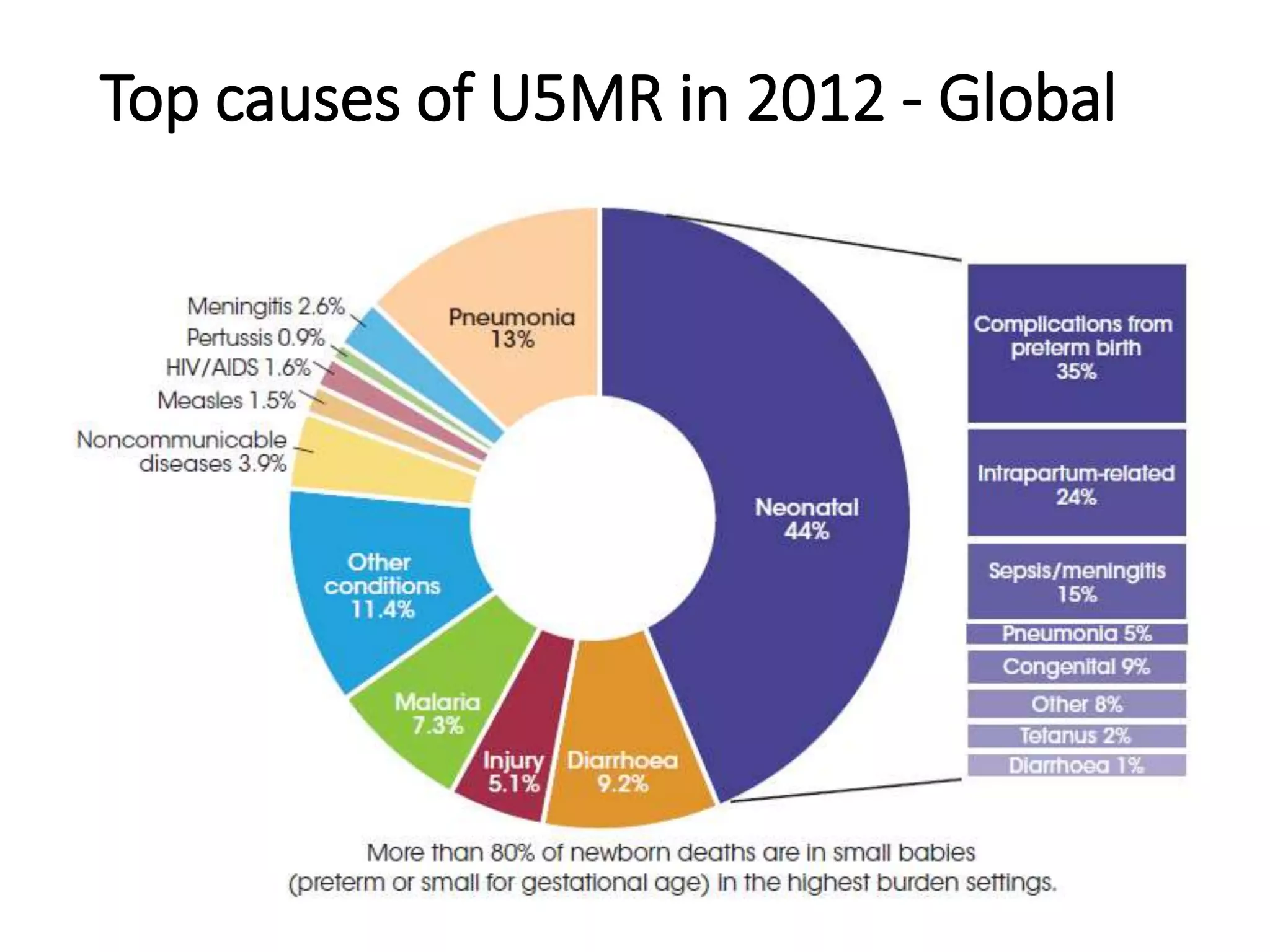
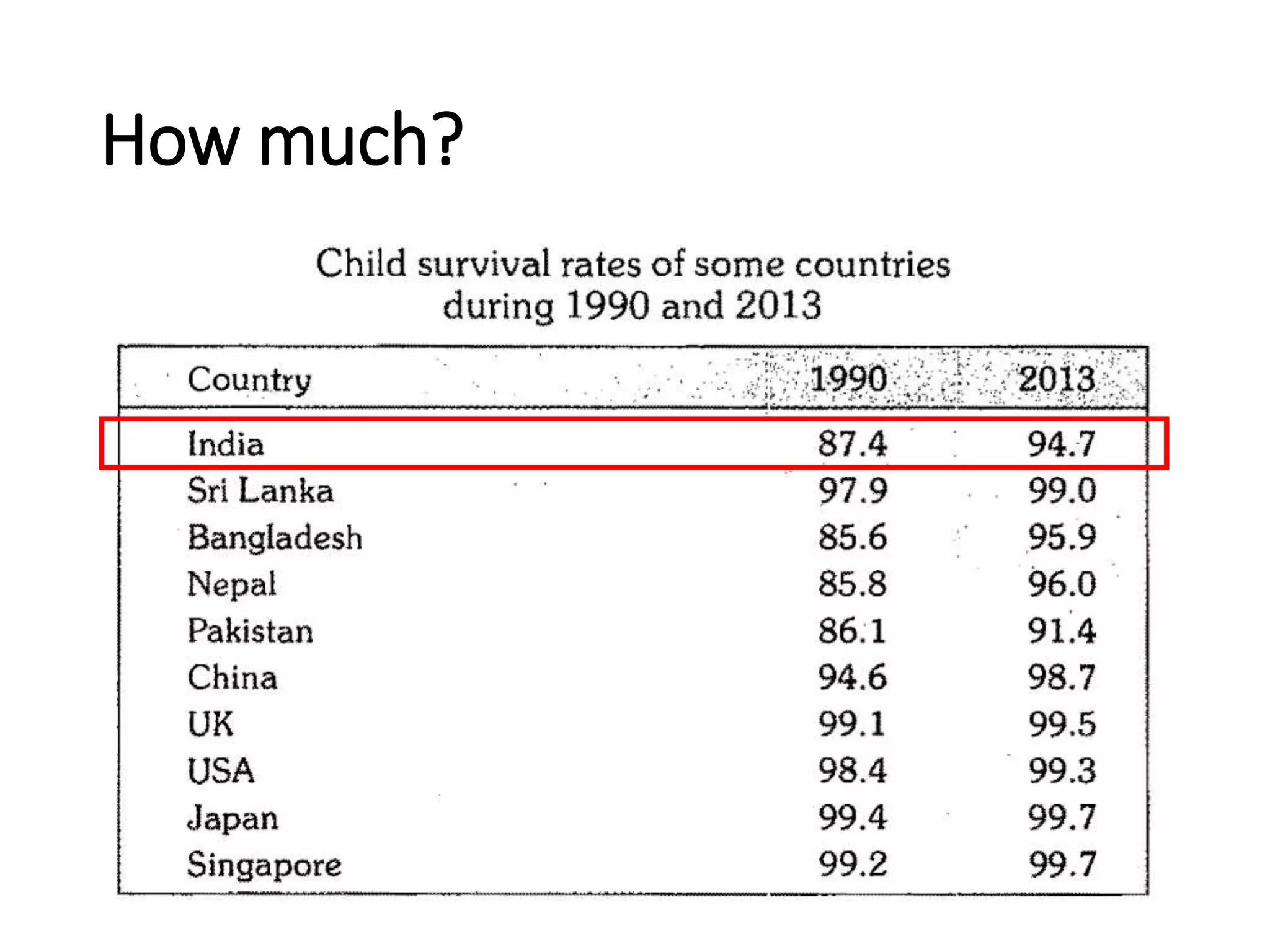
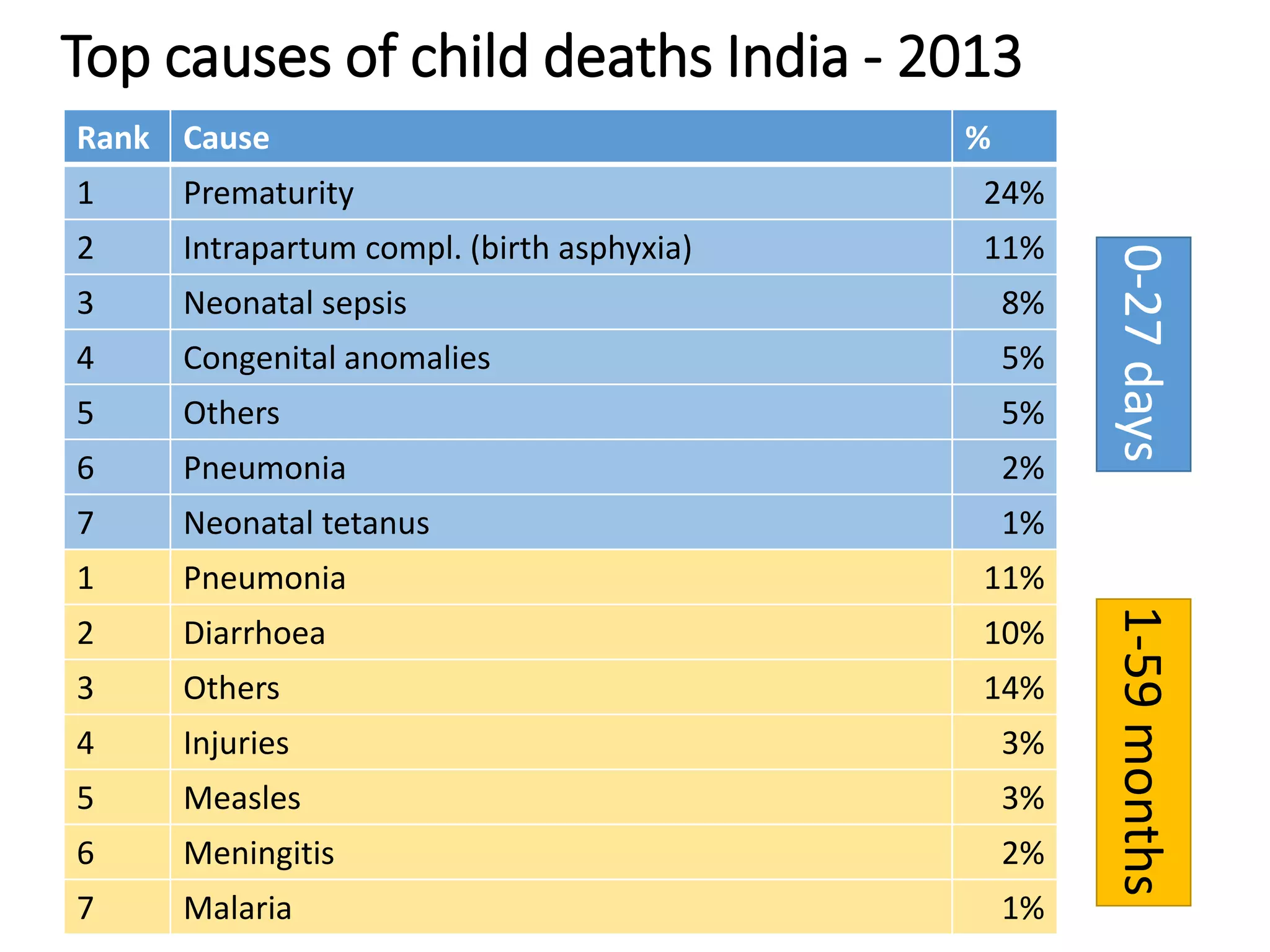
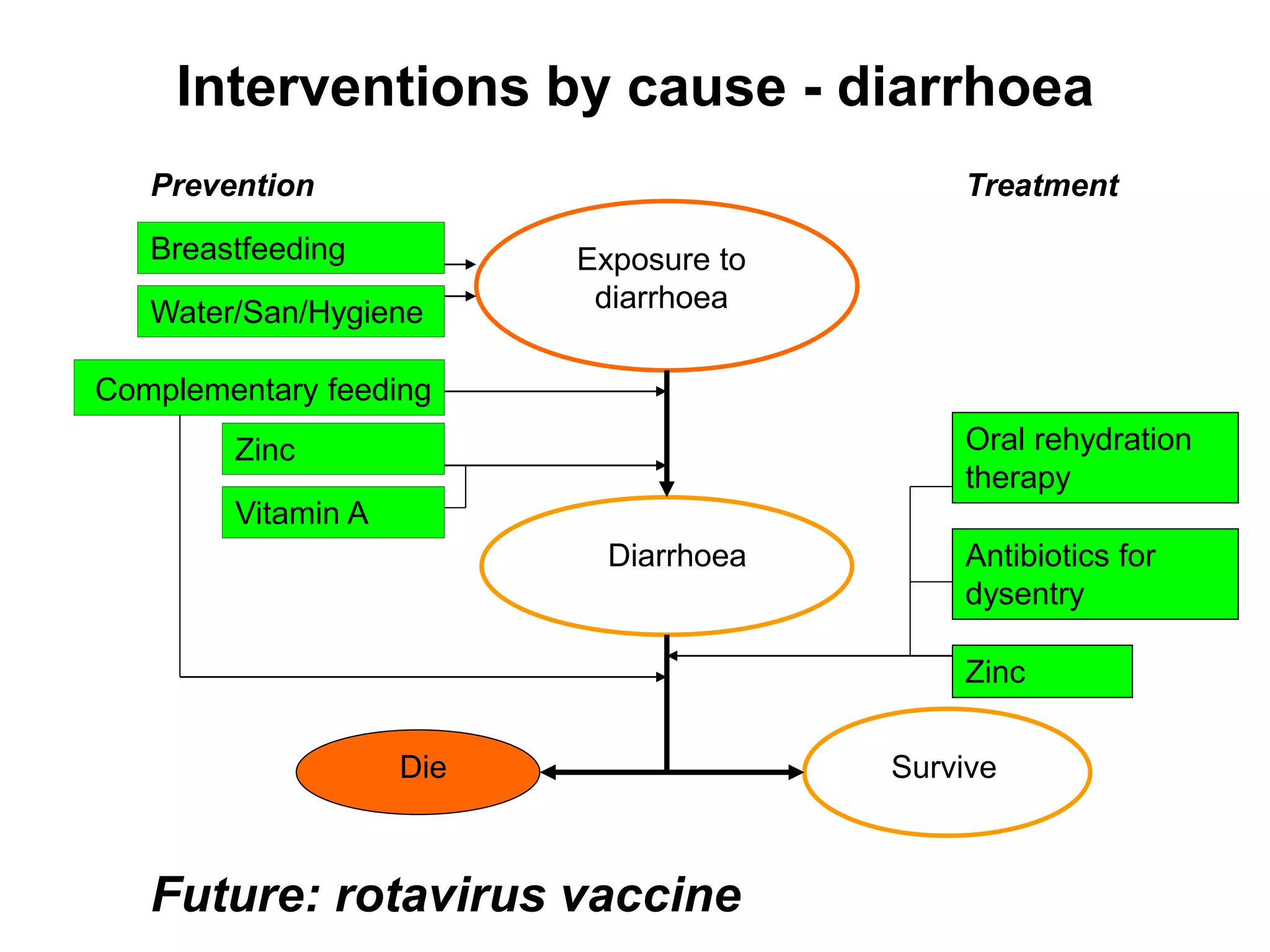
This document discusses key child mortality indicators in India such as the under-5 mortality rate and child death rate. It defines the indicators and describes trends over time. The top causes of under-5 deaths in India are prematurity, birth asphyxia, and neonatal sepsis. Pneumonia, diarrhea, and malaria are also major causes. Programs that can help reduce under-5 mortality include improving newborn care, immunization, and infant and young child feeding practices. The current under-5 mortality rate in India is 49 per 1000 live births.